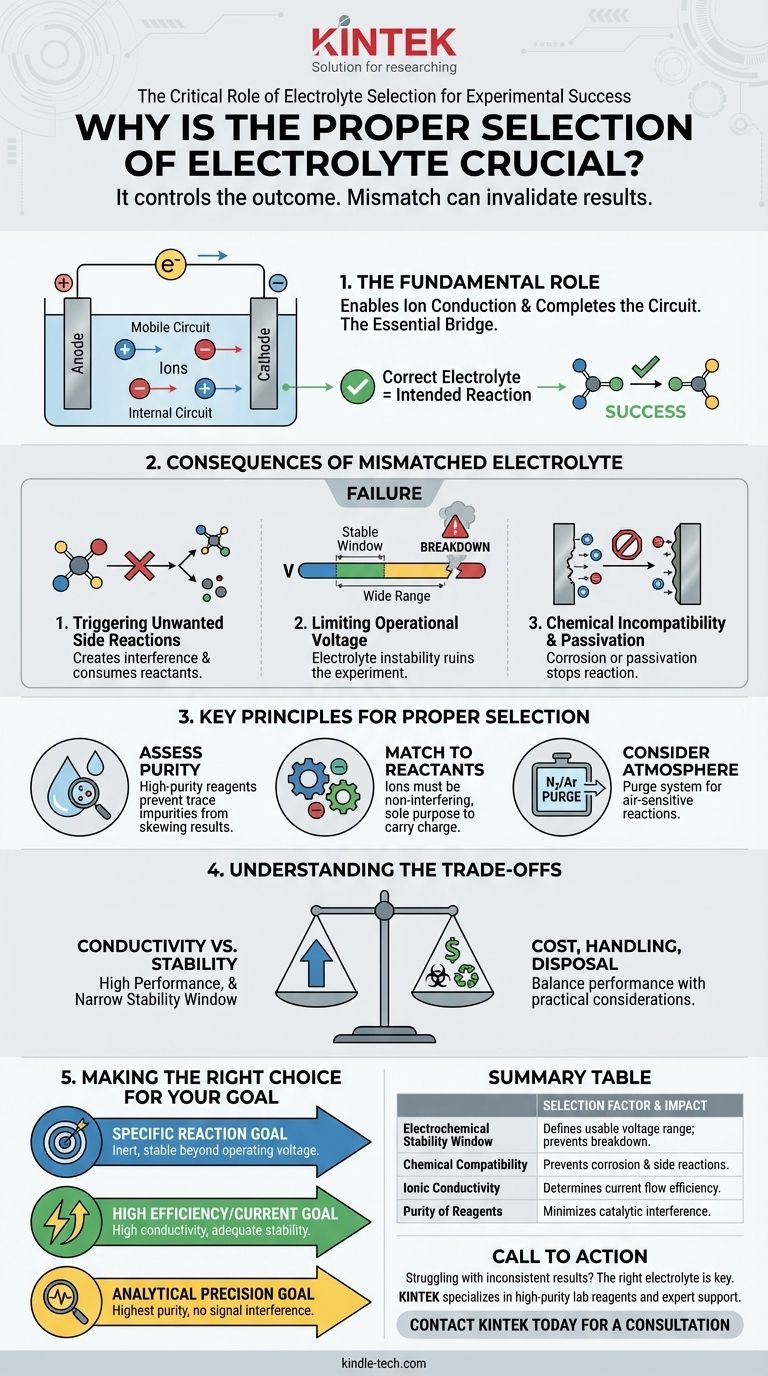
Choosing the right electrolyte is critical because it directly controls the outcome of your experiment. The electrolyte is not a passive background medium; it is an active component that must be carefully selected to ensure your intended reaction proceeds correctly and to prevent unwanted side reactions that can invalidate your results.
The core function of an electrolyte is to complete the electrical circuit by conducting ions, but its chemical properties dictate which reactions are possible. A mismatch between the electrolyte and the experimental system can lead to completely different and unintended chemical transformations.

The Fundamental Role of an Electrolyte
An electrolyte is the essential bridge in any electrochemical cell. Its primary job is to transport charge in the form of ions, allowing the circuit to be completed between the two electrodes.
Enabling Ion Conduction
The electrolyte contains mobile ions (cations and anions) that move in response to the electric field. This movement of charged particles is what constitutes the flow of current within the cell.
