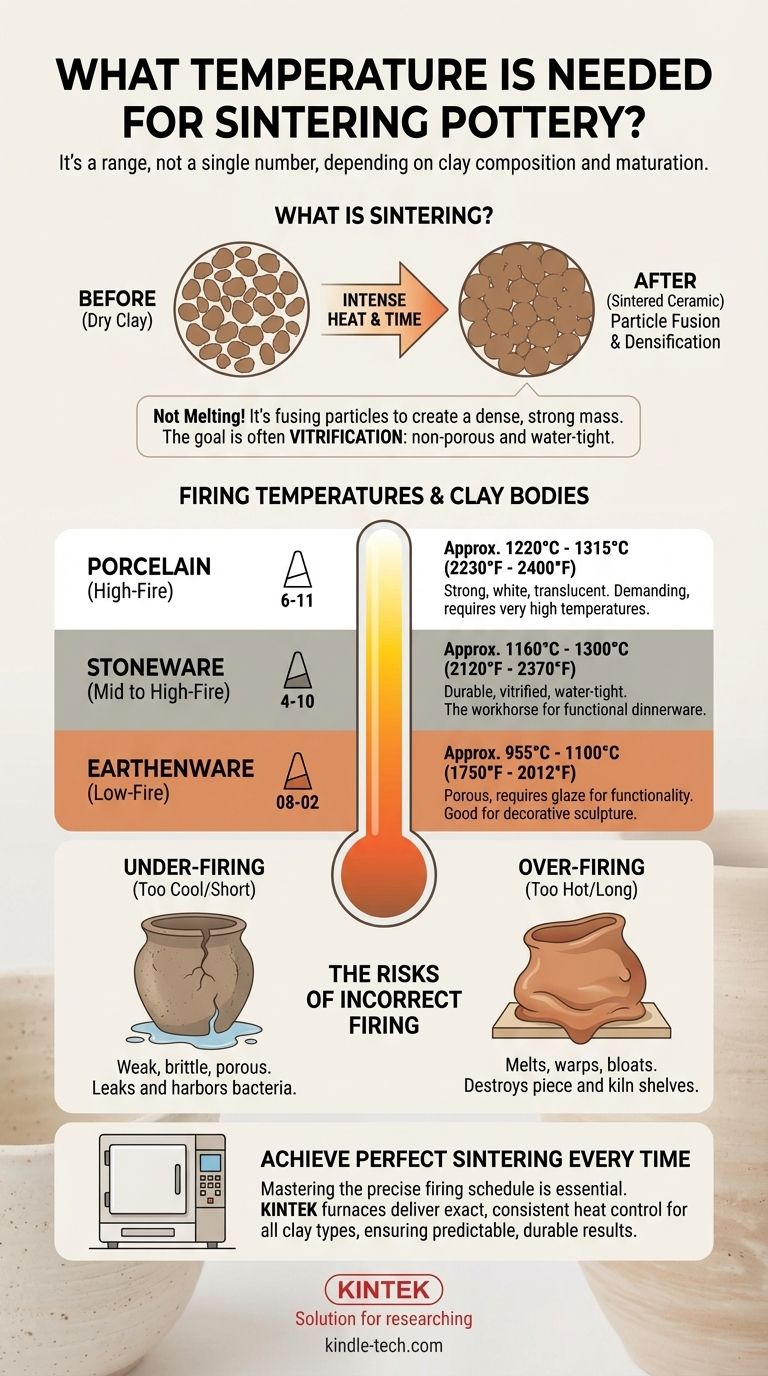
The temperature required for sintering pottery is not a single number, but a wide range that depends entirely on the chemical composition of the clay body you are using. Generally, this process occurs between 955°C (1750°F) for low-fire earthenware and can go as high as 1300°C (2370°F) for high-fire porcelain. The key is to fire the clay to its specific maturation point to achieve the desired strength and density.
Sintering is a process of particle fusion driven by heat, not just a target temperature. The fundamental task for any potter is to match the firing schedule—specifically the target "cone"—to their specific clay body. This ensures the piece becomes strong and dense without melting or warping.

What is Sintering in Ceramics?
Sintering is the critical transformation that turns a fragile, chalky piece of dry clay into a hard, stone-like ceramic object. Understanding this process is more important than memorizing a single temperature.
From Particles to a Solid Mass
At a microscopic level, clay is made of tiny, flat particles. During sintering, the intense heat causes the edges of these particles to fuse together. The particles themselves don't melt entirely, but they bond at their points of contact, reducing the space between them and creating a dense, unified mass.
