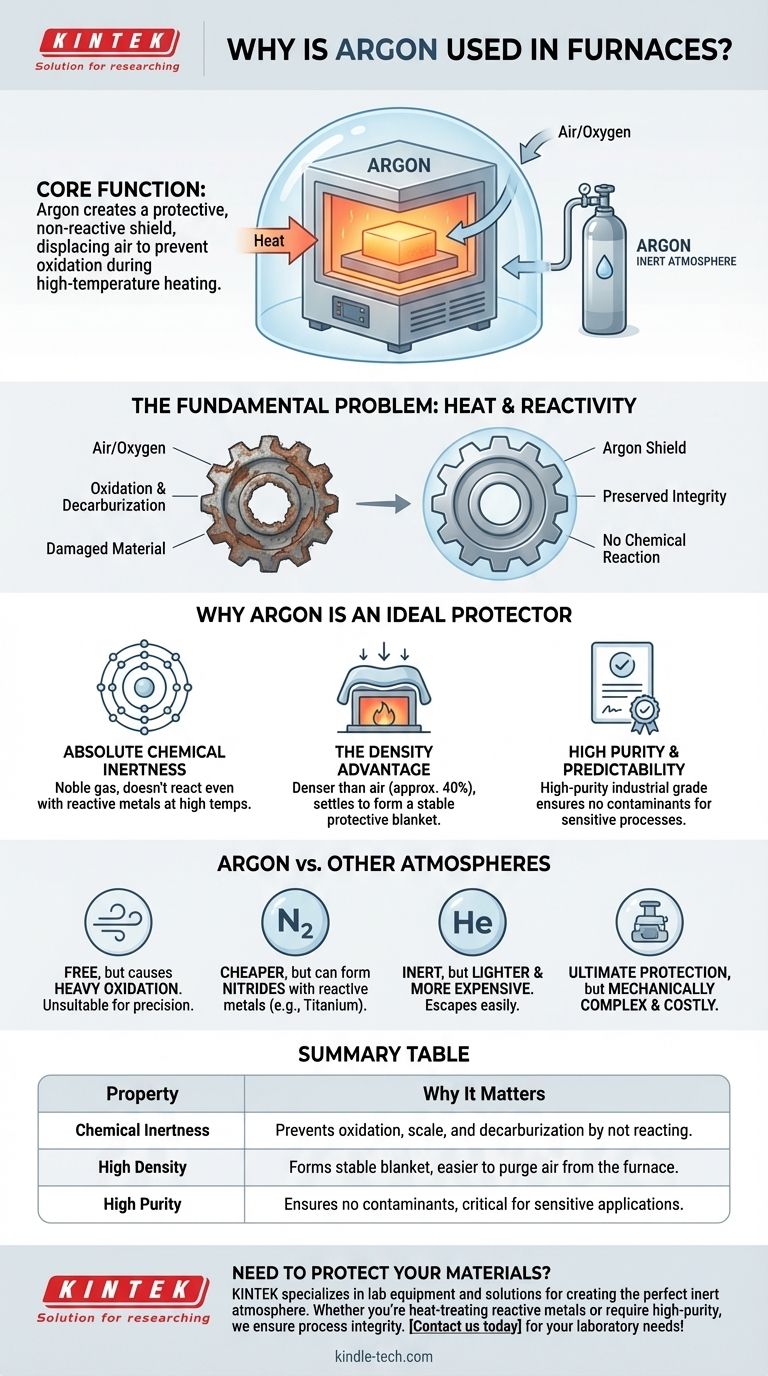
In short, argon is used in furnaces to create a protective, non-reactive shield around a material during heating. This inert atmosphere is critical because at high temperatures, most materials—especially metals—will rapidly and destructively react with the oxygen in the air, a process known as oxidation. Using argon displaces the air, preventing these unwanted chemical reactions from occurring and preserving the integrity of the material.
The core challenge in high-temperature processing is not the heat itself, but the unwanted chemical reactions that heat accelerates. Argon solves this by creating an inert environment, acting as a stable, invisible barrier that protects the material from atmospheric contamination.

The Fundamental Problem: Heat and Reactivity
High-temperature furnaces are used to fundamentally change a material's properties. However, the very energy that enables these changes also makes the material highly susceptible to damage from the surrounding atmosphere.
What Happens When Materials Meet Hot Air?
At elevated temperatures, the oxygen in the air aggressively attacks the surface of many materials. For metals, this results in oxidation—the formation of a brittle, flaky layer of scale.
