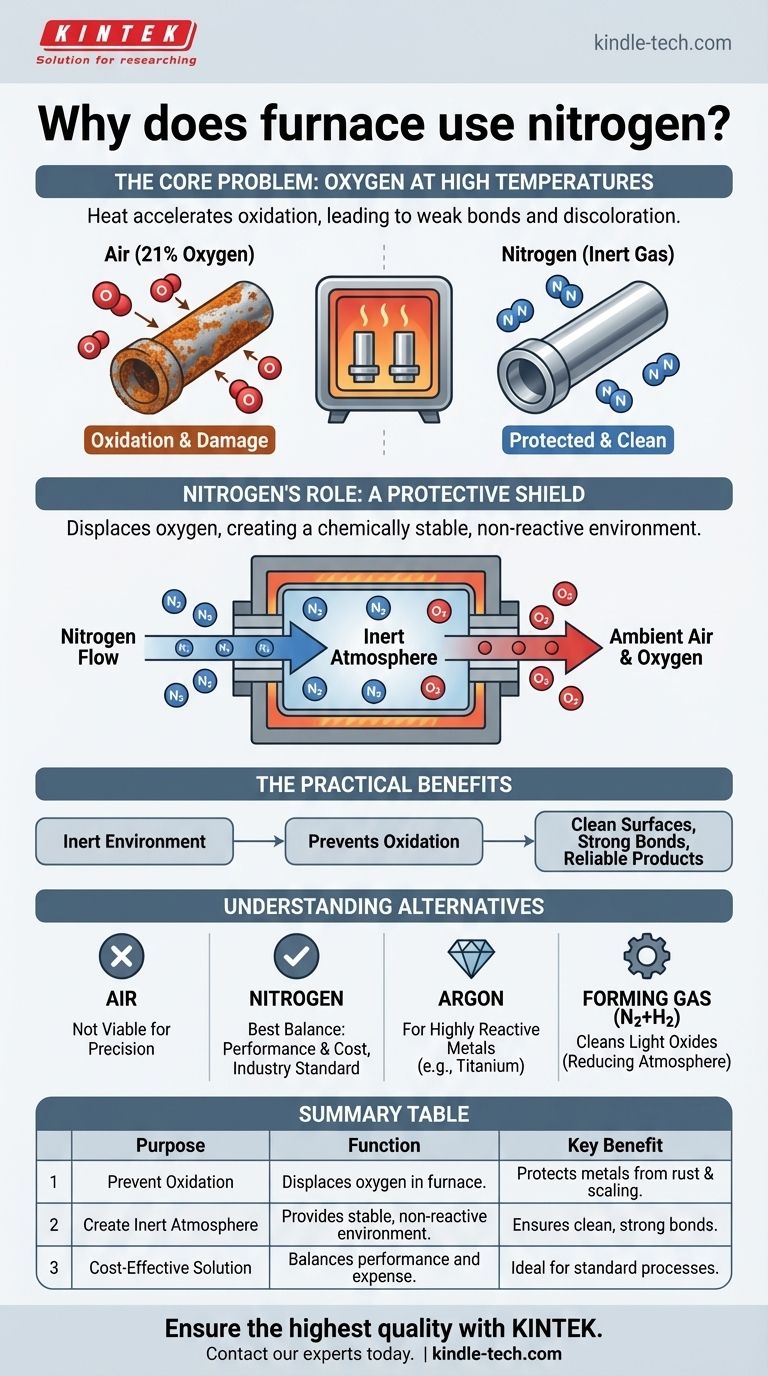
In short, industrial furnaces use nitrogen to create a controlled, oxygen-free atmosphere. This inert environment is critical for high-temperature processes like soldering, brazing, and heat treating, as it prevents the destructive chemical reaction of oxidation, ensuring the quality and integrity of the final product.
The fundamental challenge in high-temperature manufacturing is that heat drastically accelerates oxidation—the same process that causes rust. Nitrogen solves this by displacing the oxygen in the furnace, effectively blanketing the components in a protective, non-reactive gas.
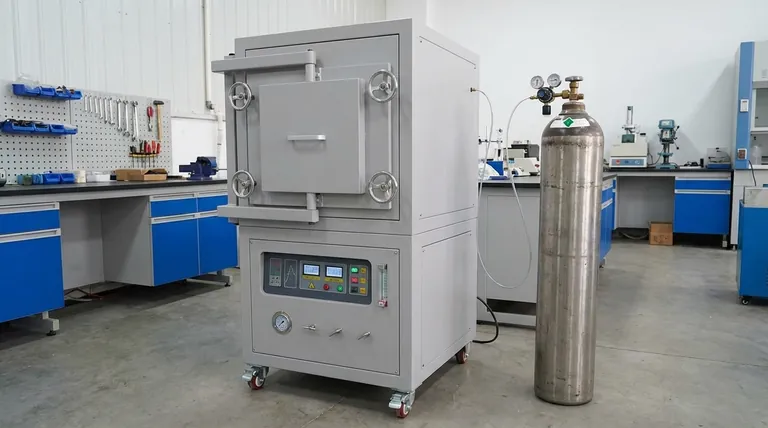

The Core Problem: Oxygen at High Temperatures
To understand nitrogen's role, we must first understand the problem it solves. The normal air we breathe is a significant threat during precision manufacturing processes that involve heat.
