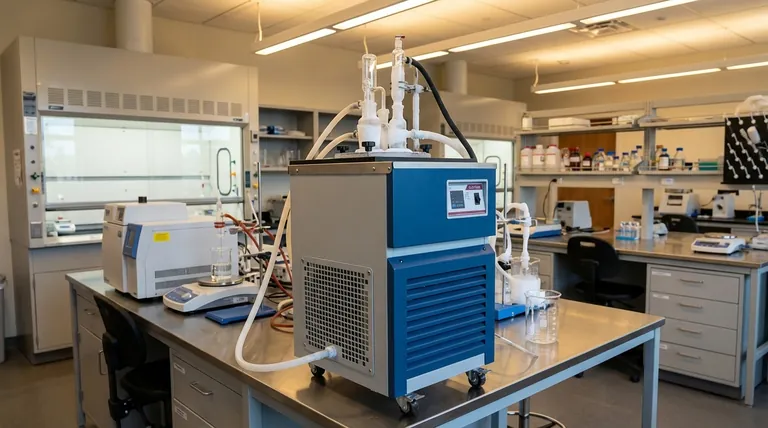
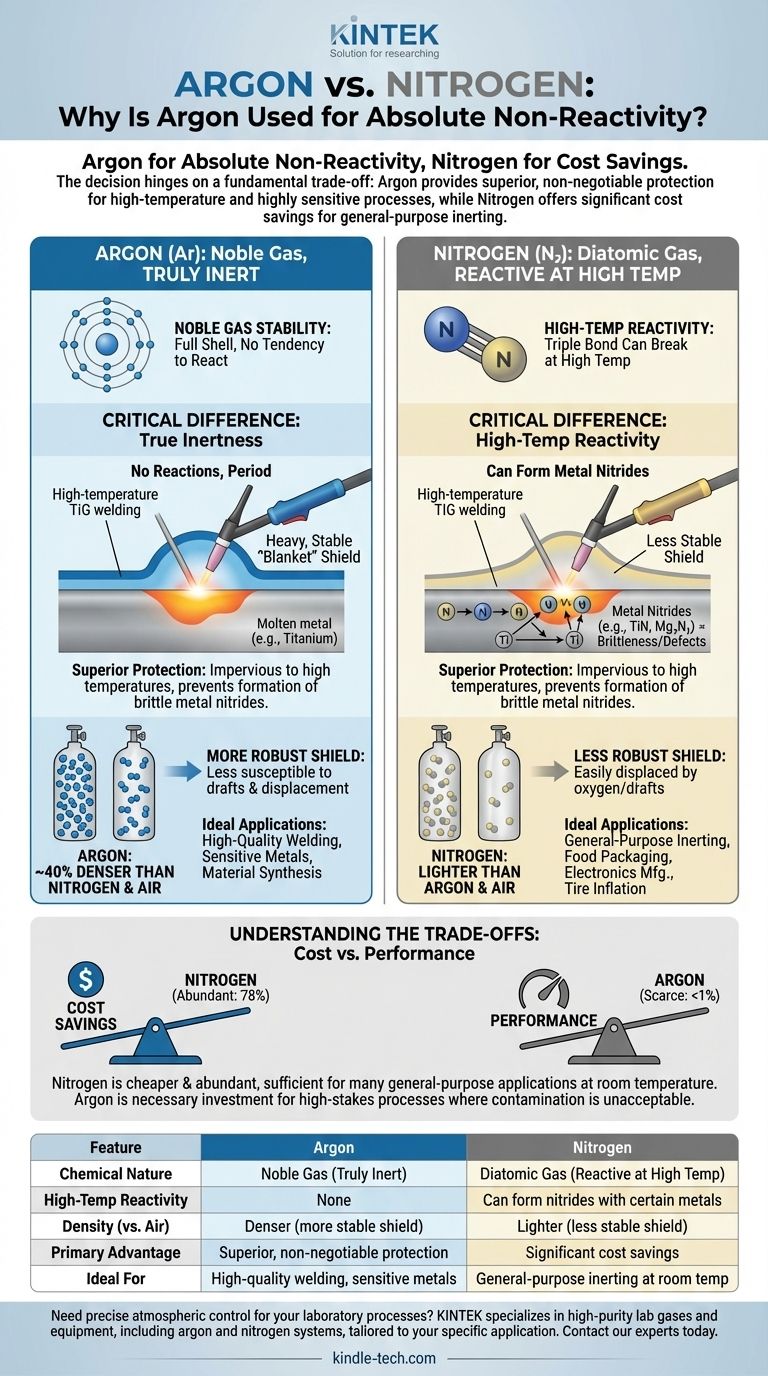
In short, argon is used instead of nitrogen when absolute chemical non-reactivity is critical. While both are considered "inert," nitrogen can react with certain metals at high temperatures, a risk that the truly inert argon completely avoids. Argon's greater density also provides a more stable protective shield than nitrogen in many applications.
