In essence, refractory materials are used in furnaces because they are uniquely engineered to withstand the extreme environment within. They maintain their physical strength and chemical integrity at incredibly high temperatures, acting as a critical thermal and chemical barrier that contains the process and protects the furnace structure itself.
The value of a refractory material isn't just its high melting point. Its true purpose is to provide a stable, predictable, and non-reactive barrier that can endure a combination of extreme heat, chemical attack, and physical stress, ensuring the furnace operates safely and efficiently.

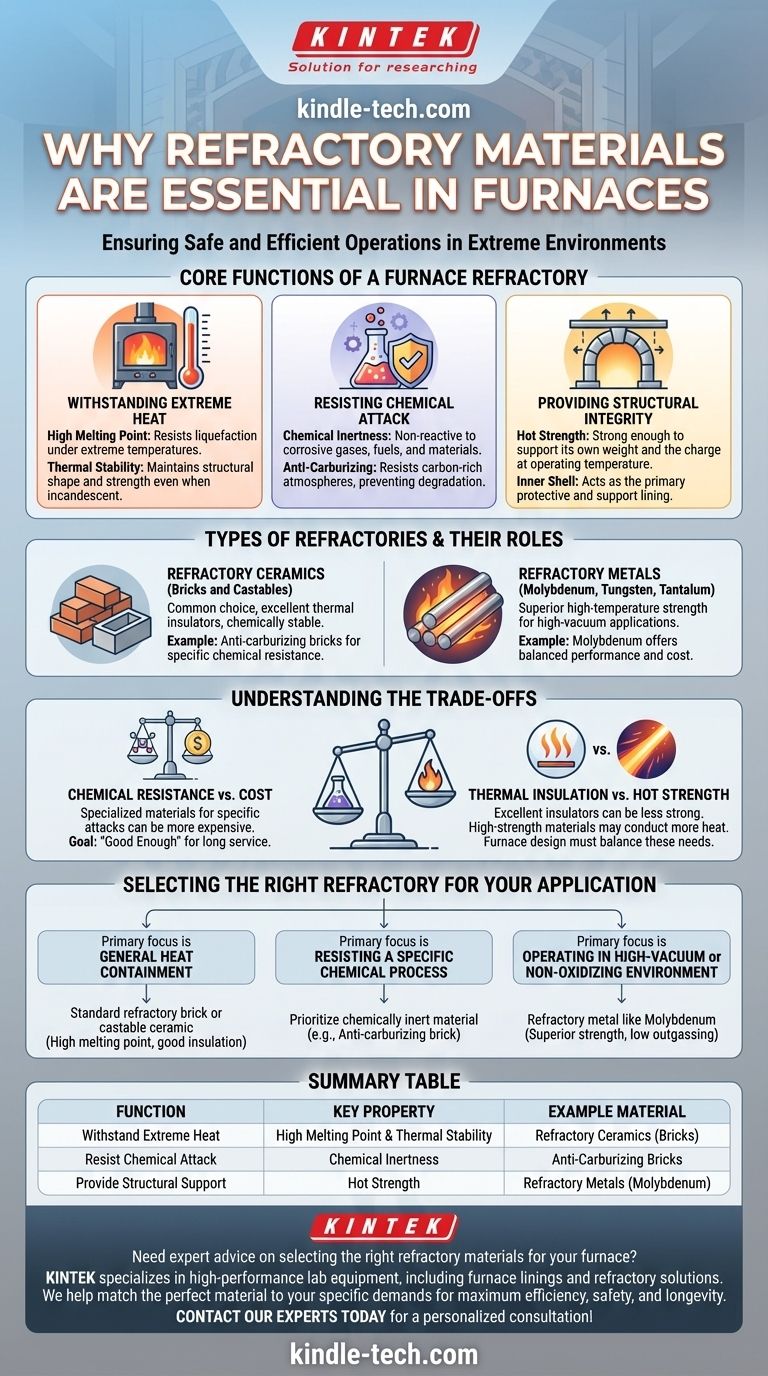
The Core Functions of a Furnace Refractory
To understand why refractories are indispensable, we must look beyond heat resistance and consider the three primary functions they serve inside a furnace.
