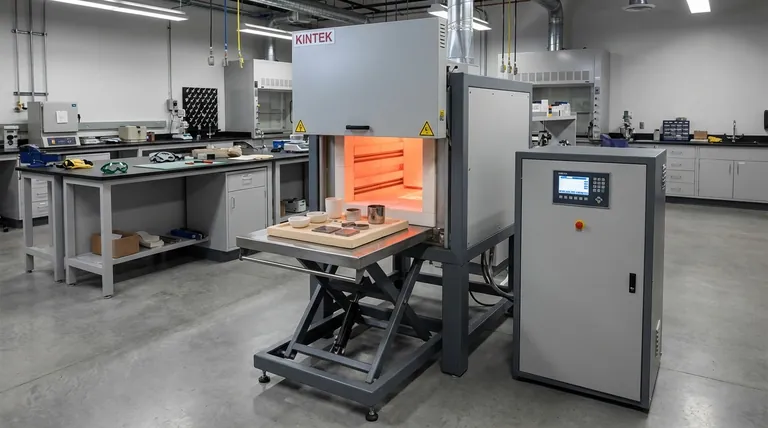
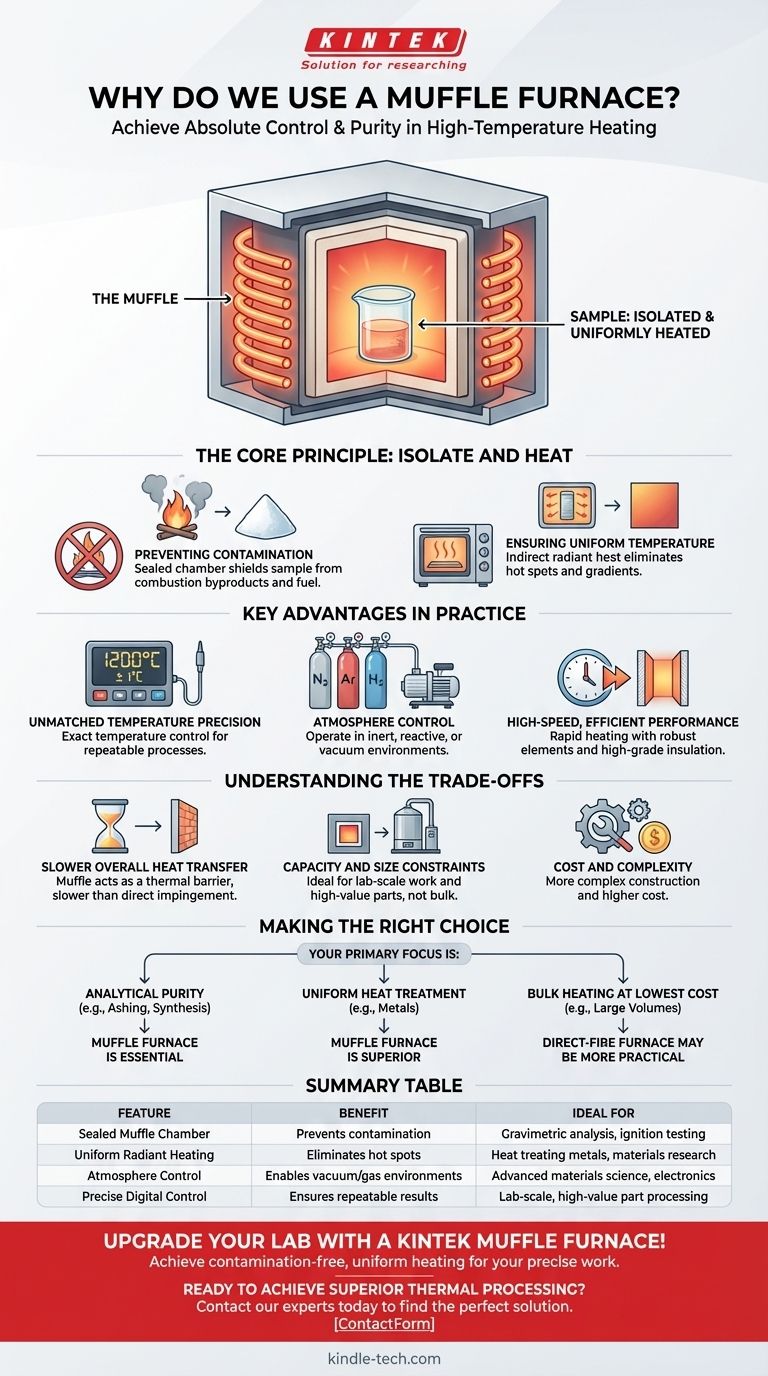
At its core, a muffle furnace is used for high-temperature heating when the material being processed must be completely isolated from the heat source and its byproducts. This ensures the sample's chemical purity is not compromised by fuel or combustion gases, and that it is heated with exceptional temperature uniformity. Common applications include gravimetric analysis, heat treating metals, and materials research.