This oxidation can ruin a component by changing its dimensions, weakening its structure, and compromising its surface finish. For certain steels, the carbon within the alloy can also react with the atmosphere, a damaging process called decarburization.
The Need for a Protective Atmosphere
To prevent this damage, the reactive air inside the furnace must be replaced with a gas that will not react with the workpiece, even at extreme temperatures.
This is known as creating an inert atmosphere. The goal is to create a chemically neutral environment where the heat treatment process can proceed without any unintended side effects from atmospheric gases.
Why Argon is an Ideal Protector
While several gases can be used to create a protective atmosphere, argon possesses a unique combination of properties that make it exceptionally effective and reliable for demanding applications.
Absolute Chemical Inertness
Argon is a noble gas. This means its atoms have a full outer shell of electrons, making it extremely stable and unwilling to form chemical bonds with other elements.
Unlike nitrogen, which can sometimes react with metals like titanium or certain stainless steels at high temperatures to form nitrides, argon remains completely non-reactive under all furnace conditions.
The Density Advantage
A critical, practical advantage of argon is its density. It is approximately 40% denser than air and significantly denser than nitrogen.
This density causes it to "settle" within the furnace chamber, effectively forming a stable protective blanket over the workpiece. This makes it easier to purge the furnace of air and less likely to escape, providing more reliable protection than lighter gases.
High Purity and Predictability
Industrial-grade argon is produced with extremely high purity. This consistency ensures that no unknown contaminants are introduced into the furnace, which is critical for sensitive processes like semiconductor manufacturing or medical implant production.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Argon vs. Other Atmospheres
Choosing a furnace atmosphere is a balance of cost, performance, and material compatibility. Argon is a superior technical choice, but not always the only option.
Argon vs. Air
Using air is free but only suitable for processes where heavy oxidation is acceptable or even desired. For nearly all precision heat treatments, air is not a viable option.
Argon vs. Nitrogen
This is the most common trade-off. Nitrogen is much cheaper than argon and is also relatively inert. It is perfectly suitable for heat treating many common steels.
However, for reactive metals (like titanium, zirconium, or certain high-alloy steels), nitrogen is not inert enough and can form undesirable nitrides, making argon the necessary choice.
Argon vs. Helium
Helium is also a completely inert noble gas. However, it is much lighter than air and escapes from a furnace chamber very easily. It is also significantly more expensive than argon, so its use is reserved for niche applications where its high thermal conductivity is specifically required.
Argon vs. Vacuum
A vacuum furnace, which removes nearly all atmosphere, provides the ultimate inert environment. However, these systems are mechanically complex, expensive to purchase and operate, and can have slower processing cycles. Argon provides a similar level of protection for many applications with simpler and more cost-effective equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct atmosphere is fundamental to achieving the desired outcome from any high-temperature process. Your decision should be guided by your material and your final goal.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general-purpose steels: A nitrogen-based atmosphere is often sufficient and more economical.
- If you are working with reactive metals like titanium or require absolute inertness without nitride formation: Argon is the essential and correct choice.
- If you need the highest possible purity for sensitive electronics or medical devices: A high-purity argon atmosphere or a vacuum furnace is necessary.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace atmosphere is a foundational decision that directly controls the quality, integrity, and performance of the final product.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Why It Matters for Furnace Use |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents oxidation, scale, and decarburization by not reacting with the workpiece. |
| High Density | Forms a stable, protective blanket over materials, making it easier to purge air from the furnace. |
| High Purity | Ensures no contaminants are introduced, which is critical for sensitive applications like semiconductors. |
Need to protect your materials during high-temperature processing? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions for creating the perfect inert atmosphere for your specific application. Whether you're heat-treating reactive metals or require high-purity conditions, our expertise ensures your process integrity. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does the chemical reduction of silica during hydrogen sintering affect the furnace's refractory materials? Ensure Longevity with the Right Lining
- Are inert gases harmful to humans? The Silent Threat of Oxygen Displacement
- Can hydrogen be used in furnaces? Yes, for Oxide-Free Metal Processing & Rapid Heating
- What is the function of a high-temperature atmosphere furnace in the carbonization of cellulose waste? Expert Guide
- Why is a high-temperature atmosphere furnace required for 70-hour alloy annealing? Achieve Material Homogenization
- What gases are used in brazing welding? Key Insights for Strong, Clean Joints
- What is an inert gas atmosphere and for what applications is it used? Essential Guide for Heat Treatment & Lab Safety
- Why is argon better than nitrogen for inert atmosphere? Ensure Absolute Reactivity & Stability



















