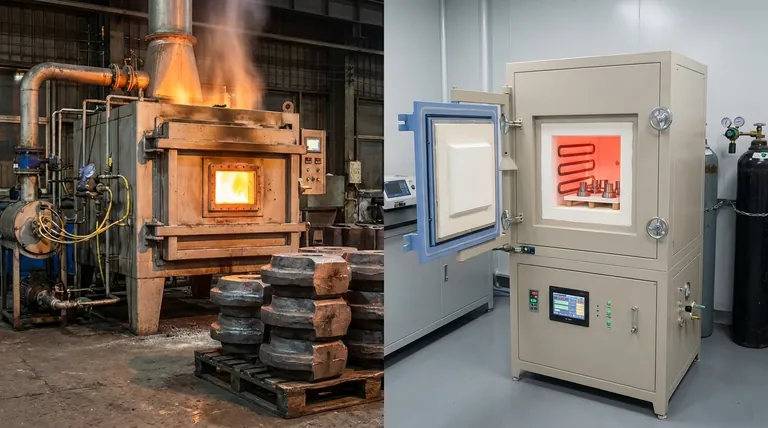
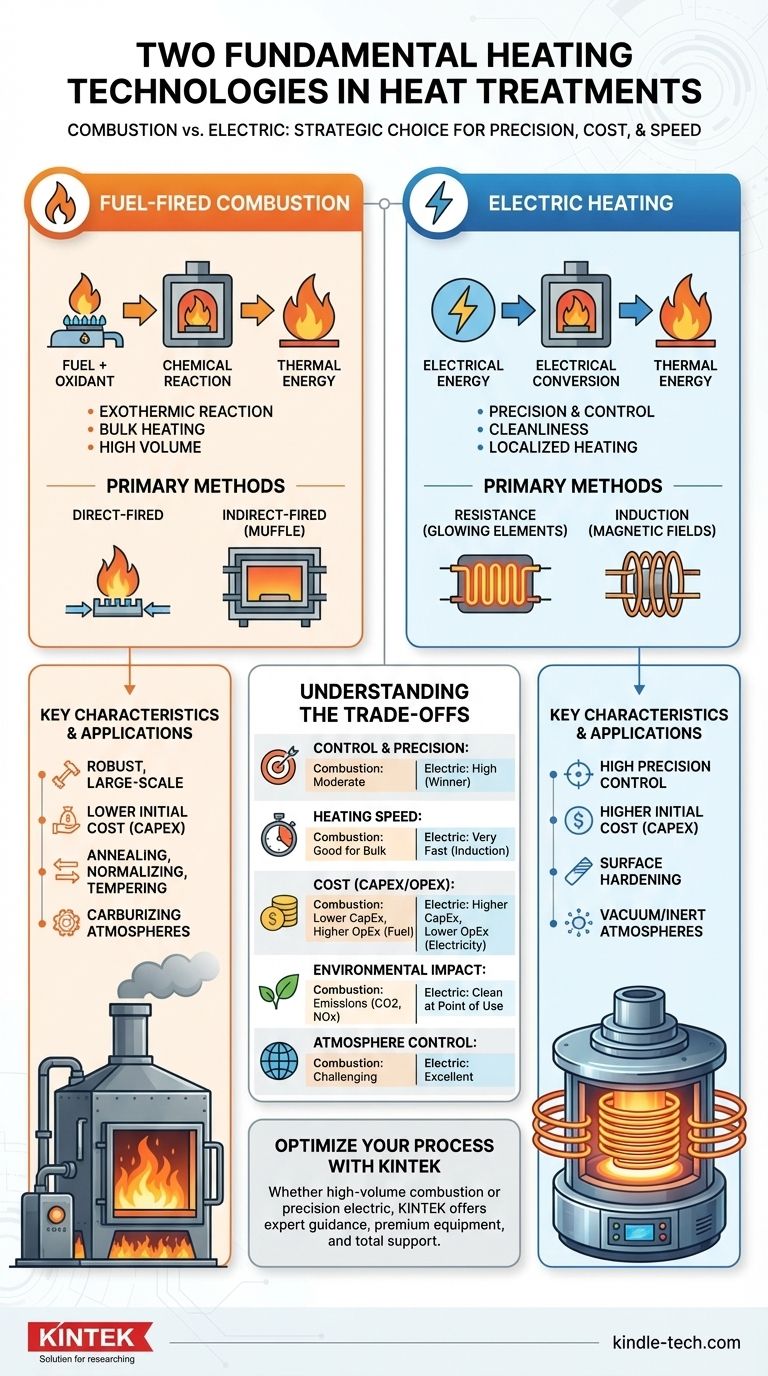
In industrial heat treatment, the two fundamental technologies used to generate heat are fuel-fired combustion and electric heating. These two categories represent entirely different methods of converting a source energy—chemical or electrical—into the thermal energy required to alter a material's microstructure. The choice between them dictates process control, speed, cost, and the final properties of the treated component.
Your choice between combustion and electric heating is not about which is universally "better." It is a strategic decision based on the specific balance of precision, operational cost, heating speed, and atmospheric control your application demands.

Understanding Fuel-Fired Combustion
Fuel-fired furnaces are the traditional workhorses of the heat-treating industry. They generate heat through the exothermic chemical reaction of burning a fuel source with an oxidant, typically air.
The Principle: Direct and Indirect Heating
Combustion furnaces burn fuels like natural gas, propane, or oil. The resulting hot gases transfer heat to the workpiece primarily through convection and radiation.