Completing the Electrical Circuit
Electrons flow through the external wire, but ions must flow through the electrolyte. Without this internal ionic pathway, the circuit would be broken, and no electrochemical reaction could occur.
Why a Mismatched Electrolyte Invalidates Results
Selecting the wrong electrolyte is one of the most common ways to derail an experiment. It can introduce variables that completely obscure the process you intend to study.
Triggering Unwanted Side Reactions
The components of the electrolyte can react with your electrodes, your solvent, or the substance you are analyzing. This creates byproducts that consume reactants and interfere with measurements.
Limiting the Operational Voltage
Every electrolyte has an electrochemical stability window. This is the voltage range where it remains inert. If your experiment requires a voltage outside this window, the electrolyte itself will break down (oxidize or reduce), ruining the experiment.
Chemical Incompatibility and Passivation
An electrolyte can be chemically aggressive toward your electrode materials, causing them to corrode or dissolve. It can also cause a passivating layer—a non-conductive film—to form on the electrode surface, which stops the reaction entirely.
Key Principles for Proper Selection
Making a deliberate choice requires understanding the properties that define a suitable electrolyte for your specific goal.
Assess the Purity of Reagents
The purity of your electrolyte's components is paramount. Even trace impurities can act as catalysts for side reactions or get deposited on the electrodes, skewing your results. Always use high-purity reagents and deionized or distilled water.
Match the Electrolyte to the Reactants
The ions within the electrolyte must be non-interfering. They should not participate in the primary electrochemical reaction you are trying to drive. Their sole purpose should be to carry charge.
Consider the Required Atmosphere
Some experiments are highly sensitive to air. If your system requires an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon), you must purge the cell before adding the electrolyte to prevent oxygen or moisture from causing parasitic reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an electrolyte often involves balancing competing factors. There is rarely a single "perfect" option.
Conductivity vs. Stability
An electrolyte with very high ionic conductivity might offer excellent performance but may have a narrow stability window. You might need to sacrifice some performance for an electrolyte that remains stable at your required voltages.
Cost and Handling
Practical considerations are important. Some high-performance electrolytes can be expensive, highly toxic, or require specialized handling procedures (like in a glovebox). These factors must be weighed against the experimental requirements.
Post-Experiment Disposal
The selection process doesn't end when the experiment does. You must choose an electrolyte for which you have a clear and safe disposal plan, whether that involves neutralization, recycling, or specialized chemical waste removal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your experimental objective should be the ultimate guide for your selection.
- If your primary focus is achieving a specific reaction: Choose an electrolyte that is completely inert to all components in your system and stable well beyond your operating voltage.
- If your primary focus is high efficiency or current: Prioritize an electrolyte with high ionic conductivity, ensuring its stability window is still adequate for your needs.
- If your primary focus is analytical precision: Use the highest purity reagents available and verify that the electrolyte ions will not interfere with the signal you are trying to measure.
Ultimately, a well-chosen electrolyte ensures that the data you collect reflects the process you intended to study.
Summary Table:
| Selection Factor | Impact on Experiment |
|---|---|
| Electrochemical Stability Window | Defines the usable voltage range; a mismatch causes electrolyte breakdown. |
| Chemical Compatibility | Prevents corrosion, passivation, and unwanted side reactions with electrodes/solvents. |
| Ionic Conductivity | Determines the efficiency of current flow within the cell. |
| Purity of Reagents | Trace impurities can catalyze side reactions and skew results. |
Struggling with inconsistent electrochemical results? The right electrolyte is key. KINTEK specializes in high-purity lab reagents and consumables, providing the reliable electrolytes and expert support your laboratory needs to ensure experimental accuracy and efficiency.
Let our experts help you select the perfect electrolyte for your application.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation to discuss your specific requirements and enhance your lab's performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Super Sealed Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Multifunctional Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Water Bath Single Layer Double Layer
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Lab Electrochemical Workstation Potentiostat for Laboratory Use
- Proton Exchange Membrane for Batteries Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- How does the design of an electrolytic cell influence evaluation of electrochemical catalytic performance? Key Factors
- What optical features does the H-type electrolytic cell have? Precision Quartz Windows for Photoelectrochemistry
- What is the general handling advice for a glass electrolysis cell? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Results
- How should the H-type electrolytic cell be connected? Expert Setup Guide for Precise Electrochemical Experiments
- What are the advantages of a PTFE-covered glass electrolytic cell? Ensure Precision in CO2-Saturated Testing















