Introduction
Table of Contents
Vacuum induction melting furnaces and arc melting furnaces are two specialized laboratory equipment used to melt and purify metals under controlled conditions. Each type of furnace has its own advantages and applications, so it is important to understand the differences between them in order to choose the right equipment for your specific needs.

Vacuum Induction Melting Furnaces
Introduction
Vacuum induction melting (VIM) furnaces employ an induction coil to induce heat within the metal, housed in a crucible within the furnace. The vacuum setting facilitates the elimination of gases and impurities from the molten metal, yielding a purer and more uniform product. VIM furnaces are commonly utilized to melt high-purity metals, particularly in the aerospace and medical sectors.
Advantages of Vacuum Induction Melting
1. Enhanced Purity and Quality:
VIM's most notable benefit is its capacity to produce materials of exceptional purity and quality. The vacuum environment precludes contamination from gases like oxygen and nitrogen, present in the atmosphere. This produces a cleaner and more consistent melt, devoid of detrimental inclusions and impurities that could compromise the material's mechanical properties.
2. Controlled Atmosphere:
Within the vacuum chamber, the atmosphere is meticulously controlled. Only designated gases are introduced at precise pressures. This degree of control enables precise regulation of the molten material's chemical composition and reactivity. Unwanted oxidation or reactions with ambient gases are effectively prevented.
3. Gas Elimination:
The vacuum induction furnace completely eliminates gases from the molten metals. The presence of these gases would otherwise lead to rapid oxidation.
4. Compositional Consistency:
Vacuum induction melting furnaces achieve extremely tight compositional tolerances. Consequently, metals melted under vacuum induction conditions exhibit exceptional consistency.
Applications of Vacuum Induction Melting
1. Aerospace and Medical Industries:
VIM furnaces are extensively employed in the aerospace and medical industries, where high-purity metals are essential for critical applications.
2. Production of Superalloys:
VIM furnaces are specifically designed for processing superalloys, which possess exceptional strength and heat resistance. These alloys are used in demanding applications, including jet engines and medical implants.
3. Melting of Stainless Steels and Other Metals:
While initially developed for specialized alloys, VIM furnaces have expanded their applications to include stainless steels and other metals.

Conclusion
Vacuum induction melting furnaces offer a unique combination of advantages, making them a preferred choice for producing high-purity and high-quality metals. Their ability to control the atmosphere, eliminate gases, and achieve precise compositional tolerances makes them indispensable for various industries, particularly aerospace, medical, and metallurgy.
Arc Melting Furnaces
Arc melting furnaces are a type of metallurgical furnace that uses an electric arc to heat and melt metal. They are often used for melting metals that are difficult to melt, such as refractory metals and alloys, or for melting metals that are contaminated with impurities.
Principle of Operation
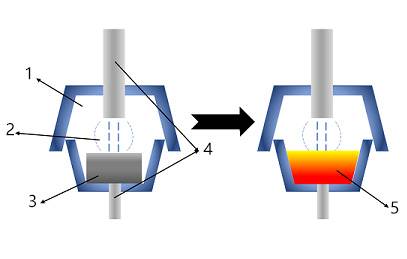
Arc melting furnaces work by creating an electric arc between an electrode and the metal being melted. The heat from the arc melts the metal, which then flows into a crucible. The crucible is water-cooled to prevent it from melting.
The temperature of the arc can be controlled by adjusting the voltage and current. The voltage is typically between 10 and 100 volts, and the current is typically between 100 and 1000 amps.
Advantages of Arc Melting Furnaces
Arc melting furnaces offer several advantages over other types of melting furnaces, including:
- High temperatures: Arc melting furnaces can reach temperatures of up to 4000 degrees Celsius, which is much higher than the melting point of most metals. This makes them ideal for melting metals that are difficult to melt, such as refractory metals and alloys.
- Low contamination: Arc melting furnaces do not use any fluxes or other chemicals to melt the metal, which can contaminate the metal. This makes them ideal for melting metals that are used in critical applications, such as in the production of semiconductors and medical devices.
- High efficiency: Arc melting furnaces are very efficient at melting metal. They can melt metal quickly and with a high degree of precision.
Applications of Arc Melting Furnaces
Arc melting furnaces are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Melting of refractory metals and alloys: Arc melting furnaces are used to melt refractory metals and alloys, such as tungsten, molybdenum, and tantalum. These metals are used in a variety of applications, including in the production of aerospace components, cutting tools, and medical devices.
- Melting of contaminated metals: Arc melting furnaces are used to melt metals that are contaminated with impurities. The arc can help to remove these impurities, making the metal more pure.
- Production of special steels: Arc melting furnaces are used to produce special steels, such as stainless steel and tool steel. These steels are used in a variety of applications, including in the production of automotive components, machinery, and medical devices.
Conclusion
Arc melting furnaces are a versatile and efficient type of melting furnace that can be used for a wide variety of applications. They offer several advantages over other types of melting furnaces, including high temperatures, low contamination, and high efficiency.
Advantages of Vacuum Induction Melting Furnaces
Vacuum induction melting furnaces offer several advantages over arc melting furnaces, including:
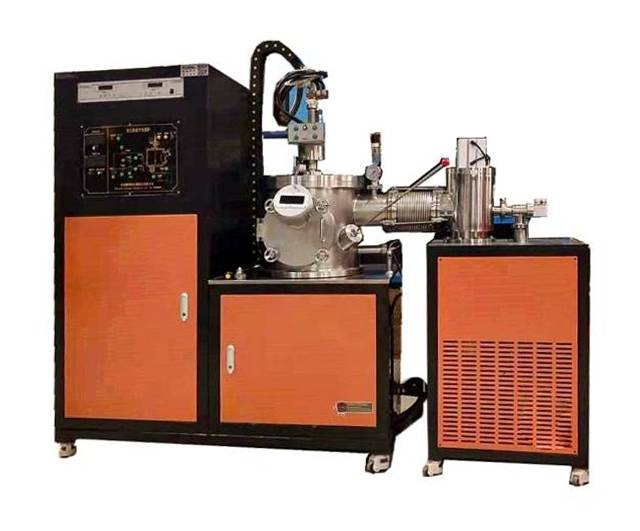

