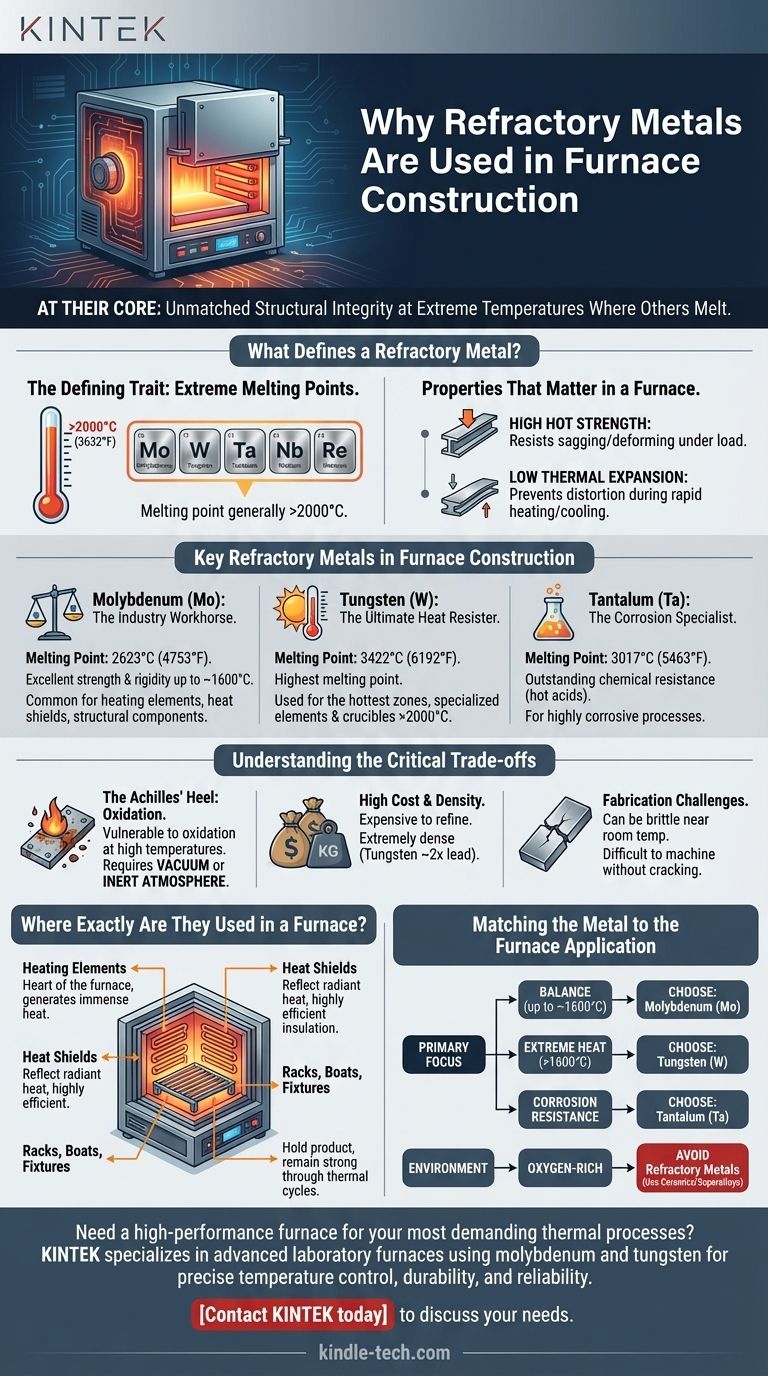
At their core, refractory metals are used in furnace construction because they are among the only materials that can maintain their structural integrity and strength at extremely high temperatures where conventional metals and alloys would melt or deform. Their uniquely high melting points and resistance to heat-induced creep make them indispensable for the hottest and most demanding components of modern high-performance furnaces.
The decision to use refractory metals is driven by one primary requirement: operational temperature. When a furnace process must exceed the limits of nickel-based superalloys (around 1200°C), refractory metals like molybdenum and tungsten become the default engineering choice for critical components, provided the atmosphere is controlled.
What Defines a Refractory Metal?
To understand their role, we must first define what makes these metals unique. They are a class of materials distinguished by a few exceptional properties.
The Defining Trait: Extreme Melting Points
The most fundamental characteristic is an exceptionally high melting point, generally considered to be above 2000°C (3632°F).
This exclusive group primarily includes molybdenum (Mo), tungsten (W), tantalum (Ta), niobium (Nb), and rhenium (Re).
The Properties That Matter in a Furnace
Beyond just resisting melting, these metals possess a suite of thermal and mechanical properties that make them ideal for furnace applications.
They exhibit high hot strength, meaning they resist sagging, stretching, and deforming under load at temperatures where other metals become soft.
They also have a low coefficient of thermal expansion, which helps prevent distortion and stress during rapid heating and cooling cycles.
