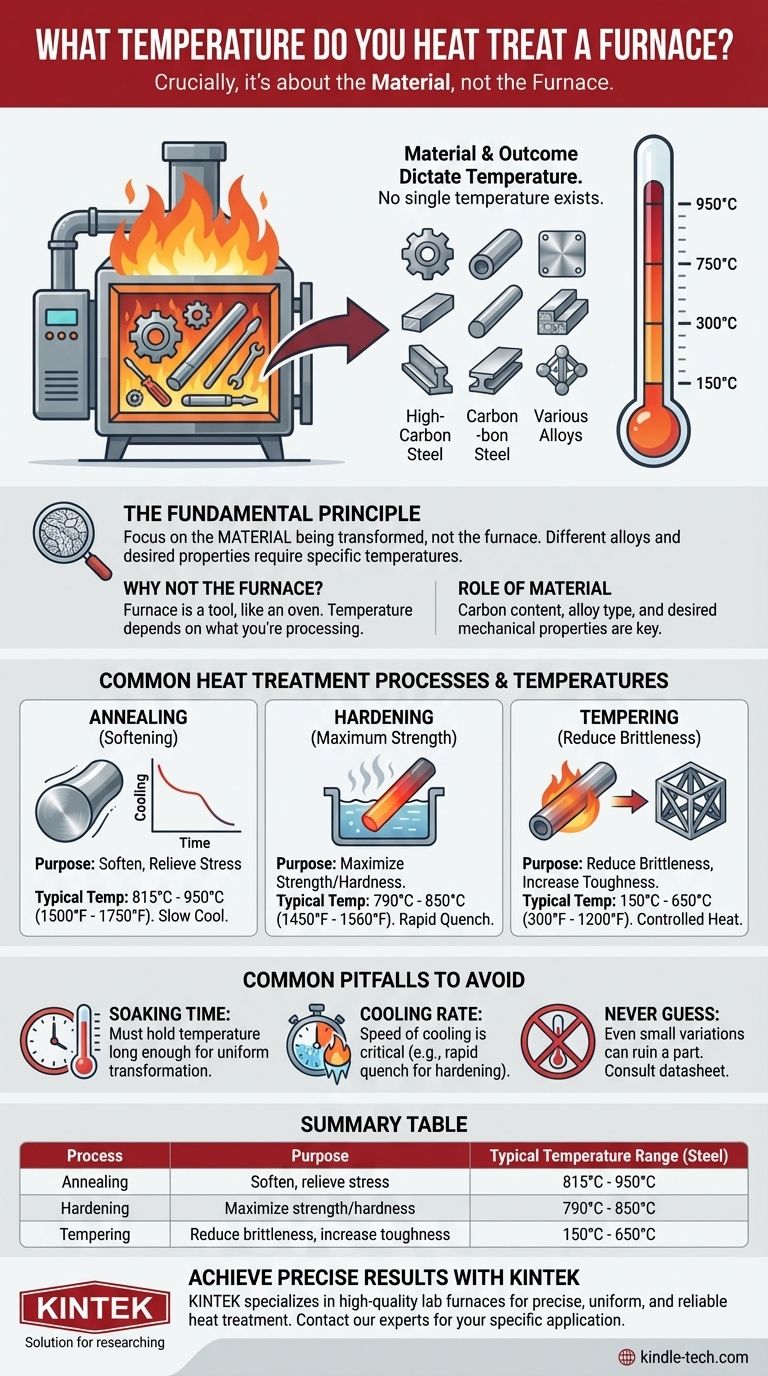
Crucially, the temperature for heat treatment is determined by the material inside the furnace, not the furnace itself. The correct temperature depends entirely on the type of metal and the desired outcome, such as hardening or softening, with typical processes for steel ranging from as low as 150°C to over 950°C.
The central principle of heat treatment is that there is no single temperature. The precise temperature is a critical variable dictated by two factors: the specific alloy you are working with and the mechanical properties you intend to achieve.
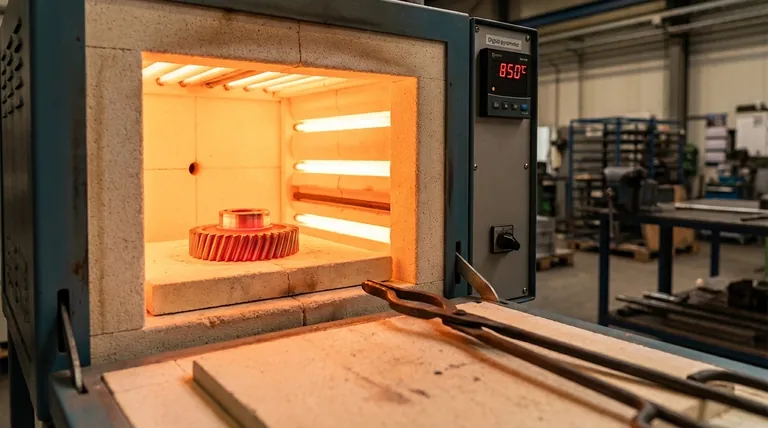

The Fundamental Principle: Material and Outcome Dictate Temperature
The most common misconception is focusing on the equipment. The furnace is simply the tool that provides controlled heat; the real subject of the process is the material being transformed.
