In short, sintering is not about a single property, but rather a process that fundamentally enhances a material's strength and structural integrity. By bonding loose particles into a solid mass, it drastically reduces internal porosity, which in turn improves key physical characteristics like electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and even optical properties such as translucency.
Sintering is a thermal process that enhances a material's properties by bonding particles together, which reduces porosity and increases density. The true value lies not in which properties are improved, but in the ability to precisely control these properties by adjusting the process parameters.

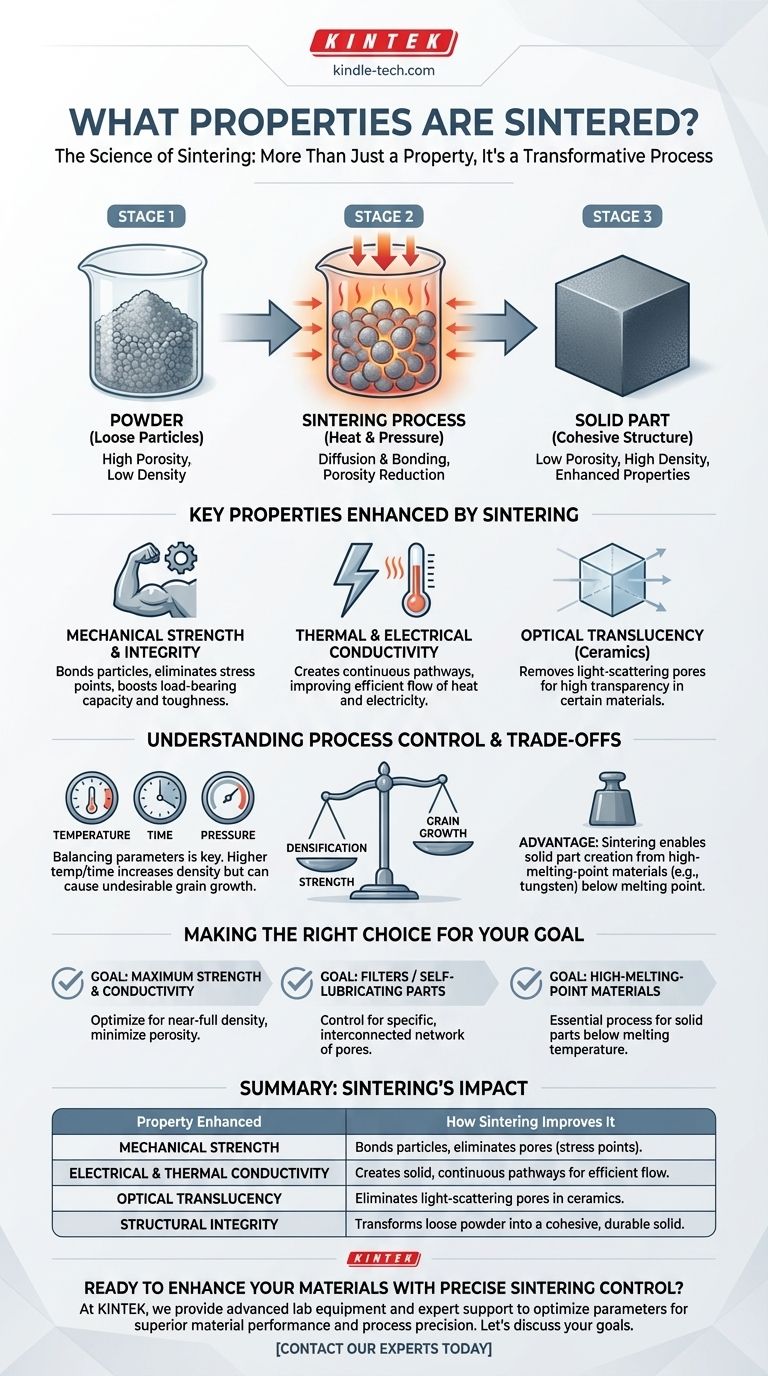
The Core Transformation: From Powder to Solid
Sintering creates a functional part from powder. The changes it imparts all stem from one fundamental structural shift: the elimination of the empty space between particles.
