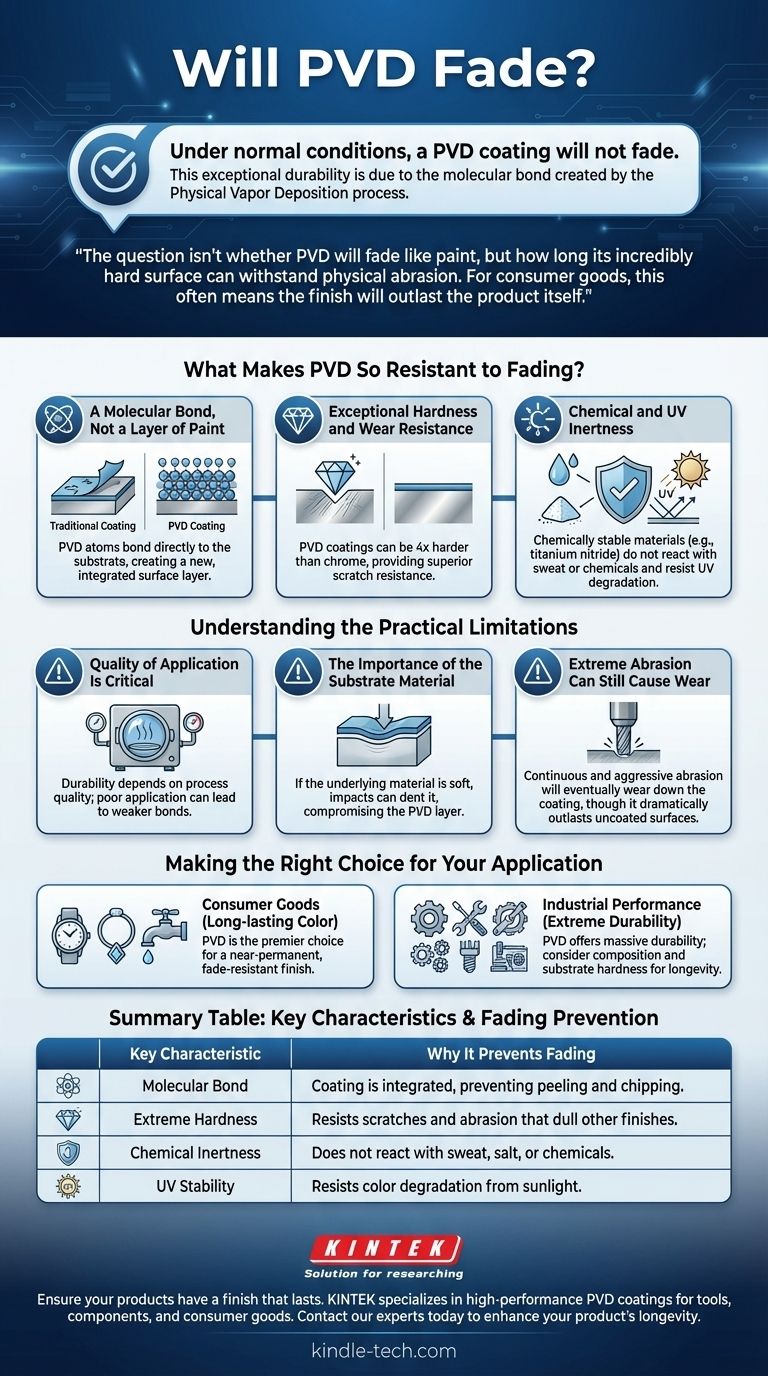
Under normal conditions, a PVD coating will not fade. This exceptional durability is due to the nature of the Physical Vapor Deposition process, which creates a molecular bond between the coating and the base material. The resulting finish is incredibly hard and inert, making it highly resistant to the UV exposure, discoloration, and wear that cause traditional coatings to fade.
The question isn't whether PVD will fade like paint, but how long its incredibly hard surface can withstand physical abrasion. For consumer goods, this often means the finish will outlast the product itself.