The decision between argon and nitrogen hinges on a fundamental trade-off: nitrogen offers significant cost savings for general-purpose inerting, while argon provides superior, non-negotiable protection for high-temperature and highly sensitive processes where contamination is unacceptable.

The Critical Difference: True Inertness
The most important distinction between these two gases lies in their chemical behavior under stress. While both are used to displace oxygen and prevent oxidation, their definitions of "inert" are not the same.
Argon's Noble Gas Stability
Argon is a noble gas. Its outermost electron shell is completely full, which means it has virtually no tendency to share, gain, or lose electrons.
This chemical stability makes argon truly inert across an extremely wide range of temperatures and conditions. It will not react with other elements, period.
Nitrogen's High-Temperature Reactivity
Nitrogen gas (N₂) is very stable at room temperature due to the powerful triple bond holding its two atoms together. For many applications, this is inert enough.
However, at the high temperatures found in processes like TIG or MIG welding, this triple bond can break. The newly freed nitrogen atoms can then react with metals like titanium, magnesium, and certain steels to form metal nitrides.
These nitrides can make a material brittle or compromise the integrity of a weld, which is often an unacceptable outcome.
The Practical Advantage of Density
Beyond chemical reactivity, the physical properties of each gas play a significant role in their selection.
Creating a Stable Protective Shield
Argon is approximately 40% denser than nitrogen and also denser than air. When used as a shielding gas, it naturally settles and forms a heavy, stable "blanket" over the work area.
This density makes the protective shield more robust and less susceptible to being disturbed by drafts or air currents.
Why This Matters in Practice
In an open-air welding environment, for example, a stable argon shield is more effective at displacing oxygen and keeping it away from the molten weld pool.
The less-dense nitrogen shield can be displaced more easily, potentially allowing oxygen to enter and contaminate the weld, leading to defects.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The decision to use argon isn't based solely on its superior performance. Practical and economic factors are often decisive.
The Deciding Factor: Cost
The single biggest reason nitrogen is used whenever possible is cost. Nitrogen makes up about 78% of the Earth's atmosphere, while argon accounts for less than 1%.
This vast difference in natural abundance makes nitrogen significantly cheaper to produce and procure than argon.
General-Purpose vs. High-Stakes Applications
For countless applications like food packaging, electronics manufacturing, or tire inflation, the goal is simply to displace oxygen at ambient temperatures.
In these scenarios, nitrogen's sufficient inertness and low cost make it the clear and logical choice. Argon would be technically effective but economically wasteful.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing between these gases requires a clear understanding of your process requirements and budget.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective inerting at or near room temperature: Nitrogen is the correct choice for preventing general oxidation without the expense of argon.
- If your primary focus is high-quality welding or protecting reactive metals at high temperatures: Argon is the necessary investment to prevent unwanted chemical reactions and ensure process integrity.
Ultimately, selecting the right gas is about matching the tool to the specific demands of the job.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Argon | Nitrogen |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Nature | Noble Gas (Truly Inert) | Diatomic Gas (Reactive at High Temp) |
| High-Temperature Reactivity | None | Can form nitrides with certain metals |
| Density (vs. Air) | Denser (more stable shield) | Lighter (less stable shield) |
| Primary Advantage | Superior, non-negotiable protection | Significant cost savings |
| Ideal For | High-quality welding, sensitive metals | General-purpose inerting at room temperature |
Need precise atmospheric control for your laboratory processes?
The right inert gas is critical for the integrity of your experiments and material synthesis. KINTEK specializes in providing high-purity lab gases and equipment, including argon and nitrogen systems, tailored to your specific application—whether it's sensitive R&D or high-temperature processing.
Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and ensure optimal results for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of an immersion chilling accessory? Expand Lab Flexibility and Thermal Range
- Why is a liquid nitrogen cold trap installed at the reactor outlet? Essential Sample Preservation & System Protection
- Why are cold traps considered essential auxiliary equipment in laboratory-scale plastic pyrolysis research? | KINTEK
- Why is it necessary to configure efficient cold traps in membrane distillation? Ensure Flux Stability & Data Accuracy
- What is the function of efficient cooling systems and cold traps in plastic pyrolysis? Maximize Yield and Purity









