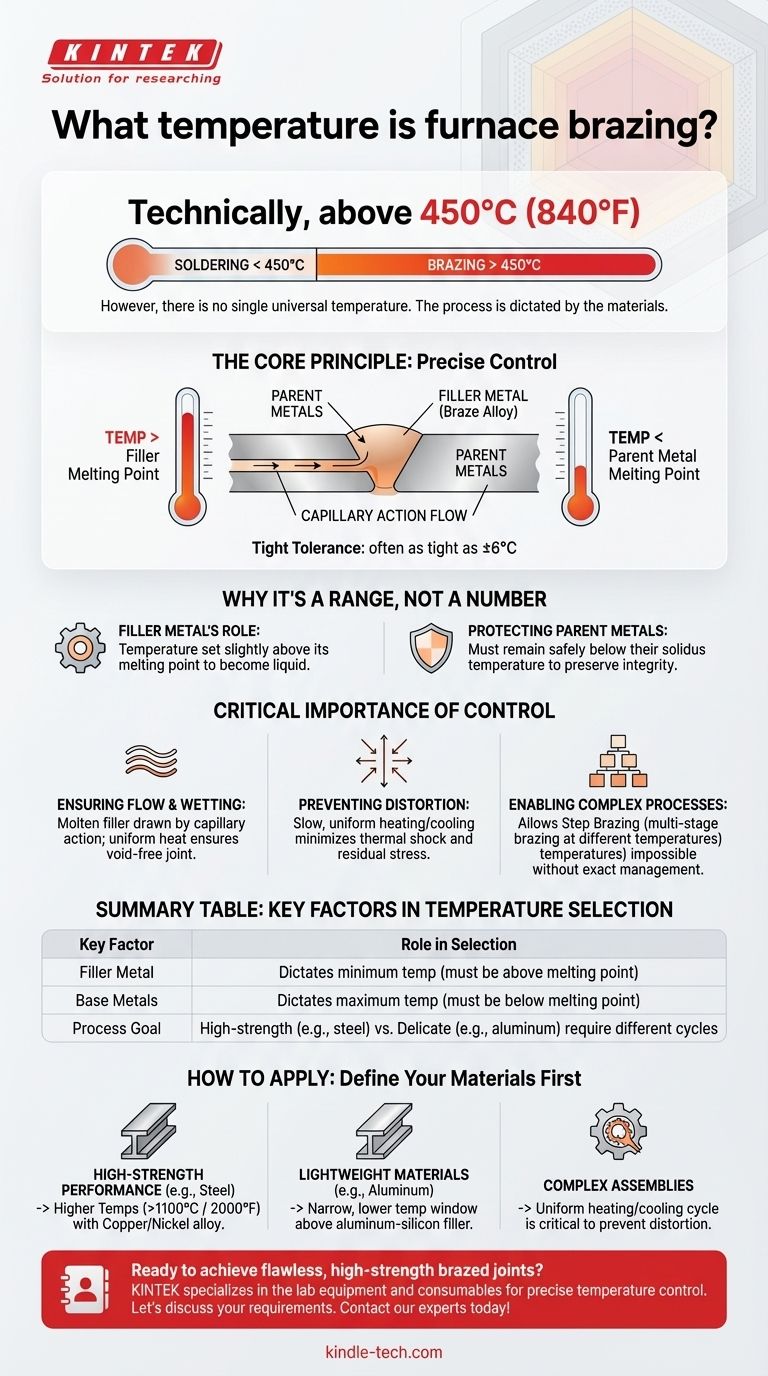
Technically, furnace brazing occurs at any temperature above 450°C (840°F). However, there is no single temperature for the process. The precise temperature is dictated entirely by the specific filler metal being used and must always be below the melting point of the base metals being joined. The key to successful furnace brazing is not a specific number, but the precise control of that temperature, often within a tolerance as tight as ±6°C.
The core principle of furnace brazing is not about hitting a universal temperature, but about selecting the right filler metal for your parent materials and then executing a precisely controlled heating and cooling cycle that activates the filler without compromising the parts themselves.