Heat as a Catalyst for Damage
Heat acts as a powerful catalyst for chemical reactions. While a piece of copper might take years to tarnish at room temperature, it can develop a layer of black oxide in mere seconds inside a hot furnace exposed to air.
The Destructive Impact of Oxidation
Oxidation is the chemical reaction between a material and oxygen. In furnace applications, this leads to severe quality issues, including weak and unreliable solder joints, discoloration of metal surfaces, and altered structural properties of the base materials.
These defects can cause catastrophic product failures, especially in high-reliability fields like aerospace, medical devices, and electronics.
Nitrogen's Role as a Protective Shield
Introducing nitrogen into the furnace is a simple but highly effective solution to the oxidation problem. It fundamentally changes the chemical environment in which the process takes place.
The Principle of Displacement
A continuous flow of nitrogen gas is pumped into the sealed furnace chamber. Being the primary component, this nitrogen flow effectively purges the chamber, pushing out the ambient air and, most importantly, its 21% oxygen content.
Creating an "Inert" Atmosphere
Nitrogen is a largely inert gas, meaning it is chemically stable and does not readily react with other elements, even under high heat. By creating an atmosphere composed almost entirely of nitrogen, you remove the oxygen reactant from the equation.
This inert environment allows the solder to flow cleanly and the metals to be treated without forming unwanted oxide layers on their surfaces.
The Practical Benefits
The result is a more robust and reliable manufacturing process. Components emerge from the furnace clean, with strong, perfectly formed metallurgical bonds and the precise material characteristics intended by the design.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
While nitrogen is the most common choice, it's essential to understand why and to recognize its alternatives for specific applications.
Why Not Just Use Air?
Using ambient air is only viable for the most rudimentary heating processes where surface finish and bond integrity are not critical concerns. For any precision application, the oxygen in the air is an unacceptable contaminant.
Nitrogen vs. Other Atmospheres
Nitrogen is the industry workhorse because it provides the best balance of performance and cost. It is far cheaper than Argon, a more truly inert gas that is reserved for highly sensitive, reactive metals like titanium.
For applications that require actively removing light surface oxides, a forming gas (typically a mix of 95% nitrogen and 5% hydrogen) is used. The hydrogen creates a "reducing" atmosphere that chemically reverses light oxidation, but it is more complex and costly to manage.
The Purity Factor
The effectiveness of the nitrogen atmosphere depends on its purity. For standard applications, a low level of residual oxygen might be acceptable. For high-end electronics, nitrogen with extremely low oxygen content—measured in parts per million (PPM)—is required to guarantee a flawless result.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace atmosphere is a critical decision that directly impacts product quality, reliability, and cost.
- If your primary focus is standard soldering or brazing of common metals (copper, steel): Nitrogen is the industry standard, offering the most cost-effective solution for preventing oxidation.
- If you are working with highly reactive or exotic metals (titanium, magnesium): A more inert gas like Argon is necessary to prevent any potential reaction with the process gas itself.
- If your process requires cleaning minor, pre-existing oxides: A reducing atmosphere with a hydrogen blend (forming gas) is the appropriate choice for its active cleaning properties.
Ultimately, controlling the furnace atmosphere is about taking direct command of the chemical environment to guarantee process repeatability and final product quality.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Prevent Oxidation | Displaces oxygen in the furnace chamber. | Protects metals from rust and scaling at high temperatures. |
| Create Inert Atmosphere | Provides a chemically stable, non-reactive environment. | Ensures clean, strong metallurgical bonds and precise material properties. |
| Cost-Effective Solution | Balances performance and expense compared to argon or hydrogen blends. | Ideal for standard processes on common metals like copper and steel. |
Ensure the highest quality for your lab's thermal processes with KINTEK.
Our expertise in lab equipment and consumables means we can provide the right furnace solutions and atmosphere control systems for your specific applications—whether you're working with standard metals or highly reactive materials. Prevent oxidation and guarantee process repeatability with equipment designed for precision and reliability.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's capabilities and protect your valuable samples.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is an inert atmosphere heat treatment? Protect Your Metals from Oxidation & Decarburization
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- What is the purpose of inert atmosphere? A Guide to Protecting Your Materials and Processes
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments



