Key Refractory Metals in Furnace Construction
While several refractory metals exist, two are the dominant workhorses in the furnace industry, with a third used for highly specialized applications.
Molybdenum (Mo): The Industry Workhorse
Molybdenum offers the best balance of performance and cost. With a melting point of 2623°C (4753°F), it provides excellent strength and rigidity for applications up to around 1600°C.
It is the most common material for furnace heating elements, layered heat shields, and structural components like hearth rails and support posts.
Tungsten (W): The Ultimate Heat Resister
When temperatures must go even higher, tungsten is the necessary choice. It has the highest melting point of any metal at 3422°C (6192°F).
Tungsten is used for the absolute hottest zones of a furnace, such as specialized heating elements and crucibles designed for processes well above 2000°C.
Tantalum (Ta): The Corrosion Specialist
Tantalum combines a high melting point of 3017°C (5463°F) with outstanding resistance to chemical attack, particularly from hot acids.
It is used in specialized furnaces where the material being processed is highly corrosive, and chemical inertness is as critical as heat resistance.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
The exceptional high-temperature performance of refractory metals comes with significant limitations that dictate how and where they can be used.
The Achilles' Heel: Oxidation
The single greatest weakness of refractory metals is their catastrophic vulnerability to oxidation at high temperatures.
When exposed to oxygen, these metals rapidly form brittle oxides that flake away, leading to swift component failure. This is why they are used almost exclusively in vacuum furnaces or furnaces with a controlled, inert atmosphere (like pure argon or hydrogen).
High Cost and Density
These are not commodity materials. Refractory metals are expensive to refine and fabricate, contributing significantly to the overall cost of a furnace.
They are also extremely dense (tungsten is nearly twice as dense as lead), which must be accounted for in the furnace's structural design and support framework.
Fabrication Challenges
Molybdenum and tungsten can be brittle at or near room temperature. This property, known as the ductile-to-brittle transition temperature, makes them challenging to machine and form without causing cracks, requiring specialized fabrication techniques.
Where Exactly Are They Used in a Furnace?
Inside a vacuum or inert-atmosphere furnace, you will find refractory metals performing three critical functions.
The "Hot Zone" and Heating Elements
This is the heart of the furnace. Heating elements, often made from molybdenum or tungsten wire, rod, or mesh, are responsible for generating the immense heat required for the process.
Heat Shields and Insulation
Instead of traditional fiber insulation (which would outgas in a vacuum), these furnaces use layered sheets of polished molybdenum. These shields reflect radiant heat back into the hot zone, creating an extremely efficient and clean insulation package.
Racks, Boats, and Fixtures
The components that hold the product being heat-treated must also withstand the furnace's temperature. Molybdenum alloys are commonly used to build racks, trays ("boats"), and fixtures that remain strong and stable through countless thermal cycles.
Matching the Metal to the Furnace Application
Your choice of material is dictated entirely by the specific demands of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is a balance of performance and cost (up to ~1600°C): Molybdenum is the industry standard for nearly all furnace components, from heating elements to racks.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature capability (>1600°C): Tungsten is the essential choice for the hottest components to ensure reliability and longevity.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance in a high-heat, non-oxidizing environment: Tantalum is the specialized solution required to prevent chemical degradation.
- If your furnace operates in an oxygen-rich atmosphere: Refractory metals are fundamentally unsuitable; you must use advanced ceramics or nickel/cobalt-based superalloys instead.
Ultimately, refractory metals enable us to achieve process temperatures and environmental purity that would otherwise be impossible.
Summary Table:
| Refractory Metal | Melting Point (°C) | Key Furnace Application |
|---|---|---|
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 2,623°C | Heating elements, heat shields, racks & fixtures (up to ~1600°C) |
| Tungsten (W) | 3,422°C | Extreme-temperature heating elements & crucibles (>1600°C) |
| Tantalum (Ta) | 3,017°C | Specialized components requiring corrosion resistance |
Need a high-performance furnace for your most demanding thermal processes?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory furnaces that leverage the superior properties of refractory metals like molybdenum and tungsten. Our solutions are engineered for precise temperature control, durability, and reliability in vacuum or inert-atmosphere environments.
Whether your application requires the balanced performance of molybdenum or the extreme-temperature capability of tungsten, our team can help you select the right equipment for your specific needs.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our refractory metal-based furnace systems can enhance your lab's capabilities and drive your research forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is a muffle furnace used to estimate? A Key Tool for Precise Ash Determination
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Precision Heating
- What is the importance of a muffle? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temperature Processes
- What is a muffle furnace consist of? A Guide to Its 3 Core Systems for Pure, High-Temp Processing
- What is the difference between a retort and a muffle furnace? Uncover the Truth About Indirect Heating



