Why Temperature is a Range, Not a Number
Understanding the function of temperature is more critical than memorizing a specific value. The brazing temperature is a carefully chosen variable in a complex equation involving multiple materials.
The Role of the Filler Metal
The entire process hinges on the filler metal (or braze alloy). The furnace temperature is set to be slightly above the melting point of this specific alloy. This allows the filler to become liquid and flow into the joint.
Protecting the Parent Metals
Critically, the brazing temperature must remain safely below the solidus temperature (the point at which it begins to melt) of the metals being joined. This ensures the parent metals are not damaged or melted, preserving their structural integrity.
The 450°C (840°F) Threshold
The 450°C (840°F) mark is the internationally recognized dividing line. Metal joining processes that use a filler metal below this temperature are defined as soldering, while those that occur above it are defined as brazing.
The Critical Importance of Temperature Control
The advantages of furnace brazing are directly tied to its ability to manage heat with exceptional precision. The references to uniform heating, minimal distortion, and combining heat treatments all stem from this control.
Ensuring Proper Flow and Wetting
Once the furnace reaches the correct temperature, the molten filler metal is drawn through the tight gap between the parent metals by capillary action. Consistent, uniform heat ensures this flow is complete, creating a strong, void-free joint.
Preventing Distortion and Stress
Slow, uniform heating and cooling rates are hallmarks of the furnace brazing process. This controlled thermal cycle minimizes the risk of thermal shock, distortion, or residual stress in the final assembly, which is critical for high-precision components.
Enabling Complex Processes
Precise temperature control allows for advanced techniques. Step brazing, for instance, involves joining a component with a high-temperature filler, then performing a second braze on the same assembly at a lower temperature using a different filler alloy. This would be impossible without exact thermal management.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, furnace brazing is not a universal solution. Its advantages come with specific requirements and limitations.
High Initial Equipment Cost
Industrial furnaces, particularly those with vacuum or controlled atmosphere capabilities, represent a significant capital investment. The process is designed for production environments.
Atmosphere Control is Non-Negotiable
One of the process's main advantages is the use of a clean atmosphere (like a vacuum or inert gas) to prevent oxidation, eliminating the need for flux. This is a powerful benefit, but it also means the equipment is more complex and requires careful monitoring.
Best Suited for Production Volumes
Furnace brazing excels at producing many identical parts with repeatable, high-quality results. It is generally not a cost-effective or practical method for one-off repairs or very small batch sizes.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Instead of asking for a single temperature, the effective approach is to define your materials and desired outcome first.
- If your primary focus is high-strength performance (e.g., steel assemblies): Your process will likely involve a copper or nickel-based filler alloy, requiring furnace temperatures that can exceed 1100°C (2000°F).
- If your primary focus is joining lightweight materials (e.g., aluminum): You will operate in a much lower and narrower temperature window, carefully managed to be just above the aluminum-silicon filler's melting point.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing complex assemblies: The critical factor is the uniformity of the heating and cooling cycle, ensuring all joints reach the target temperature without overheating or distorting delicate components.
Ultimately, selecting the correct brazing temperature is a function of careful engineering, driven by the materials you intend to join.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Temperature Selection |
|---|---|
| Filler Metal | Dictates the minimum temperature (must be above its melting point). |
| Base Metals | Dictates the maximum temperature (must be below their melting point). |
| Process Goal | High-strength joints (steel) vs. delicate materials (aluminum) require different thermal cycles. |
Ready to achieve flawless, high-strength brazed joints? The precise temperature control of furnace brazing is key to success. At KINTEK, we specialize in the lab equipment and consumables that make this precision possible. Our expertise helps laboratories and manufacturers select the right materials and processes for joining everything from high-performance steels to delicate aluminum assemblies. Let's discuss your project requirements and how we can support your brazing success. Contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What is brazing in heat treatment? Achieve Superior Joint Quality and Efficiency
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries



















