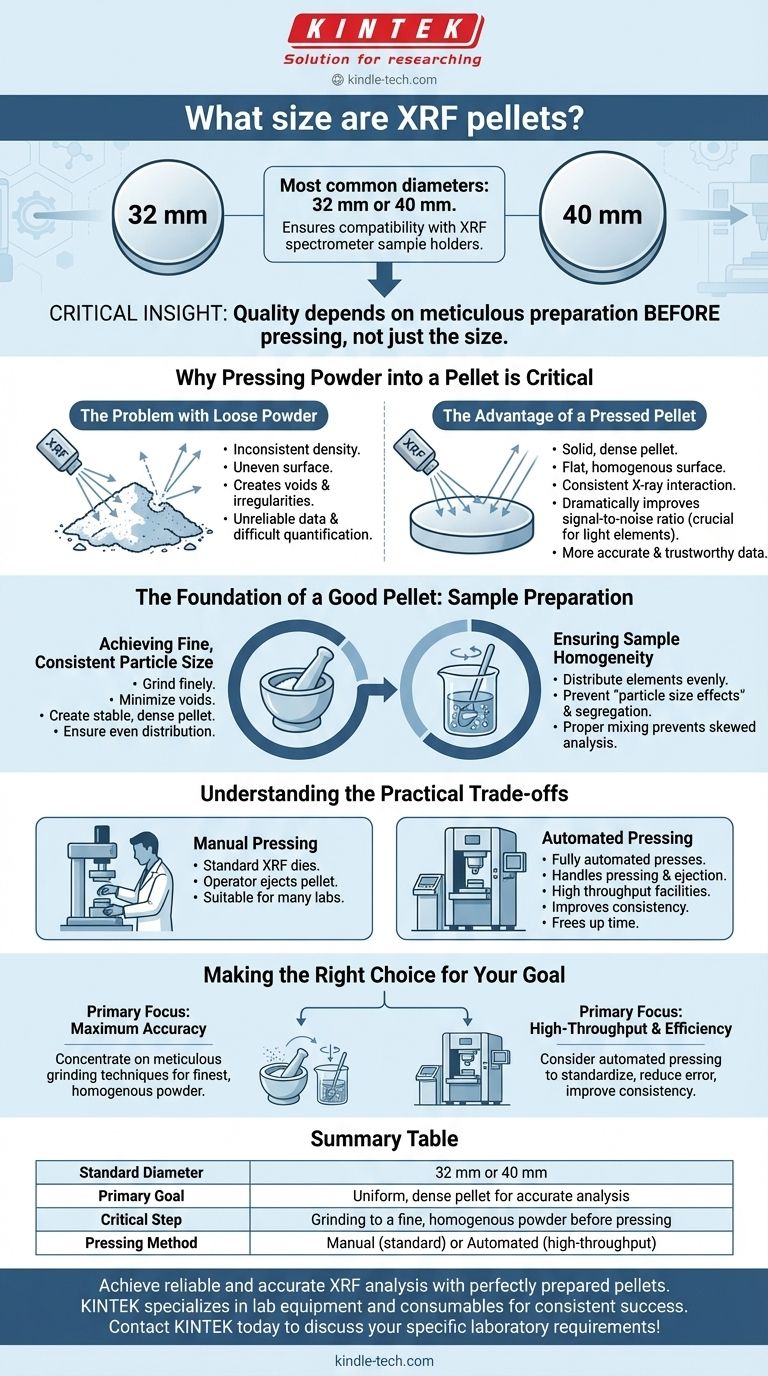
To be precise, the most common sizes for round XRF pellets are 32 mm or 40 mm in diameter. These standardized dimensions ensure compatibility with the sample holders used in a wide range of XRF spectrometers.
While the physical dimensions are straightforward, the critical insight is that the quality of your XRF analysis depends less on the pellet's exact size and more on the meticulous preparation of the sample before it is pressed.

Why Pressing Powder into a Pellet is Critical
Simply analyzing loose powder can introduce significant errors into your results. The process of pressing a sample into a dense, uniform pellet is fundamental to achieving accurate and repeatable measurements.
The Problem with Loose Powder
Loose powders have an inconsistent density and an uneven surface. This creates voids and irregularities that can scatter the X-ray beam unpredictably, leading to unreliable data.
Discrepancies in elemental composition are often observed in loose powder samples, making accurate quantification difficult.
The Advantage of a Pressed Pellet
Pressing a sample creates a solid pellet with a flat, homogenous surface. This ensures the X-ray beam interacts with a consistent amount of material on every measurement.
This uniformity dramatically improves the signal-to-noise ratio, which is especially crucial for detecting lighter elements. A well-made pellet eliminates the inconsistencies seen with loose powder, resulting in far more accurate and trustworthy data.
The Foundation of a Good Pellet: Sample Preparation
The quality of your final pellet is determined entirely by the quality of your starting powder. Two factors are paramount: particle size and homogeneity.
Achieving Fine, Consistent Particle Size
For optimal results, your sample powder should be ground as finely as possible.
Fine particles pack together more tightly, minimizing voids and creating a more stable and dense pellet. A consistent particle size ensures an even distribution of all components throughout the sample.
Ensuring Sample Homogeneity
A homogenous sample is one where the elements are distributed evenly. Proper grinding and mixing prevent "particle size effects," where different elements or minerals might segregate, skewing the analysis of the pellet's surface.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
The process of creating the pellet itself involves choices that depend on your lab's specific needs, particularly regarding sample throughput.
Manual vs. Automated Pressing
Standard XRF dies require an operator to manually intervene to eject the finished pellet. This method is perfectly suitable for many labs.
For facilities with a high sample throughput, fully automated presses exist. These systems handle the entire pressing and ejection process, freeing up operator time and improving consistency from sample to sample.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to sample preparation should align directly with your analytical objectives.
- If your primary focus is maximum accuracy on individual samples: Concentrate on meticulous grinding techniques to achieve the finest, most homogenous powder possible before pressing.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput and lab efficiency: Consider an automated pressing system to standardize pellet creation, reduce manual error, and improve overall consistency.
Ultimately, a well-prepared pellet is the foundation of reliable XRF analysis.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Consideration |
|---|---|
| Standard Diameter | 32 mm or 40 mm |
| Primary Goal | Create a uniform, dense pellet for accurate analysis |
| Critical Step | Grinding to a fine, homogenous powder before pressing |
| Pressing Method | Manual (standard) or Automated (high-throughput) |
Achieve reliable and accurate XRF analysis with perfectly prepared pellets. The quality of your sample preparation directly impacts your results. KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables you need for consistent success, from durable pellet presses to grinding aids. Let our experts help you optimize your workflow for maximum accuracy or high-throughput efficiency. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific laboratory requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- XRF Boric Acid Lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for Laboratory Use
- XRF & KBR plastic ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- XRF & KBR steel ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Assemble Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between two plate and three plate mold? Choose the Right Mold for Your Project
- What is the function of a metal mold in cold press forming of Al2O3/ZrO2 ceramics? Achieve Precision Shaping
- What roles do graphite molds play in the production of superhard materials? Optimize Sintering with High-Precision Tools
- What is the primary function of high-purity graphite molds in vacuum hot pressing? Enhance Your Composite Fabrication
- What roles do high-strength graphite dies play in SPS of WC composites? Optimize Heat & Pressure for Density
- What is the purpose of customized pressure test molds for [email protected] batteries? Ensure Peak Interface Stability
- How do specialized molds and presses work in solid-state battery assembly? Achieve Superior Densification
- What are the primary functions of a stainless steel mold in CSP? Enhancing CaF2 Ceramic Densification



