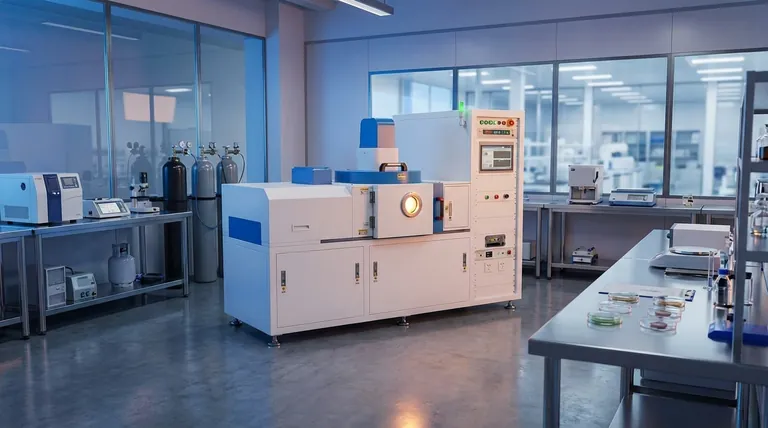

What Makes PVD So Resistant to Fading?
The remarkable longevity of a PVD finish isn't magic; it's a result of the physics behind its application. Unlike painting or electroplating, PVD fundamentally changes the surface of the object.
A Molecular Bond, Not a Layer of Paint
Traditional coatings simply sit on top of a material, making them susceptible to chipping and peeling.
PVD works in a vacuum by vaporizing a solid metal (like titanium or zirconium) into a plasma of atoms. These atoms are then bonded directly to the substrate, creating a new, integrated surface layer that is part of the object itself.
Exceptional Hardness and Wear Resistance
PVD coatings are extremely hard. High-quality PVD finishes can be four times harder than chrome, providing superior resistance to the scratches and minor abrasions that dull other finishes over time.
This hardness is what prevents the most common form of "fading," which is actually the slow wearing away of a softer surface layer.
Chemical and UV Inertness
The materials used in PVD, such as titanium nitride and zirconium nitride, are chemically stable.
This means they do not react with human sweat, salt water, or other common corrosive agents. They are also stable under UV light, preventing the color degradation seen in paints and plastics.
Understanding the Practical Limitations
While PVD is a superior coating technology, its performance is not infinite. Understanding its limitations is key to setting realistic expectations.
Quality of Application Is Critical
The durability of a PVD coating is heavily dependent on the quality of the deposition process.
Factors like vacuum chamber cleanliness, temperature control, and surface preparation are paramount. A poorly executed PVD application can result in a weaker bond, leading to premature wear.
The Importance of the Substrate Material
PVD coating is only a few microns thick. If the underlying material (the substrate) is soft, a significant impact can dent the substrate and compromise the PVD layer on top of it.
The coating itself won't have failed, but the damage to the underlying object will be visible.
Extreme Abrasion Can Still Cause Wear
No coating is indestructible. While PVD is highly resistant to scratches from everyday use, continuous and aggressive abrasion will eventually wear it down.
For example, a PVD-coated tool bit will eventually wear after extensive industrial use, but it will dramatically outlast an uncoated equivalent.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by your primary goal for the product.
- If your primary focus is long-lasting color on consumer goods (watches, jewelry, fixtures): PVD is the premier choice and can be considered a near-permanent finish that will not fade.
- If your primary focus is extreme industrial performance (tools, components): PVD offers a massive durability advantage, but you must consider the specific PVD composition and the substrate's hardness as the primary factors for longevity.
Ultimately, choosing a product with a quality PVD finish is the most effective way to ensure its color and luster remain intact for years to come.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | Why It Prevents Fading |
|---|---|
| Molecular Bond | Coating is integrated into the substrate, preventing peeling and chipping. |
| Extreme Hardness | Highly resistant to scratches and abrasion that dull other finishes. |
| Chemical Inertness | Does not react with sweat, salt, or chemicals, maintaining color integrity. |
| UV Stability | Resists color degradation from sunlight, unlike paints and plastics. |
Ensure your products have a finish that lasts. KINTEK specializes in high-performance PVD coatings for tools, components, and consumer goods. Our expertise in lab equipment and consumables ensures a durable, fade-resistant finish that meets your exact specifications. Contact our experts today to enhance your product's longevity and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating



















