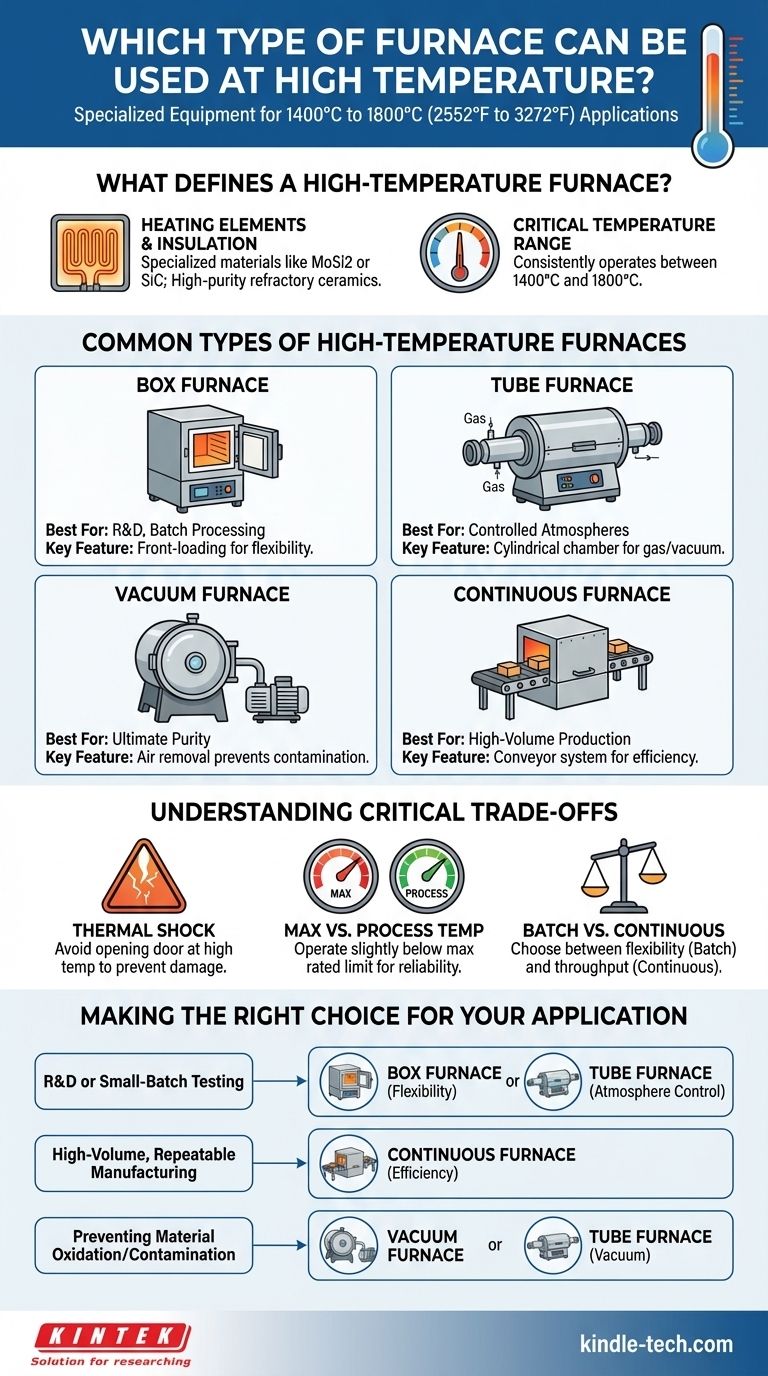
For high-temperature applications, you will typically use specialized equipment like a box furnace, tube furnace, or vacuum furnace. These are distinct from standard furnaces as they are engineered with materials and heating elements capable of reliably reaching and maintaining temperatures between 1400°C and 1800°C (2552°F to 3272°F).
The best type of high-temperature furnace is not determined by temperature alone. The choice fundamentally depends on your operational scale—whether you are processing materials in individual batches or in a continuous, high-volume flow.