In direct-fired furnaces, the combustion products are in direct contact with the parts being treated. In indirect-fired (or muffle) furnaces, the combustion occurs in a separate chamber, heating the process chamber from the outside to protect the parts from the flue gases.
Key Characteristics
Fuel-fired systems are known for their ability to generate massive amounts of thermal energy relatively inexpensively, making them ideal for large-scale operations.
They are robust and well-suited for heating large, heavy components or sizable batches of parts where pinpoint temperature accuracy is secondary to bulk throughput.
Common Applications
This technology excels in processes like the annealing, normalizing, and tempering of large steel forgings and castings. It is also commonly used for carburizing, where the carbon-rich atmosphere created by combustion can be beneficial to the process.
Understanding Electric Heating
Electric heating converts electrical energy into thermal energy. This method is defined by its precision and cleanliness, offering several distinct techniques for heat generation and transfer.
The Principle: Resistance vs. Induction
The two most common forms of electric heating are resistance and induction.
Electric resistance heating works like a toaster. Electricity passes through high-resistance heating elements, causing them to glow hot. This heat is then transferred to the workpiece through radiation and convection.
Induction heating is fundamentally different. It uses an alternating magnetic field to induce an electric current (an eddy current) directly within the conductive workpiece. The material's own resistance to this internal current flow generates rapid, localized heat from the inside out.
Key Characteristics
Electric heating's defining feature is control. Temperature can be regulated with exceptional precision, and the process is inherently clean as there are no products of combustion.
Induction heating offers unparalleled speed and the ability to heat very specific areas of a part, making it ideal for surface hardening. Resistance heating provides excellent temperature uniformity within a sealed, controlled atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Combustion vs. Electric
Choosing the right technology requires a clear-eyed assessment of the primary trade-offs between capital cost, operational control, and environmental factors.
Control and Precision
Electric heating is the clear winner for precision. Resistance furnaces can hold temperatures within a very narrow band, and induction allows for precise control over both the heated area and the depth of heat penetration. Combustion heating is less precise due to the nature of burning fuel.
Heating Speed and Efficiency
For localized heating, induction is the fastest method available, often completing a cycle in seconds. For bulk heating, the overall efficiency of both combustion and electric resistance furnaces depends heavily on furnace design, insulation, and recuperation systems that recover waste heat.
Cost: Capital vs. Operational
Combustion furnaces typically have a lower initial capital cost (CapEx). However, their operational cost (OpEx) is tied to fluctuating fuel prices and often lower thermal efficiency.
Electric systems have a higher CapEx, especially for sophisticated induction setups. Their OpEx is dependent on electricity prices, but they often achieve higher overall energy efficiency and require less maintenance.
Environmental Impact and Atmosphere Control
Electric heating is significantly cleaner at the point of use, producing no emissions. This makes it easy to maintain a specific furnace atmosphere, such as a vacuum or an inert gas like argon, which is critical for preventing oxidation on sensitive alloys.
Combustion generates CO2, NOx, and other byproducts. While direct-fired furnaces can create a specific carburizing atmosphere, achieving a neutral or inert atmosphere requires a more complex and expensive indirect-fired design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection should be guided by the metallurgical outcome you need to achieve and the operational realities of your facility.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost processing of large parts: Fuel-fired combustion is often the most economical and practical solution.
- If your primary focus is high precision, surface finish, and process repeatability: Electric resistance heating in a controlled-atmosphere furnace is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is extreme speed and localized surface hardening: Induction heating is the unmatched technology for the job.
By understanding how these two core technologies generate and transfer heat, you can confidently select the method that delivers your required material properties with maximum efficiency and control.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Fuel-Fired Combustion | Electric Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Generation | Chemical reaction (burning fuel) | Electrical energy conversion |
| Primary Methods | Direct-fired, Indirect-fired (muffle) | Resistance, Induction |
| Best For | High-volume, large parts, cost-effective bulk heating | Precision, cleanliness, controlled atmospheres, localized heating |
| Control & Precision | Moderate | High (Excellent temperature uniformity with resistance; precise localization with induction) |
| Speed | Good for bulk heating | Very fast (especially induction for localized heating) |
| Cost (CapEx/OpEx) | Lower initial cost (CapEx), operational cost tied to fuel prices | Higher initial cost (CapEx), operational cost tied to electricity prices |
| Environmental Impact | Produces emissions (CO2, NOx) | Clean at point of use, no direct emissions |
| Atmosphere Control | Challenging for inert atmospheres; can create carburizing atmospheres | Excellent for vacuum, inert gas, or precise atmospheric conditions |
Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process with KINTEK
Choosing between fuel-fired combustion and electric heating is a critical decision that impacts your product quality, efficiency, and bottom line. Whether you need the robust, high-volume capabilities of combustion systems or the precision and control of electric resistance and induction furnaces, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your laboratory's unique needs.
Why Partner with KINTEK?
- Expert Guidance: Our specialists will help you select the ideal heating technology based on your specific materials, desired outcomes, and operational constraints.
- Premium Equipment: We supply reliable, high-performance lab furnaces and heating systems designed for accuracy and durability.
- Total Support: From initial consultation to installation and maintenance, we ensure your heat treatment processes run smoothly and efficiently.
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your heat treatment requirements and discover how our solutions can drive better results for your research and production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of nitrogen in annealing process? Creating a Controlled, Protective Atmosphere
- What are the inert gases in a heat treatment furnace? Choose the Right Shield for Your Metal
- What are the functions of nitrogen (N2) in controlled furnace atmospheres? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment Results
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained














