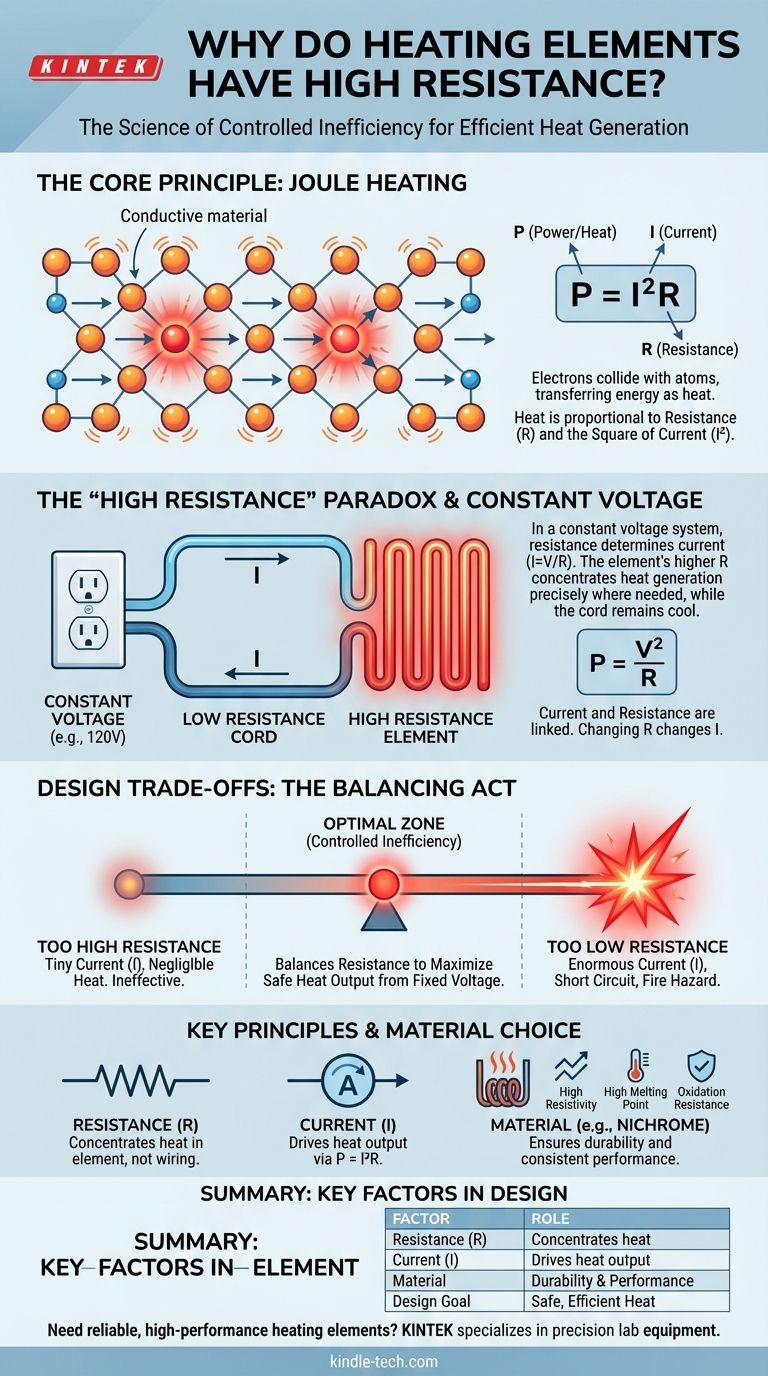
At its core, a heating element has high resistance because this property is what allows it to efficiently convert electrical energy into heat. When electrical current flows through a material that resists it, the moving electrons collide with the material's atoms, transferring their energy and causing the material to heat up—a principle known as Joule heating.
The key is understanding that "high resistance" is relative. The element's resistance is engineered to be much higher than the copper wires connecting it, but low enough to draw a significant amount of current from a fixed voltage source, thereby concentrating heat generation precisely where it is needed.

How Resistance Generates Heat
The Principle of Joule Heating
Every conductor resists the flow of electricity to some degree. This resistance causes a predictable effect.
As electrons are pushed through the material by an electric voltage, they collide with the atoms that make up the conductor.
These collisions transfer kinetic energy from the electrons to the atoms, causing the atoms to vibrate more intensely. This increased atomic vibration is what we perceive as heat.
The Critical Role of Current
The amount of heat generated is defined by the formula P = I²R, where P is power (heat), I is current, and R is resistance.
This formula reveals that the heat generated is proportional to the resistance, but it is proportional to the square of the current.
This means that the flow of current is the most significant factor in heat generation. Without current, no matter how high the resistance, no heat will be produced.
The "High Resistance" Paradox Explained
A common point of confusion arises from two different formulas for electrical power: P = I²R and P = V²/R. One seems to suggest higher resistance increases heat, while the other suggests it decreases it. The answer lies in understanding the circuit's context.
Constant Voltage is the Key
Your toaster, oven, or space heater plugs into a wall outlet, which provides a constant voltage (e.g., 120V in the US).
In a constant voltage system, the resistance of the heating element is what determines how much current it draws (Ohm's Law: I = V/R).
Therefore, we can't treat current and resistance as independent variables. Changing the resistance directly changes the current.
The Real Goal: Concentrating Heat
The true purpose of a "high resistance" element is to concentrate the heat generation in a specific location.
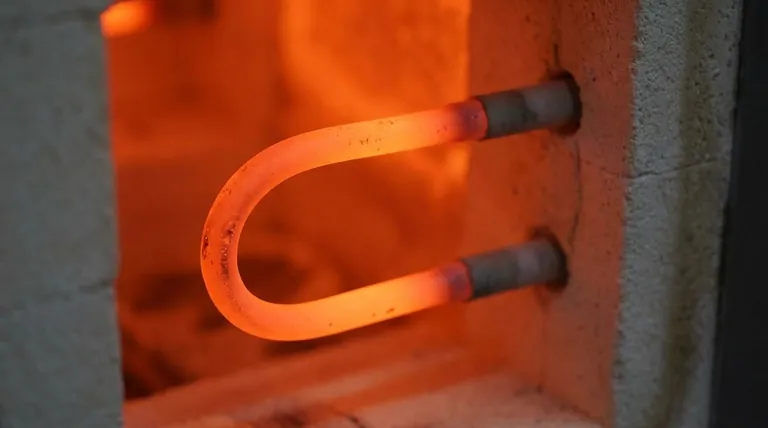
The copper cord plugging the appliance into the wall has very low resistance. The heating element, often made of a material like nichrome wire, has a much higher resistance.
Because both the cord and the element are in the same series circuit, they experience the same current. According to the P = I²R formula, the component with the vastly higher R will dissipate vastly more power as heat. This is why your toaster element glows red-hot, but the power cord remains cool.
Understanding the Design Trade-offs
Designing a heating element is a balancing act. It's not simply a matter of maximizing resistance.
Too High Resistance is Ineffective
If the resistance is too high, it will severely limit the amount of current that can flow from the constant voltage source (I = V/R).
An extremely high resistance would draw a tiny amount of current, resulting in negligible power (heat) generation. An open circuit, with infinite resistance, draws zero current and produces zero heat.
Too Low Resistance is Dangerous
Conversely, if the resistance is too low, it creates a short circuit.
This would cause an enormous amount of current to be drawn from the outlet. While this would generate immense heat, it would do so throughout the circuit, including the low-resistance wiring in your walls, creating a significant fire hazard.
The Importance of Material Choice
The material used must not only have high electrical resistivity but also a very high melting point and resistance to oxidation at high temperatures. This is why alloys like Nichrome (nickel and chromium) are commonly used instead of materials that would quickly burn out or melt.
Key Principles for Effective Heating
Choosing the right resistance is about achieving a specific goal within the constraints of a standard electrical system.
- If your primary focus is maximum heat output: You must use a resistance low enough to draw a high, but safe, amount of current from the fixed voltage source.
- If your primary focus is safety and efficiency: The element's resistance must be strategically higher than the rest of the circuit's wiring to ensure heat is generated only where you want it.
Ultimately, an effective heating element is a product of controlled inefficiency, designed to deliberately obstruct electrical current to convert its energy into useful heat.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Heating Element Design |
|---|---|
| Resistance (R) | Concentrates heat generation in the element, not the wiring |
| Current (I) | Drives heat output via P = I²R; determined by R and voltage |
| Material (e.g., Nichrome) | Provides high resistivity, high melting point, and oxidation resistance |
| Design Goal | Balances resistance to maximize safe heat output in a constant voltage system |
Need reliable, high-performance heating elements for your laboratory equipment? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, ensuring your heating applications are both efficient and safe. Our expertise in materials like Nichrome guarantees durability and consistent performance. Contact us today to find the perfect heating solution for your lab's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Gold Disc Electrode
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design
- What is molybdenum disilicide used for? Powering High-Temperature Furnaces Up to 1800°C
- Is molybdenum disulfide a heating element? Discover the best material for high-temperature applications.
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab















