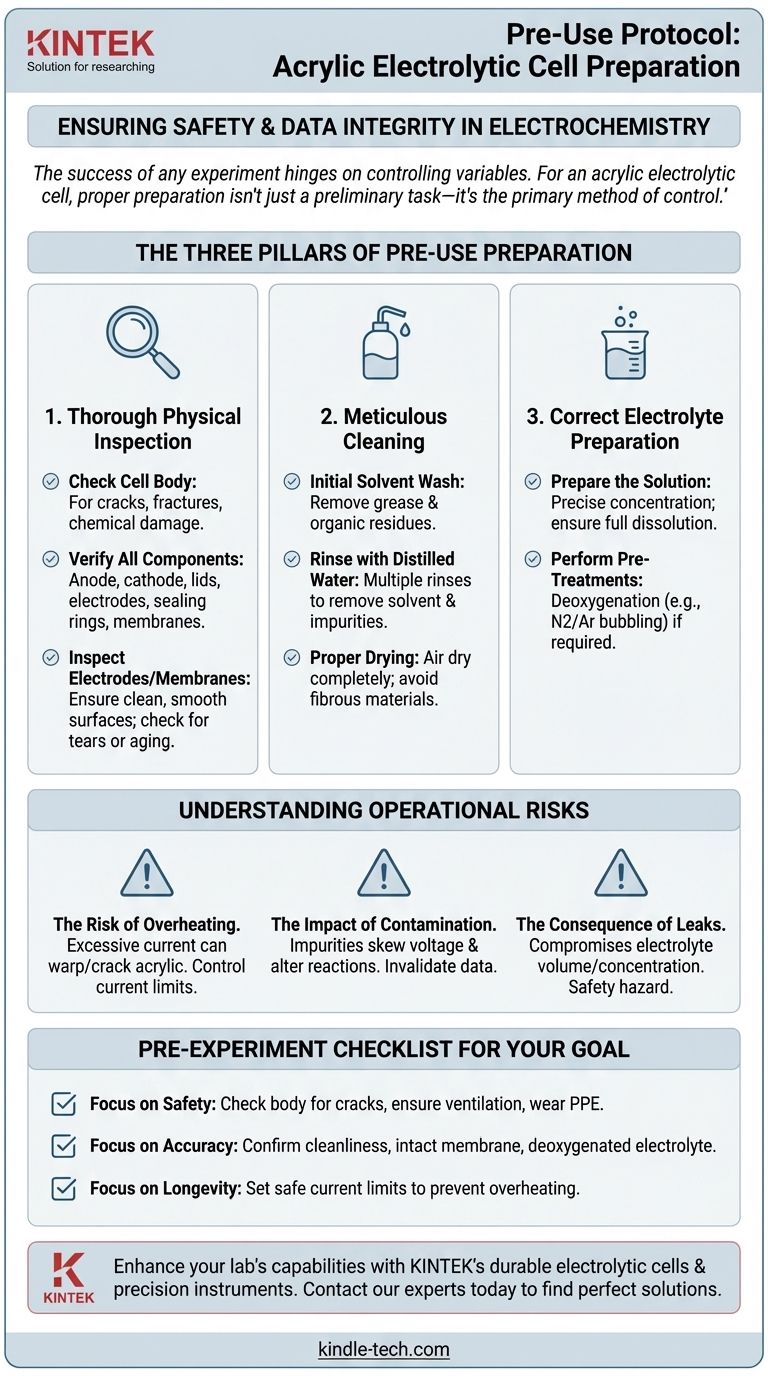
Before using an acrylic electrolytic cell, you must perform a three-step process: physically inspect the cell for any damage or leaks, meticulously clean all components to remove contaminants, and properly prepare the electrolyte according to your experiment's specific requirements. This foundational protocol is essential for ensuring both the safety of the operator and the accuracy of the electrochemical results.
The success of any experiment hinges on controlling variables. For an acrylic electrolytic cell, proper preparation isn't just a preliminary task—it's the primary method of control, safeguarding against equipment failure, safety hazards, and compromised data.
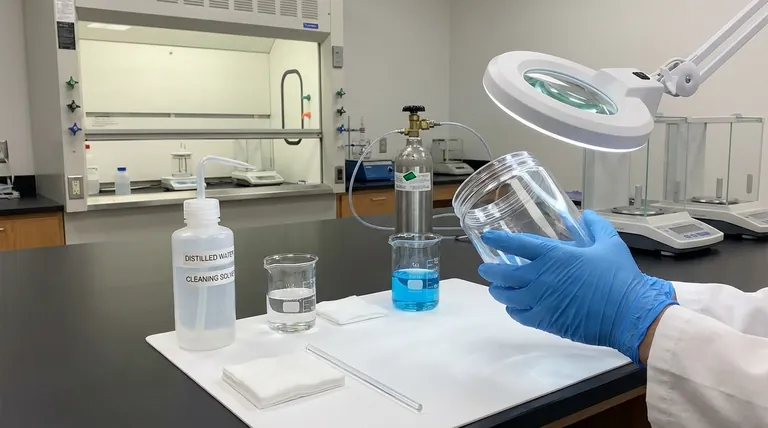

The Three Pillars of Pre-Use Preparation
A systematic approach to preparing your cell ensures that the equipment itself does not become an unintended variable in your experiment. This process can be broken down into three critical stages.