Reducing Porosity
The primary goal of most sintering operations is to reduce or eliminate porosity—the tiny voids between the starting powder particles. Heat and sometimes pressure cause atoms to diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, effectively closing these gaps.
Increasing Density
As the volume of pore space decreases, the material's density naturally increases. This increase in density is directly responsible for the dramatic improvements in most other material properties.
Creating Strength and Integrity
A loose collection of powder has virtually no mechanical strength. The atomic bonding that occurs during sintering creates a strong, cohesive part that can withstand mechanical stress. This imparts the strength and structural integrity necessary for real-world applications.
Key Properties Enhanced by Sintering
By increasing a material's density and bonding its particles, sintering directly improves a range of functional properties.
Mechanical Strength
A denser, more solid structure is inherently stronger and more resistant to fracture. By minimizing internal voids, which act as stress concentration points, sintering significantly boosts a material's toughness and load-bearing capacity.
Thermal & Electrical Conductivity
Pores filled with air or a vacuum are excellent insulators. By eliminating these pores and creating solid, continuous pathways through the material, sintering allows heat and electricity to flow much more efficiently, improving thermal and electrical conductivity.
Optical Translucency
In certain ceramic materials, pores are the primary obstacle to transparency because they scatter light. Achieving high translucency or transparency requires sintering the material to near-full density, eliminating the pores that make it appear opaque.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Control
Sintering is a highly controllable process, but it requires understanding the key variables and their associated trade-offs. It is not simply about maximizing all properties at once.
Temperature and Time as Levers
The properties of a sintered part are directly controlled by parameters like temperature, time, and pressure. Higher temperatures and longer times generally lead to greater densification, but can also cause undesirable grain growth, which might negatively impact strength.
The Porosity-Property Balance
Achieving 100% density is not always the objective. For applications like filters or self-lubricating bearings, a specific amount of interconnected porosity is a desirable feature. Sintering allows engineers to precisely control the final porosity to meet these functional requirements.
An Advantage for High-Melting-Point Materials
One of the greatest strengths of sintering is its ability to create solid parts from materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten and many advanced ceramics. Since the process occurs below the melting point, it enables the fabrication of components that would be difficult or impossible to produce via casting.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The way you approach sintering depends entirely on the desired outcome for your component.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and conductivity: Your goal is to achieve near-full density by optimizing sintering temperature and time to minimize residual porosity.
- If your primary focus is creating a filter or self-lubricating part: You will intentionally use lower sintering temperatures or shorter times to preserve a specific, interconnected network of pores.
- If your primary focus is working with high-melting-point materials: Sintering is your essential process, as it allows you to create solid parts far below the material's actual melting point.
Ultimately, viewing sintering as a tool for the precise control of a material's internal structure is the key to unlocking its full engineering potential.
Summary Table:
| Property Enhanced | How Sintering Improves It |
|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | Bonds particles, eliminates pores (stress points), increases load-bearing capacity. |
| Electrical & Thermal Conductivity | Creates solid, continuous pathways for efficient flow of electricity and heat. |
| Optical Translucency | Eliminates light-scattering pores in ceramics, allowing light to pass through. |
| Structural Integrity | Transforms loose powder into a cohesive, durable solid part. |
Ready to enhance your materials with precise sintering control?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and expert support you need to optimize sintering parameters like temperature, time, and pressure for your specific application—whether you require maximum density for strength and conductivity or controlled porosity for filtration.
We help you achieve:
- Superior Material Performance: Tailor mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties.
- Process Precision: Fine-tune sintering to meet exact specifications for high-melting-point metals and ceramics.
Let's discuss your project goals. Contact our sintering experts today to find the ideal solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does the vacuum hot-press furnace play in C-SiC-B4C-TiB2 synthesis? Achieve 2000°C Precision Densification
- How does the mechanical pressure from a vacuum hot-pressing furnace facilitate the densification of B4C/Al composites?
- How does the pressure control system of vacuum hot press equipment contribute to preventing material defects? Learn More
- What is the purpose of introducing hydrogen or argon gas into a vacuum hot pressing furnace during sintering or cooling?
- Why is it necessary to maintain a high vacuum environment during the hot pressing and sintering of CuCrFeMnNi alloys?



















