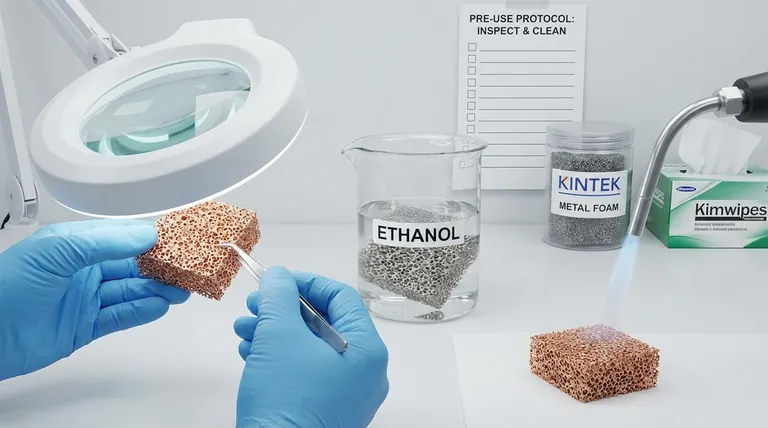
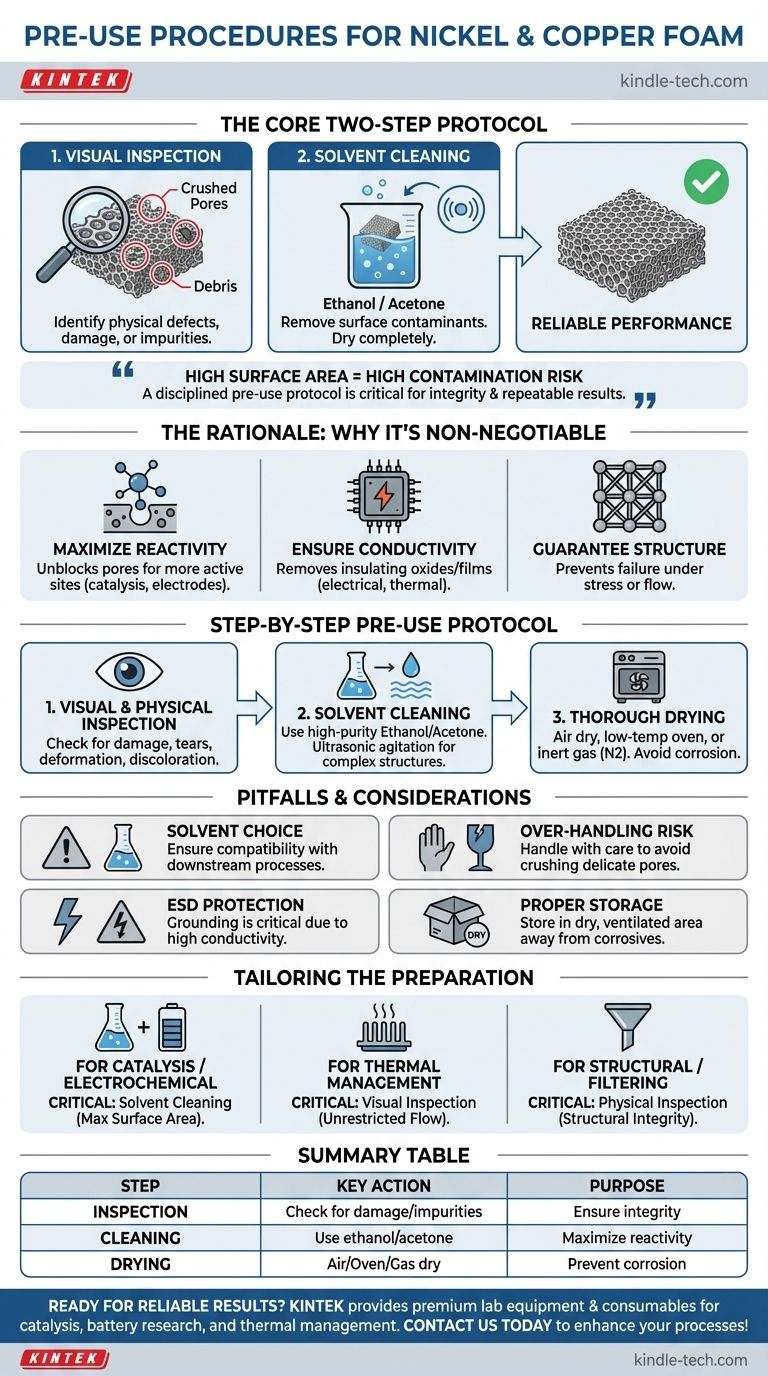
Before deploying nickel or copper foam in any application, a two-step procedure is essential to ensure performance and reliability. First, you must conduct a thorough visual inspection for any physical defects like damage, deformation, or impurities. Second, the foam must be cleaned with a suitable solvent, such as ethanol or acetone, to remove surface contaminants before being dried completely.