Pillar 1: Thorough Physical Inspection
Your first action should always be a detailed physical check of the entire apparatus.
Check the Cell Body: Carefully examine the acrylic body for any cracks, fractures, or signs of chemical damage. A compromised cell body can lead to dangerous electrolyte leaks.
Verify All Components: Ensure all parts are present and in good condition. This includes the anode and cathode chambers, lids, electrodes, and especially any sealing rings or ion-exchange membranes.
Inspect Electrodes and Membranes: The electrode surfaces must be clean, smooth, and free of corrosion or pitting. If necessary, polish them according to standard procedures. Critically, inspect the ion-exchange membrane for any tears, discoloration, or signs of aging, as its integrity is vital for the cell's function.
Pillar 2: Meticulous Cleaning
Contaminants can significantly interfere with electrochemical reactions, leading to inaccurate and non-reproducible results.
Initial Solvent Wash: Thoroughly clean the cell with a suitable solvent to remove any grease, oils, or organic residues from manufacturing, handling, or previous experiments.
Rinse with Distilled Water: After the solvent wash, rinse all components multiple times with distilled or deionized water to remove any remaining solvent and inorganic impurities.
Proper Drying: Allow the cell to air dry completely. Avoid wiping with materials that could leave behind lint or other fibrous contaminants.
Pillar 3: Correct Electrolyte Preparation
The electrolyte is the heart of the cell, and its preparation is just as critical as the hardware.
Prepare the Solution: Prepare the electrolyte solution to the precise concentration required for your experiment. Ensure all components are fully dissolved.
Perform Necessary Pre-Treatments: Many experiments require pre-treatment of the electrolyte. This often involves deoxygenation (e.g., by bubbling nitrogen or argon gas) to remove dissolved oxygen, which can interfere with certain reactions.
Understanding the Operational Risks
Proper preparation directly mitigates the primary risks associated with using an acrylic cell. Failing to adhere to these steps introduces predictable points of failure.
The Risk of Overheating
An acrylic cell body is sensitive to high temperatures. You must control the electric current according to the cell's specifications. Excessive current can cause electrodes to overheat, creating localized hot spots that can warp, crack, or permanently damage the acrylic.
The Impact of Contamination
Even microscopic impurities can ruin an experiment. A fingerprint inside the cell or residual solvent can act as an unintended reactant or catalyst, skewing voltage readings, altering reaction pathways, and ultimately invalidating your data.
The Consequence of Leaks
A small crack or a faulty seal isn't just a minor issue. It can lead to a slow leak that changes the electrolyte volume and concentration over time, compromising the experiment's integrity and posing a safety hazard.
A Pre-Experiment Checklist for Your Goal
Before you connect the power supply, run through this final checklist based on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is safety: Double-check the cell body for any cracks, ensure ventilation is adequate for potential gas byproducts, and confirm you are wearing acid-resistant gloves and safety goggles.
- If your primary focus is experimental accuracy: Confirm the cell and electrodes are immaculately clean, the ion-exchange membrane is intact, and the electrolyte has been properly prepared and deoxygenated if required.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Verify that your power supply's current limit is set to a safe level for the cell's specifications to prevent any risk of overheating the acrylic.
Ultimately, disciplined and thorough preparation is the foundation of reliable and successful electrochemistry.
Summary Table:
| Preparation Step | Key Action | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Inspection | Check for cracks, verify seals & electrodes | Prevent leaks and equipment failure |
| Meticulous Cleaning | Wash with solvent, rinse with distilled water, air dry | Eliminate contaminants for accurate data |
| Electrolyte Preparation | Precise concentration, deoxygenation if needed | Ensure consistent and reliable reactions |
Ensure your electrochemical experiments are built on a foundation of reliability and safety. Proper preparation is critical, and having the right equipment is the first step. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including durable electrolytic cells and precision instruments designed for accurate, repeatable results.
Let us help you enhance your lab's capabilities and safeguard your research. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solutions for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-precision electrochemical workstation play in the leaching process of Sm2(Co,Fe,Cu,Zr)17 magnets?
- What are the ideal storage conditions for an all-PTFE electrolytic cell? Protect Your Lab's Critical Asset
- What is the objective of bubbling nitrogen (N2) gas into a plutonium nitrate solution? Ensure Precise Deoxygenation
- How is electrochemical fragmentation used to increase liquid metal surface area? Boost Catalytic Efficiency
- What are the standard opening configurations for non-sealed and sealed all-PTFE electrolytic cells?
- What is the function of a three-electrode electrolytic cell? Enhance EIS Accuracy for Polyester Coating Evaluation
- Function of 2-Compartment Electrolytic Cells in Resin Decontamination: Faster & Efficient Cleaning
- What engineering challenges are addressed by specialized pressure-applying cells for testing all-solid-state batteries?