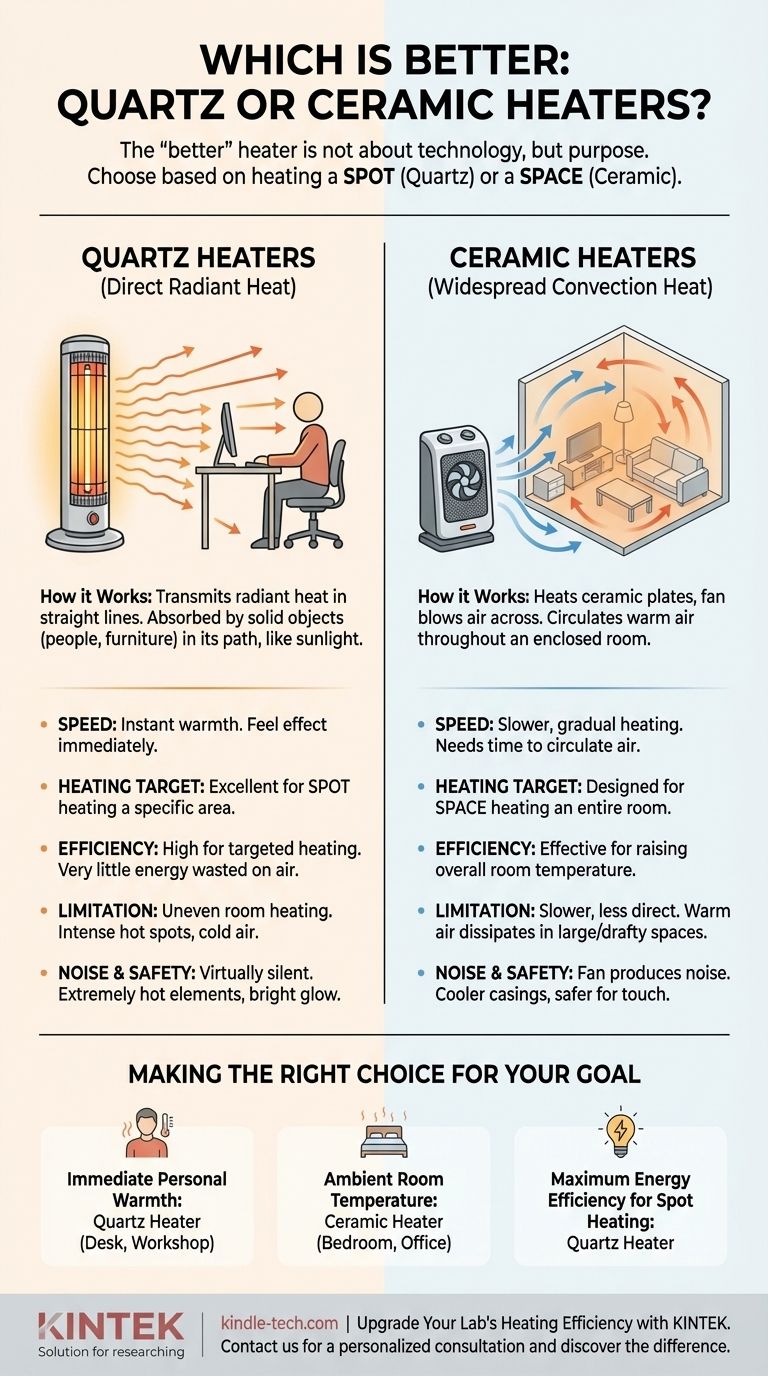
For fast, direct heating of objects and people, quartz heaters are better. They operate by transmitting radiant heat, similar to the sun, providing instant warmth to anything in their path with high energy efficiency. For heating the air in an entire enclosed space, however, ceramic heaters are often the more effective choice.
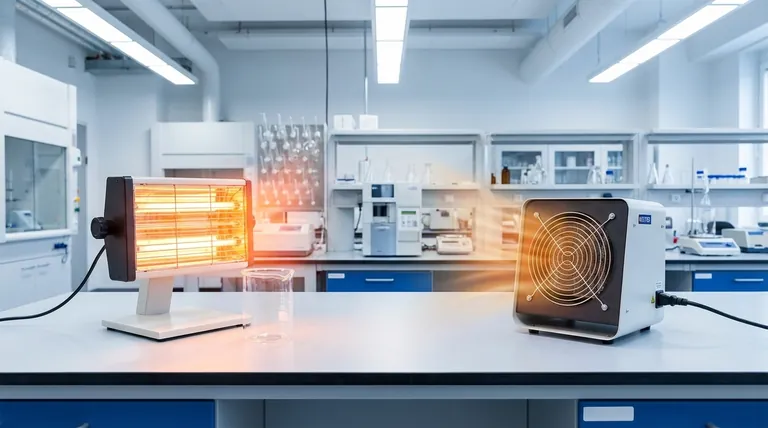
The "better" heater is not a question of technology, but of purpose. Your choice depends entirely on whether you need to heat a specific spot (quartz) or an entire space (ceramic).