Withstanding Extreme Temperatures
The most obvious function is to resist heat. Refractory materials have very high melting points, preventing them from liquefying under operating conditions.
This goes beyond just melting. They also possess thermal stability, meaning they resist deformation and maintain their structural shape and strength even when heated to incandescence.
Resisting Chemical Attack
A furnace is often a highly reactive chemical environment. The materials being heated, the fuel being burned, and the resulting gases can be highly corrosive.
Refractories are chosen for their chemical inertness. For example, anti-carburizing bricks are used in carburizing furnaces specifically because they resist the carbon-rich atmosphere that would degrade other materials. This prevents the lining from reacting with and contaminating the process.
Providing Structural Integrity
The refractory material is the furnace's inner shell. It must be strong enough to support its own weight and sometimes the weight of the material being processed (the "charge").
This strength must be maintained at operating temperature, a property known as hot strength. A material that is strong when cold but slumps or creeps when hot is unsuitable.
Types of Refractories and Their Roles
The term "refractory" covers a wide range of materials, each suited for different conditions. The choice depends entirely on the specific demands of the furnace.
Refractory Ceramics (Bricks and Castables)
These are the most common types of refractories. They are excellent thermal insulators and are generally very stable in chemically aggressive environments.
The anti-carburizing bricks mentioned in carburizing furnaces are a perfect example. They are a specialized ceramic formulation designed to be non-reactive in a specific chemical atmosphere.
Refractory Metals
In certain applications, such as high-vacuum furnaces, metals are the superior choice. Materials like molybdenum, tungsten, and tantalum offer exceptional high-temperature strength and stability.
Molybdenum is frequently used because it provides an excellent balance of performance and cost compared to other refractory metals. They are essential where the presence of ceramic oxides would be a contaminant.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a refractory material is a process of balancing competing properties. No single material is perfect for every application.
Chemical Resistance vs. Cost
Highly specialized refractories designed to resist a specific chemical attack are often more expensive than general-purpose materials.
The goal is to select a material that is "good enough" to ensure a long service life without over-engineering the solution and incurring unnecessary cost. The choice of molybdenum, for instance, is a cost-based decision over more exotic metals.
Thermal Insulation vs. Hot Strength
Materials that are excellent insulators are often more porous and have lower strength at high temperatures.
Conversely, dense, high-strength materials often have higher thermal conductivity, meaning more heat can escape. The furnace design must balance the need to contain heat with the need for a durable, long-lasting structure.
Selecting the Right Refractory for Your Application
The optimal choice is always dictated by the primary demand of the process.
- If your primary focus is general heat containment: A standard refractory brick or castable ceramic with a high melting point and good insulating properties is the most common solution.
- If your primary focus is resisting a specific chemical process: You must prioritize a material, like an anti-carburizing brick, that is chemically inert to the specific atmosphere inside your furnace.
- If your primary focus is operating in a high-vacuum or non-oxidizing environment: A refractory metal like molybdenum is often required for its superior strength and lack of outgassing at extreme temperatures.
Ultimately, selecting the right refractory is about matching the material's specific strengths to the unique thermal, chemical, and mechanical demands of the furnace environment.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Property | Example Material |
|---|---|---|
| Withstand Extreme Heat | High Melting Point & Thermal Stability | Refractory Ceramics (Bricks) |
| Resist Chemical Attack | Chemical Inertness | Anti-Carburizing Bricks |
| Provide Structural Support | Hot Strength | Refractory Metals (Molybdenum) |
Need expert advice on selecting the right refractory materials for your furnace?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including furnace linings and refractory solutions. We can help you match the perfect material to your specific thermal, chemical, and mechanical demands for maximum efficiency, safety, and longevity.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
People Also Ask
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost



