Why the Furnace Isn't the Focus
A furnace is designed to operate across a wide range of temperatures. Asking for the heat treatment temperature of a furnace is like asking for the cooking temperature of an oven—it depends entirely on whether you are baking bread or roasting a chicken.
The critical temperature is the one that causes a specific microstructural change within the metal alloy.
The Role of Material Composition
Different metals and alloys transform at vastly different temperatures. The carbon content in steel, for example, is a primary driver of its heat treatment temperatures.
A high-carbon steel used for a cutting tool will require a different temperature cycle than a low-carbon steel used for a structural bracket.
The Goal of the Treatment
The purpose of the heat treatment dictates the temperature range. Are you trying to make the metal harder or softer?
- Hardening requires heating the metal above a critical transformation point.
- Tempering, which reduces brittleness in already hardened steel, occurs at temperatures below that same point.
Common Heat Treatment Processes and Their Temperatures
To provide a practical framework, let's look at three common processes for a typical carbon steel. These are representative examples; exact values require a material datasheet.
Annealing: For Softening and Stress Relief
Annealing is used to make metal as soft and ductile as possible, often to make it easier to machine. This requires heating the steel to a high temperature and then cooling it very slowly.
For many common steels, this temperature is between 815°C and 950°C (1500°F to 1750°F).
Hardening (Quenching): For Maximum Strength
Hardening involves heating steel to a temperature where its internal crystal structure changes to a phase called austenite, then rapidly cooling (quenching) it to lock in a very hard, brittle structure called martensite.
This "austenitizing" temperature is typically between 790°C and 850°C (1450°F to 1560°F).
Tempering: For Reducing Brittleness
A freshly hardened part is often too brittle for practical use. Tempering is a secondary, lower-temperature treatment that increases toughness by slightly reducing hardness.
The temperature is precisely controlled and can range from 150°C to 650°C (300°F to 1200°F), depending on the desired balance of hardness and toughness.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Achieving the correct properties involves more than just hitting a target temperature. Misunderstanding the complete process leads to failed parts.
The Importance of "Soaking" Time
It is not enough to simply reach the target temperature. The material must be held at that temperature—a process called soaking—long enough for the entire part, from surface to core, to undergo the desired transformation.
The Cooling Rate is Just as Critical
The speed at which the material is cooled after heating is as important as the heating temperature itself.
A rapid quench in water or oil is necessary for hardening, while a very slow cool inside the furnace is required for annealing. The wrong cooling rate will completely negate the effects of the heating cycle.
Never Guess the Temperature
Using the wrong temperature by even 25-50 degrees can ruin a part. Overheating can cause excessive grain growth, making the part weak. Underheating will result in an incomplete transformation, failing to achieve the desired hardness.
Determining the Correct Temperature for Your Application
To find the right temperature, you must first define your material and your goal.
- If your primary focus is to soften steel for easier machining (Annealing): You will use a high heat, typically above 800°C, followed by a very slow cooling period.
- If your primary focus is to make a steel part as hard as possible (Hardening): You must heat the material to its specific austenitizing temperature and then quench it rapidly.
- If your primary focus is to toughen an already hardened part (Tempering): You will use a precise, much lower temperature to carefully balance the trade-off between hardness and brittleness.
Always consult the material's specific datasheet to ensure a precise, safe, and successful heat treatment.
Summary Table:
| Process | Purpose | Typical Temperature Range (for Steel) |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Soften, relieve stress | 815°C - 950°C (1500°F - 1750°F) |
| Hardening | Maximize strength/hardness | 790°C - 850°C (1450°F - 1560°F) |
| Tempering | Reduce brittleness, increase toughness | 150°C - 650°C (300°F - 1200°F) |
Achieve Precise and Repeatable Heat Treatment Results
Navigating the complexities of heat treatment requires not just knowledge, but the right equipment. The precise temperature control, uniform heating, and reliable performance of your furnace are critical to achieving your desired material properties, batch after batch.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and equipment designed to meet the exacting demands of heat treatment processes. Whether you are annealing, hardening, or tempering, our solutions provide the accuracy and consistency your laboratory needs.
Let us help you equip your lab for success. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect furnace for your materials and processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials can be used in sintering? Explore Metals, Ceramics & Composites
- What is the composition of sintered iron? An Engineered System of Iron, Alloys, and Porosity
- Does hardening increase tensile strength? Boost Material Strength for Demanding Applications
- Why is it necessary to perform annealing treatment in a furnace after vacuum hot pressing Lithium Niobate samples?
- Which materials are used for high temperature applications? Choose the Right Material for Extreme Heat
- How does a 3 stage furnace work? Achieve Superior Comfort and Efficiency
- Why is a vacuum drying oven necessary for Pt/Nb-TiO2 catalyst preparation? Optimize Your Material Activity
- What are the sources of materials for biochar production? From Wood to Waste, Choose the Right Feedstock



















