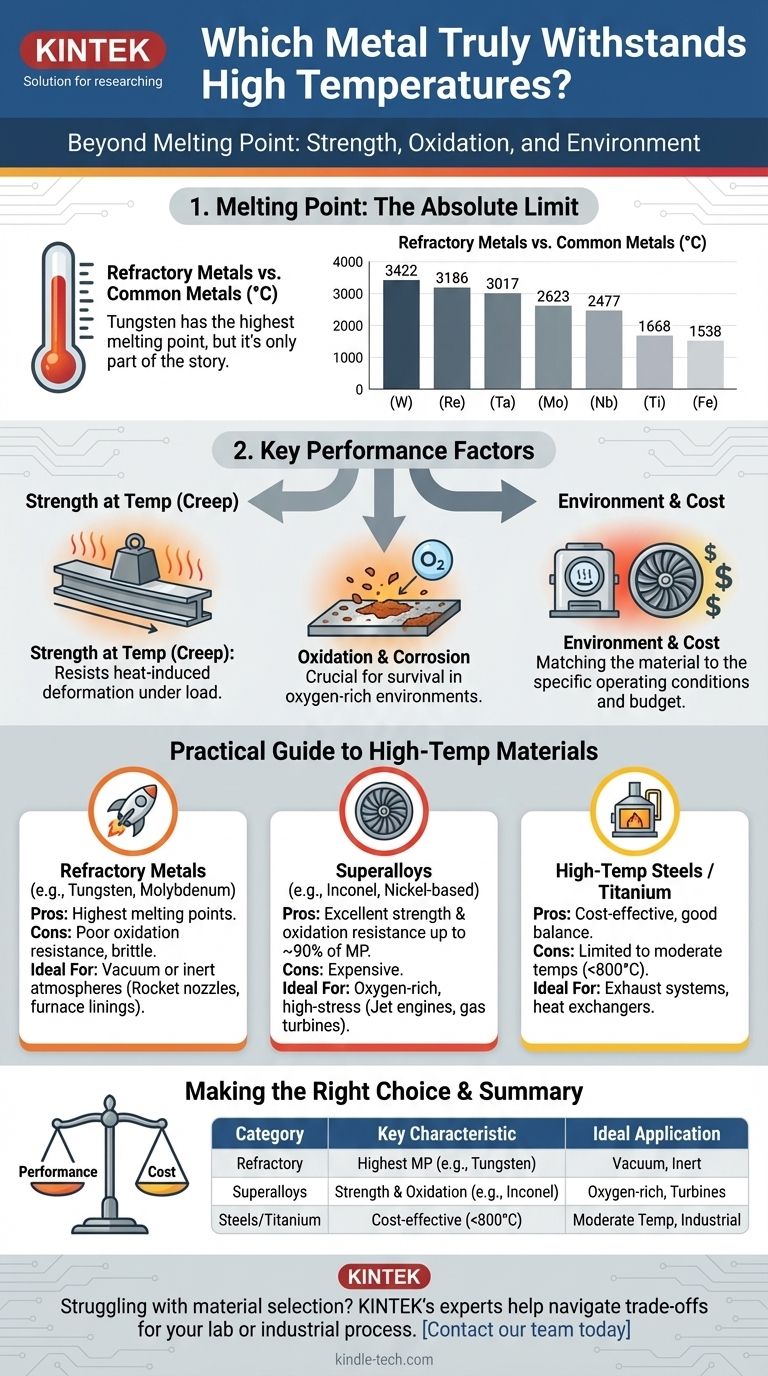
Technically, the pure metal with the highest melting point is Tungsten. With a melting point of 3,422 °C (6,192 °F), it stands far above common metals like iron or aluminum. However, simply knowing the melting point is not enough to select a metal for a high-temperature application.
The most critical challenge in high-temperature material science is not just resisting melting, but maintaining mechanical strength and resisting environmental degradation—primarily oxidation—as temperatures rise. The "best" material is therefore highly dependent on the specific operating environment.
Beyond Melting Point: What "Withstanding Heat" Really Means
Answering this question properly requires looking past a single data point. Several properties collectively determine a material's performance and survival under extreme heat.
Melting Point: The Absolute Limit
The melting point is the temperature at which a material turns from a solid to a liquid. It is the absolute upper ceiling for any structural application.
The class of materials with the highest melting points are known as refractory metals.
| Metal | Melting Point (°C) | Melting Point (°F) |
|---|---|---|
| Tungsten (W) | 3422 | 6192 |
| Rhenium (Re) | 3186 | 5767 |
| Tantalum (Ta) | 3017 | 5463 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 2623 | 4753 |
| Niobium (Nb) | 2477 | 4491 |
These temperatures are significantly higher than those of iron (1538 °C) or titanium (1668 °C).