Sintering vs. Melting
This is a crucial distinction. Sintering is the fusion of particles without turning the entire object into a liquid. If you exceed the correct sintering range, the clay will begin to fully melt, a process called slumping or bloating, which results in a ruined piece.
The Goal: Vitrification
For functional pottery like mugs or bowls, the ideal result of sintering is vitrification. This is a state where the clay particles have fused so densely that the final object is no longer porous and will not absorb water. Low-fire clays sinter but do not fully vitrify, remaining porous unless covered in a glaze.
Firing Temperatures for Common Clay Bodies
The ceramic world categorizes clay by the temperature required to bring it to maturity. This is most accurately measured using a system of pyrometric cones, which bend at a specific "heat work" value—a combination of time and temperature.
Earthenware (Low-Fire)
Earthenware is fired at the lowest temperatures. It sinters to become hard but remains porous, making it unsuitable for functional dinnerware unless properly glazed.
- Cone Range: Cone 08 to Cone 02
- Temperature Range: Approx. 955°C to 1100°C (1750°F to 2012°F)
Stoneware (Mid to High-Fire)
Stoneware is the workhorse of functional pottery. When fired correctly, it becomes vitrified, making it extremely durable, strong, and water-tight. It has a broad firing range depending on the specific clay body.
- Cone Range: Cone 4 to Cone 10
- Temperature Range: Approx. 1160°C to 1300°C (2120°F to 2370°F)
Porcelain (High-Fire)
Porcelain is known for its strength, whiteness, and potential for translucency. It is a demanding clay body that must be fired at very high temperatures to achieve its signature vitrified state.
- Cone Range: Cone 6 to Cone 11
- Temperature Range: Approx. 1220°C to 1315°C (2230°F to 2400°F)
Understanding the Trade-offs: Under-firing vs. Over-firing
Achieving the correct level of sintering is a balancing act. Errors in either direction will compromise your final result.
The Risks of Under-firing
An under-fired piece has not sintered sufficiently. The clay particles have not fused together properly, resulting in a piece that is weak, brittle, and porous. For functional ware, this means it will leak and can harbor bacteria.
The Dangers of Over-firing
An over-fired piece has been heated beyond its maturation point. The clay begins to melt, causing it to bloat, warp, and slump into a puddle. In a worst-case scenario, it can melt onto and destroy your kiln shelves, a costly and frustrating mistake.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your firing strategy should always be dictated by your clay choice and the intended use of the final piece.
- If your primary focus is functional dinnerware: You must fire to the clay's specified maturation point (typically mid-to-high fire stoneware or porcelain) to ensure it is fully vitrified and food-safe.
- If your primary focus is decorative sculpture: You have more flexibility. Low-fire earthenware is an excellent choice that offers vibrant glaze colors and requires less energy to fire.
- If you are ever unsure about your clay: Always trust the manufacturer's recommendation. The clay's packaging will state the ideal firing cone, which is the most reliable guide for achieving proper sintering.
Matching your firing process to your specific clay body is the fundamental skill for achieving predictable and durable ceramic results.
Summary Table:
| Clay Body Type | Firing Range (Cone) | Temperature Range (°C) | Temperature Range (°F) | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Earthenware (Low-Fire) | Cone 08 - Cone 02 | 955°C - 1100°C | 1750°F - 2012°F | Porous, requires glaze for functionality |
| Stoneware (Mid to High-Fire) | Cone 4 - Cone 10 | 1160°C - 1300°C | 2120°F - 2370°F | Durable, vitrified, and water-tight |
| Porcelain (High-Fire) | Cone 6 - Cone 11 | 1220°C - 1315°C | 2230°F - 2400°F | Strong, white, and potentially translucent |
Achieve Perfect Sintering Every Time with KINTEK
Mastering the precise temperature for your clay body is essential for creating strong, functional, and beautiful pottery. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab furnaces and kilns that deliver the exact, consistent heat control needed for perfect sintering results—from low-fire earthenware to high-fire porcelain.
Our equipment helps you avoid the risks of under-firing (weak, porous pieces) and over-firing (warping, melting), ensuring your ceramics reach their full potential. Whether you're a studio artist, educator, or professional potter, we have the solutions to meet your specific firing needs.
Ready to elevate your ceramic work? Contact our experts today to find the ideal kiln for your studio and achieve predictable, durable results with every firing.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing



