The Fundamental Difference: Radiant vs. Convection Heat
To choose correctly, you must first understand the two different ways these heaters work. The technology defines the application.
How Quartz Heaters Work: Direct Radiant Heat
A quartz heater uses a heating element encased in a quartz tube. This element produces infrared radiation, a form of energy that travels in a straight line.
This energy does not heat the air it passes through. Instead, it is absorbed by solid objects in its path—people, furniture, walls—which then feel warm. Think of it like standing in the sunlight on a cold day; you feel warm even if the air around you is chilly.
How Ceramic Heaters Work: Widespread Convection Heat
A ceramic heater uses an electrical current to heat a series of ceramic plates. A fan then blows air across these hot plates.
This process, called convection, heats the air itself. The warm air then circulates throughout an enclosed room, gradually raising the overall ambient temperature. This is similar to how a home's central forced-air furnace operates.
Head-to-Head Comparison
Based on these different methods, their performance characteristics vary significantly.
Speed and Responsiveness
Quartz heaters provide nearly instantaneous warmth. Because they emit radiant heat, you feel their effect as soon as they are turned on. They also cool down very quickly.
Ceramic heaters are much slower. They must first heat their internal elements and then heat enough air to circulate and raise the room's temperature, which can take considerable time.
Heat Targeting and Area of Effect
Quartz heaters excel at spot heating. Their radiant energy is directional, making them perfect for warming a specific area like a person at a desk or a workbench in a cold garage.
Ceramic heaters are designed for space heating. The convection heat they produce warms the air in an entire room, providing a more even, widespread temperature increase, assuming the space is enclosed and reasonably insulated.
Energy Efficiency
The claim that quartz heaters are more efficient is only true for a specific goal. They are highly efficient at converting electricity into direct, targeted radiant heat. Very little energy is wasted heating the surrounding air.
If your goal is to heat one person, a quartz heater uses far less energy than a ceramic heater trying to heat the entire room for that one person. However, if your goal is to heat the whole room, a ceramic heater is designed for that task and will be more effective.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technology is perfect. Acknowledging their limitations is key to avoiding frustration.
The Quartz Limitation: Uneven Room Heating
Using a quartz heater to warm an entire room is ineffective. It will create intense hot spots on objects in its line of sight while leaving other parts of the room cold. The air temperature itself will remain largely unchanged.
The Ceramic Limitation: Slower and Less Direct
A ceramic heater offers no immediate, targeted warmth. You must wait for the convection process to work. If you are in a large or drafty space, the warm air it produces can be easily dissipated, making it feel ineffective.
Other Considerations: Noise and Safety
Quartz heaters are virtually silent, as they typically do not require a fan. Ceramic heaters, by definition, use a fan and thus produce a constant background noise.
The heating elements in quartz heaters become extremely hot and emit a bright glow, which can pose a higher burn risk if touched and may be disruptive in a dark room. Ceramic heaters often have casings that remain cooler to the touch, making them a potentially safer choice in homes with children or pets.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your heater based on a clear understanding of your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is immediate, personal warmth at a desk or in a workshop: Choose a quartz heater for its fast, direct, and efficient radiant heat.
- If your primary focus is raising the ambient temperature of an entire, well-defined room like a bedroom or office: Choose a ceramic heater for its ability to provide even, circulating convection heat.
- If your primary focus is maximum energy efficiency for spot heating a person: The quartz heater is the clear winner, as it heats the target directly without wasting energy on the surrounding air.
By matching the heater's fundamental method of heat transfer to your specific need, you ensure you are selecting the most effective and efficient tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Quartz Heater | Ceramic Heater |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Type | Radiant (direct) | Convection (air) |
| Best For | Spot heating people/objects | Heating entire enclosed spaces |
| Speed | Instant warmth | Slower, gradual heating |
| Energy Efficiency | High for targeted heating | Effective for room heating |
| Noise Level | Virtually silent | Fan produces noise |
Upgrade Your Lab's Heating Efficiency with KINTEK
Struggling to maintain precise temperatures for your experiments or processes? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including reliable heating solutions tailored for laboratory environments. Whether you need targeted heating for a specific application or consistent ambient warmth for your workspace, our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for maximum efficiency and accuracy.
Let our specialists help you select the ideal heating system to enhance your lab's productivity and results. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and discover the difference professional lab equipment can make!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What material is used for making heating element? Choose the Right Alloy for Your Application
- What are silicon carbide heating elements used for? Reliable High-Temp Heating for Industrial Processes
- What is the maximum temperature for silicon carbide heating element? The Real Limit for Your High-Temp Furnace
- What is silicon carbide rod heated to high temperature used as? A Premier Heating Element for Extreme Environments
- What is SiC elements? The Ultimate High-Temperature Heating Solution
