Strength at Temperature (Creep Resistance)
Long before a metal melts, it begins to soften and lose its structural integrity. This slow, heat-induced deformation under load is called creep.
A material with excellent high-temperature performance must resist creep to remain useful. This is a primary reason why alloys are almost always used instead of pure metals in demanding applications.
Oxidation and Corrosion Resistance
This is often the most significant real-world limitation. Many materials with extremely high melting points, including tungsten, react aggressively with oxygen at high temperatures.
This oxidation can cause the material to rapidly degrade, flake away, or fail catastrophically. A truly effective high-temperature metal must be able to operate in its intended atmosphere, which often includes oxygen.
A Practical Guide to High-Temperature Materials
Engineers choose materials based on a balance of these properties. The three most important categories are refractory metals, superalloys, and specialized steels.
Refractory Metals (The Champions of Melting Point)
Tungsten, Molybdenum, Tantalum, and their counterparts are defined by their incredibly high melting points.
Their primary strength is their heat resistance in a vacuum or an inert (non-reactive) gas environment. This makes them ideal for applications like rocket nozzles, vacuum furnace linings, and electrical contacts.
Superalloys (The Workhorses of Extreme Environments)
Superalloys are typically based on nickel, cobalt, or iron. While their melting points are lower than refractory metals, their performance is exceptional up to about 80-90% of those temperatures.
Their key advantage is the formation of a stable, protective oxide layer on their surface at high heat. This layer, often composed of aluminum or chromium oxides, acts as a shield against further oxidation. This unique property makes nickel-based superalloys (like Inconel) the material of choice for the hottest parts of jet engines and gas turbines—environments where both extreme heat and oxygen are present.
High-Temperature Steels and Titanium
For moderately high temperatures—typically below 800°C (1475°F)—specialized stainless steels and titanium alloys offer a practical balance of performance and cost.
They provide good strength and corrosion resistance at a fraction of the cost of superalloys, making them suitable for exhaust systems, industrial furnaces, and heat exchangers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right material involves navigating a series of critical compromises. There is no single "best" metal for all situations.
The Oxidation Dilemma
The most common mistake is selecting a material based on melting point alone. Tungsten is essentially unusable in the open air at high temperatures because it will rapidly oxidize and fail. A superalloy with a lower melting point will vastly outperform it in such an environment.
The Brittleness Problem
Many high-performance materials, especially tungsten, are notoriously brittle and difficult to machine at room temperature. This significantly increases the complexity and cost of manufacturing parts.
Cost vs. Performance
The highest-performing materials come with the highest costs. Nickel, cobalt, and especially rhenium are expensive elements. This economic reality often dictates that engineers use the most affordable material that can safely meet the minimum performance requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by the specific demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is the absolute highest temperature resistance in a vacuum or inert atmosphere: Refractory metals, particularly Tungsten, are the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is high strength in an oxygen-rich environment (e.g., a turbine): Nickel-based superalloys are the undisputed industry standard for their unique blend of strength and oxidation resistance.
- If your primary focus is a cost-effective solution for moderately high temperatures: Specialized stainless steels or titanium alloys provide the most practical balance of properties.
Ultimately, selecting the right metal is about matching its complete property profile—not just its melting point—to the unique challenges of the application.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Key Characteristic | Ideal Application |
|---|---|---|
| Refractory Metals | Highest melting point (e.g., Tungsten: 3422°C) | Vacuum furnaces, rocket nozzles (inert atmosphere) |
| Superalloys | Excellent strength & oxidation resistance (e.g., Inconel) | Jet engines, gas turbines (oxygen-rich environments) |
| High-Temp Steels/Titanium | Cost-effective for moderate temperatures (<800°C) | Exhaust systems, industrial furnaces, heat exchangers |
Struggling to select the right high-temperature material for your lab or industrial process? KINTEK specializes in providing lab equipment and consumables designed for extreme environments. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between melting point, oxidation resistance, and cost to find the optimal solution for your specific needs—whether you require furnace components, heating elements, or custom high-temp parts. Contact our team today to discuss your application and ensure your project's success with the right materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
People Also Ask
- What is the suitability of tungsten as an electrical conducting material for heating applications? Master Extreme High-Temperature Heating
- Can tungsten be used as a heating element? Unlocking Extreme Heat for High-Temperature Applications
- What is the melting point of tungsten? Discover the Metal That Withstands Extreme Heat
- What happens when tungsten is heated? Harnessing Extreme Heat for Demanding Applications
- What are heating elements with tungsten? Unlock Extreme Heat for Vacuum & Industrial Processes



















