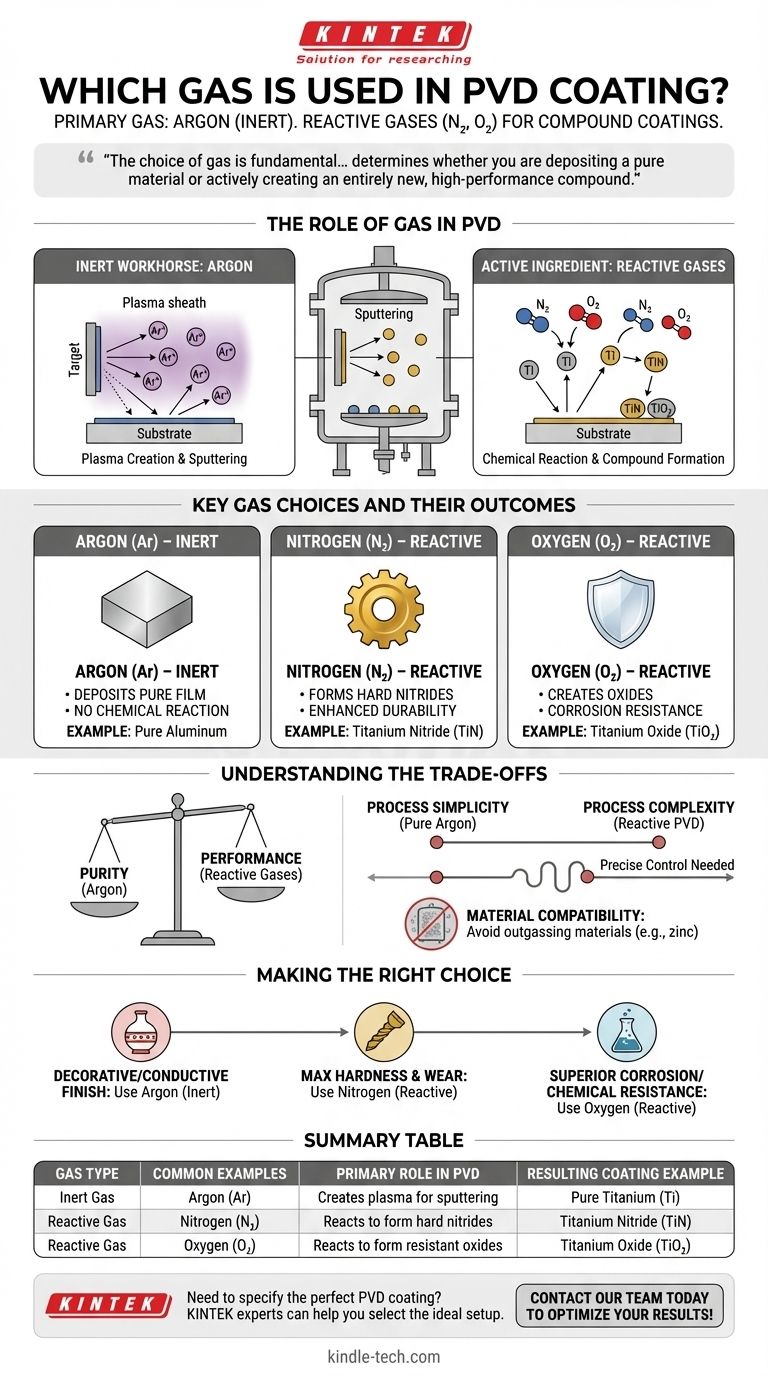
The primary gas used in Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is Argon. This is because Argon is an inert gas, meaning it will not chemically react with the coating material during the process. However, other "reactive" gases like nitrogen or oxygen are also intentionally introduced to create specific, highly durable compound coatings.
The choice of gas is fundamental to the PVD process. It determines whether you are depositing a pure material onto a surface or actively creating an entirely new, high-performance compound as the coating itself.
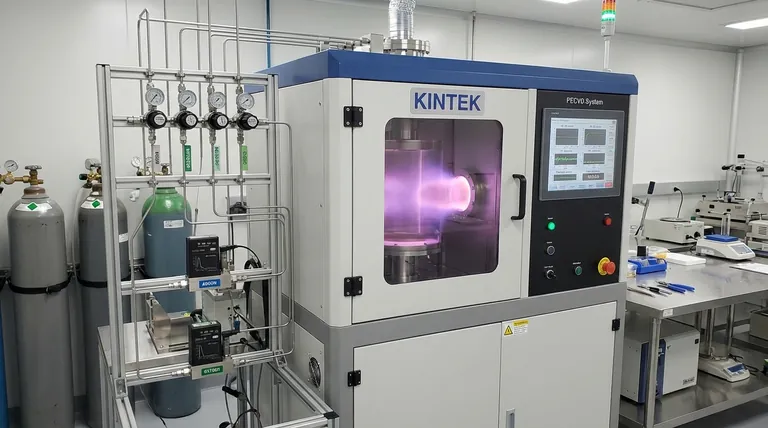

The Role of Gas in the PVD Process
Even though PVD occurs in a high-vacuum chamber, gas is a critical and functional element. It isn't just filler; it's the medium that makes the entire process possible.