What Defines a High-Temperature Furnace?
A furnace's ability to operate at extreme temperatures is a result of its fundamental design and materials. Understanding these elements is key to selecting the right equipment.
The Critical Temperature Range
High-temperature furnaces are a specific class of thermal processing equipment. They are designed to operate consistently in the 1400°C to 1800°C range, far exceeding the capabilities of standard industrial ovens.
The Role of Heating Elements and Insulation
Reaching these temperatures requires specialized heating elements, often made from materials like molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) or silicon carbide (SiC). The furnace chamber, or muffle, is constructed from high-purity refractory ceramics to withstand the intense heat and prevent contamination.
Common Types of High-Temperature Furnaces
The furnace type you choose should align directly with your process requirements, particularly your production volume and the need for atmospheric control.
Box Furnaces for Batch Processing
A box furnace is the standard for lab work and low-volume production. It features a front-opening door for loading and unloading materials in individual batches. This design offers flexibility for processing various parts or running different test cycles.
Tube Furnaces for Controlled Atmospheres
A tube furnace uses a cylindrical chamber, which is ideal for creating a tightly controlled atmosphere. By flowing specific gases (like argon or nitrogen) or creating a vacuum, you can process materials while preventing oxidation or other unwanted chemical reactions.
Continuous Furnaces for High-Volume Production
For medium- to high-volume manufacturing, a continuous furnace is often required. These systems use a conveyor to move products through the heating chamber, ensuring a consistent and efficient process for a large number of identical parts.
Vacuum Furnaces for Ultimate Purity
A vacuum furnace is a specialized type that removes the air from the chamber before heating. This is critical for processes where even trace amounts of oxygen or other gases would contaminate or damage the material, such as in aerospace or medical applications.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Operating at high temperatures introduces significant challenges and risks. Being aware of these trade-offs is crucial for equipment longevity and process success.
The Danger of Thermal Shock
You must avoid opening the furnace door while it is at a high temperature. The rush of cool air creates thermal shock, a rapid temperature change that can cause the ceramic insulation and heating elements to crack, leading to costly damage.
Maximum Temperature vs. Process Temperature
A furnace's advertised maximum temperature is not the same as its recommended process temperature. For reliability and longevity, you should plan to operate the furnace slightly below its maximum rated limit to ensure stable performance.
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
The most significant trade-off is between flexibility and throughput. Batch furnaces (like box furnaces) offer the versatility to run different processes but are inefficient for large volumes. Continuous furnaces offer high efficiency but are dedicated to a single, repetitive process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct furnace, start by defining the primary goal of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is research and development or small-batch testing: A box furnace offers the most flexibility, while a tube furnace adds the ability to control the processing atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repeatable manufacturing: A continuous furnace is the most efficient solution for integrating into a production line.
- If your primary focus is preventing any material oxidation or contamination: A vacuum furnace, or a tube furnace capable of maintaining a vacuum, is essential.
Selecting the right furnace begins with a clear understanding of your process requirements, from temperature and atmosphere to production scale.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Best For | Key Feature | Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Box Furnace | R&D, Batch Processing | Front-loading door for flexibility | Up to 1800°C |
| Tube Furnace | Controlled Atmospheres | Cylindrical chamber for gas/vacuum | Up to 1800°C |
| Vacuum Furnace | Ultimate Purity | Air removal prevents contamination | Up to 1800°C |
| Continuous Furnace | High-Volume Production | Conveyor system for efficiency | Up to 1800°C |
Need a High-Temperature Furnace for Your Lab or Production Line?
Choosing the right furnace is critical for your process success. KINTEK specializes in high-temperature lab equipment, from compact box furnaces for R&D to robust continuous furnaces for manufacturing. Our experts will help you select the perfect furnace to ensure precise temperature control, process efficiency, and material integrity.
Contact our thermal processing specialists today to discuss your specific application requirements and get a personalized solution from KINTEK.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- How does a tube furnace work? Master Precise Thermal and Atmospheric Control
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.



