The central challenge in many high-temperature processes is preventing sample contamination and uneven heating from a direct flame. A muffle furnace solves this by using an enclosed chamber—the "muffle"—to separate the material from the heating elements, guaranteeing both process purity and precise, uniform thermal control.

The Core Principle: Isolate and Heat
The name "muffle furnace" comes from its defining component: the muffle. This is a sealed, high-temperature chamber that houses the material, effectively muffling it from the external environment.
Preventing Contamination
The primary function of the muffle is to act as a physical barrier. In a direct-fire furnace, byproducts of combustion can react with or settle on the sample, altering its chemical composition.
This isolation is non-negotiable for sensitive analytical procedures like gravimetric analysis or ignition testing, where any change in mass from contamination would render the results invalid.
Ensuring Uniform Temperature
By heating the outside of the muffle chamber, the furnace provides indirect, radiant heat to the material inside. This is analogous to a convection oven rather than a gas grill.
This indirect approach eliminates hot spots and temperature gradients that are common in furnaces where a flame directly contacts the workpiece. The result is exceptionally uniform heating, which is critical for consistent heat treatment and predictable material transformations.
Key Advantages in Practice
The design of a muffle furnace delivers several distinct operational advantages for both laboratory and industrial settings.
Unmatched Temperature Precision
Modern muffle furnaces use advanced digital controllers and high-quality thermocouples to achieve and maintain exact temperatures. This precise control, combined with uniform heat distribution, ensures that processes are repeatable and reliable.
Atmosphere Control
Because the muffle is a sealed chamber, the atmosphere inside can be controlled. The air can be evacuated to create a vacuum, or it can be replaced with specific gases.
This allows for processing in inert atmospheres (like nitrogen or argon) to prevent oxidation, or in reactive atmospheres (like hydrogen) for specialized chemical processes. This capability is vital in advanced materials science and electronics manufacturing.
High-Speed, Efficient Performance
Despite providing indirect heat, muffle furnaces are designed for efficiency. They use high-grade insulation to retain heat and robust heating elements that can reach high temperatures rapidly, saving valuable time in a lab or production environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is not the universal solution for all heating applications. Objectivity requires acknowledging its limitations.
Slower Overall Heat Transfer
The muffle chamber that provides uniformity and purity also acts as a thermal barrier. Heat must first transfer to the muffle and then radiate to the sample, which can be slower than the intense, direct heat of a flame-impingement furnace.
Capacity and Size Constraints
Muffle furnaces are often smaller than their direct-fire industrial counterparts. The complexity of constructing a sealed, high-temperature chamber generally limits their size, making them ideal for lab-scale work or smaller batches of high-value parts rather than bulk material processing.
Cost and Complexity
The robust construction, high-quality insulation, sealing mechanisms, and precise control systems make muffle furnaces more complex and typically more expensive than simple ovens or direct-fire furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating technology depends entirely on your process requirements.
- If your primary focus is analytical purity: A muffle furnace is essential for any process, like ashing or materials synthesis, where contamination would compromise the results.
- If your primary focus is uniform heat treatment: A muffle furnace is the superior choice for components that require precise and even thermal properties without surface defects.
- If your primary focus is bulk heating at the lowest cost: A direct-fire furnace may be more practical for large volumes where slight surface contamination or minor temperature variations are acceptable.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is the definitive tool when you require absolute control over your thermal processing environment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Sealed Muffle Chamber | Prevents contamination from fuel/byproducts | Gravimetric analysis, ignition testing |
| Uniform Radiant Heating | Eliminates hot spots for consistent results | Heat treating metals, materials research |
| Atmosphere Control | Enables vacuum or inert/reactive gas environments | Advanced materials science, electronics |
| Precise Digital Control | Ensures repeatable, reliable temperature management | Lab-scale processes, high-value part processing |
Upgrade your lab's capabilities with a muffle furnace from KINTEK!
Whether you're conducting precise gravimetric analysis, heat-treating metals, or advancing materials research, our muffle furnaces deliver the contamination-free environment and uniform heating your work demands.
Ready to achieve superior thermal processing? Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, ensuring you get the reliability and precision your research deserves.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and an oven? Choose the Right High-Temperature Tool
- What is the muffle furnace analysis? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing for Your Materials
- What is the significance of a muffle furnace? Achieve Uncontaminated, High-Purity Heating
- Why is the melting point different for different substances? The Key Role of Bond Strength
- What is the principle of muffle furnace in laboratory? Master Precise High-Temp Heating



