The high surface area that makes metal foams uniquely valuable also makes them highly susceptible to performance-degrading contaminants. A disciplined pre-use protocol of inspection and cleaning is not merely a suggestion—it is a critical step to guarantee material integrity and achieve repeatable, accurate results.

The Rationale: Why Pre-Use Procedures Are Non-Negotiable
The unique, porous structure of nickel and copper foam is the source of its utility. Protecting the integrity of this structure is the primary goal of any pre-use preparation.
Maximizing Surface Area and Reactivity
Contaminants like oil, dust, or grease physically block the intricate network of pores. In applications like catalysis or battery electrodes, this directly reduces the number of active sites available for chemical reactions, severely limiting the material's efficiency.
Ensuring Electrical and Thermal Integrity
Surface oxides or organic films can act as insulating layers. These layers create unwanted resistance, compromising the foam's innate high electrical and thermal conductivity, which is critical for electronics, heat sinks, and current collectors.
Guaranteeing Structural Soundness
A pre-use visual inspection is your first line of defense against mechanical failure. Identifying crushed pores, tears, or deformations ensures the foam will perform as expected under mechanical stress or fluid flow.
A Step-by-Step Pre-Use Protocol
Follow these three steps to prepare your metal foam for any high-performance application.
Step 1: Visual and Physical Inspection
Carefully examine the entire surface of the foam. Look for any signs of physical damage, such as crushed areas, tears in the ligaments, or significant deformation that could impede flow or create weak points. Check for discoloration that may indicate oxidation or the presence of foreign particles lodged within the pores.
Step 2: Solvent Cleaning
To remove surface contaminants, clean the foam with a high-purity solvent. Ethanol and acetone are common choices because they effectively dissolve oils and grease without reacting with the base metal. Submerging the foam and using ultrasonic agitation can enhance the cleaning process for highly complex structures.
Step 3: Thorough Drying
After cleaning, all residual solvent must be removed. This can be achieved by air drying, placing the foam in a low-temperature oven, or using a stream of dry, inert gas like nitrogen. Incomplete drying can lead to contamination in your process or promote corrosion of the foam.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Considerations
While the procedure is straightforward, awareness of potential issues is key to success.
Choosing the Right Solvent
While ethanol and acetone are excellent general-purpose cleaners, your specific application may require a different approach. Always ensure the solvent is compatible with your downstream processes and is capable of removing the specific contaminants you expect.
The Risk of Over-Handling
Nickel and copper foams, particularly those with high porosity, can be delicate. Handle them with care during inspection and cleaning to avoid inadvertently crushing or deforming the pore structure, which would negate the purpose of the preparation.
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Protection
Due to their excellent electrical conductivity, these foams can easily conduct static electricity. When working in an ESD-sensitive environment, proper grounding and other electrostatic protection measures are crucial to prevent damage to the foam or other electronic components.
Proper Storage
Preparation begins with proper storage. Keep all metal foams in a dry, well-ventilated environment away from corrosive substances like strong acids or alkalis. This prevents degradation before you even begin your work.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific application should guide the focus of your preparation.
- If your primary focus is catalysis or electrochemical work: Your most critical step is the solvent cleaning to ensure maximum surface area is active and uncontaminated.
- If your primary focus is thermal management or heat exchange: The visual inspection for crushed pores or blockages is paramount to guarantee unrestricted fluid or air flow.
- If your primary focus is a structural or filtering application: The physical inspection for tears, deformations, and uniform porosity is essential to prevent mechanical failure.
Ultimately, a consistent and thorough pre-use protocol transforms metal foam from a raw material into a reliable, high-performance component.
Summary Table:
| Pre-Use Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Inspection | Check for damage, deformation, or impurities | Ensure structural integrity and functionality |
| Cleaning | Use ethanol or acetone to remove contaminants | Maximize surface area and reactivity |
| Drying | Air dry or use low-temperature oven | Prevent corrosion and process contamination |
Ready to achieve reliable, high-performance results with your metal foams? KINTEK specializes in providing premium lab equipment and consumables, including nickel and copper foams, tailored for applications in catalysis, battery research, and thermal management. Our expert team ensures you have the right materials and support for your laboratory needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your processes and deliver consistent, accurate outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Nickel Aluminum Tabs for Soft Pack Lithium Batteries
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Gold Plating Tungsten Molybdenum Crucible for Evaporation
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Quartz Plate JGS1 JGS2 JGS3
- Button Battery Tablet Press Sealing Mold for Lab Use
- Float Soda-Lime Optical Glass for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What procedures should be followed after using nickel or copper foam? A Guide to Reliable Reuse and Performance
- How long does it take to solder? A guide to timing and technique for perfect joints
- How do you test the capacity of a lithium-ion battery? A Guide to Accurate Measurement
- What is the purpose of laminating? Protect and Enhance Your Documents for Long-Term Use
- What is the correct shutdown procedure after an experiment? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe Deactivation



