The Inert Workhorse: Argon
Argon is the default choice for most PVD applications, particularly in a method called sputtering.
Its primary role is to create a plasma. When a high voltage is applied in the low-pressure argon environment, the argon atoms are ionized, creating positively charged argon ions (Ar+).
These ions are then accelerated by an electric field and slam into the source material (the "target"), such as a block of pure titanium. This high-energy bombardment physically knocks atoms off the target, which then travel through the vacuum and deposit onto your substrate as a thin, pure film.
The Active Ingredient: Reactive Gases
Sometimes, the goal isn't to deposit a pure metal, but to create a much harder ceramic compound on the surface.
This is achieved through reactive PVD. In this process, a reactive gas like nitrogen, oxygen, or acetylene (a source of carbon) is bled into the vacuum chamber along with the argon.
As the metal atoms are sputtered from the target, they chemically react with the gas on their way to the substrate. For example, titanium atoms will combine with nitrogen gas to form a gold-colored Titanium Nitride (TiN) coating, which is significantly harder than pure titanium.
Key Gas Choices and Their Outcomes
The specific gas introduced dictates the final properties of the coating. This is a highly controlled process where the gas mixture is tailored to the desired outcome.
Argon (Ar)
Argon is used alone when the goal is to deposit a pure film of the target material. For example, sputtering an aluminum target with only argon will result in a pure aluminum coating.
Nitrogen (N₂)
Nitrogen is the most common reactive gas. It is used to form hard, wear-resistant nitride coatings. Popular examples include Titanium Nitride (TiN) and Chromium Nitride (CrN), known for their durability and low friction.
Oxygen (O₂)
Oxygen is introduced to create oxide coatings. These films, such as Titanium Oxide (TiO₂) or Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃), are often used for their excellent corrosion resistance, dielectric properties, or specific optical characteristics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a gas is a deliberate decision based on the end goal, and it involves critical trade-offs in process control and final properties.
Purity vs. Performance
Using only argon ensures the highest purity of the deposited film, mirroring the source material exactly. Introducing a reactive gas sacrifices this purity to create a new compound with enhanced performance characteristics, such as superior hardness or corrosion resistance.
Process Simplicity vs. Complexity
A pure argon process is relatively straightforward. Reactive PVD, however, requires precise control over gas flow rates and partial pressures. A slight imbalance can result in a coating with incorrect chemical composition and poor performance.
Material Compatibility
The choice of gas and process is also linked to the substrate material. Certain materials, like zinc or un-galvanized brass, are unsuitable for high-vacuum processes because they "outgas," releasing vapors that contaminate the chamber and interfere with the desired gas reactions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The gas you select is directly tied to the final function of your coated part.
- If your primary focus is a pure decorative or conductive metallic finish: You will use an inert gas like Argon to deposit the target material without any chemical changes.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: You will use a reactive gas like nitrogen to form a hard ceramic compound, such as Titanium Nitride.
- If your primary focus is superior corrosion or chemical resistance: You will likely use a reactive gas like oxygen to form a stable, non-reactive oxide layer.
Ultimately, understanding the role of each gas transforms the PVD process from a simple coating method into a precise tool for surface engineering.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Common Examples | Primary Role in PVD | Resulting Coating Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inert Gas | Argon (Ar) | Creates plasma to sputter pure metal atoms | Pure Titanium (Ti) |
| Reactive Gas | Nitrogen (N₂) | Reacts with metal to form hard nitrides | Titanium Nitride (TiN) |
| Reactive Gas | Oxygen (O₂) | Reacts with metal to form resistant oxides | Titanium Oxide (TiO₂) |
Need to specify the perfect PVD coating for your application? The right gas mixture is critical for achieving the desired hardness, corrosion resistance, or decorative finish. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced coating processes. Our experts can help you select the ideal setup for your laboratory's specific surface engineering goals.
Contact our team today to discuss your PVD coating requirements and optimize your results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