Cleaner Melts:
The vacuum environment helps remove gases and impurities from the molten metal, resulting in a purer and more consistent product. This is particularly beneficial for metals and alloys that are sensitive to contamination, such as titanium, zirconium, and high-temperature alloys.
Reduced Oxidation:
Vacuum induction melting helps reduce oxidation of the molten metal, which can lead to improved material properties. This is important for metals that are prone to oxidation, such as aluminum, copper, and magnesium.
Better Process Control:
The vacuum environment and the use of an induction coil allow for better control over the melting process. This enables precise temperature control, reduced stirring, and minimized contamination, leading to a more consistent and repeatable product.
Improved Material Properties:
Vacuum induction melting can enhance the material properties of the finished product. The reduced gas content and oxidation result in improved mechanical properties, electrical conductivity, and corrosion resistance.
Applications in High-Tech Industries:
Vacuum induction melting is widely used in high-tech industries, including aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. It is particularly suitable for producing high-purity materials, components with tight tolerances, and materials for critical applications.
Environmental Benefits:
Vacuum induction melting furnaces have certain environmental benefits. The absence of combustion eliminates air pollution and slag generation, reducing the environmental impact of the melting process.
Advantages of Arc Melting Furnaces

Arc melting furnaces offer several advantages over other melting methods, including:
Higher Melting Temperatures: Arc melting furnaces can achieve higher melting temperatures than other furnace types, making them suitable for melting metals with high melting points.
Faster Melting Times: Arc melting furnaces can melt metals more quickly than other furnaces, which can be important for high-volume applications.
Lower Cost: Arc melting furnaces are typically less expensive than other furnaces, making them a more cost-effective option for budget-conscious buyers.
Additional Advantages:
Direct Exposure to Electric Arc: In arc furnaces, the charged material is directly exposed to an electric arc, allowing for efficient heat transfer and faster melting.
Versatility in Charged Material: Arc furnaces can accommodate a wide variety of charged materials, making them suitable for melting different types of metals.
Large Batch Capacity: Arc furnaces typically have large batch capacities, making them ideal for large-scale melting operations.
Precise Temperature Control: Arc furnaces offer precise temperature control, allowing for accurate melting and the production of high-quality metals.
Ability to Smelt Special Steels: Arc furnaces can smelt special steels containing refractory elements such as tungsten and molybdenum.
Degassing and Desulfurization: Arc furnaces can remove toxic gases and inclusions during the melting process, resulting in cleaner and purer metals.
Flexibility: Arc furnaces can be operated continuously or intermittently, providing flexibility in production schedules.
Conclusion
Vacuum induction melting furnaces are highly advanced and versatile equipment that enables the production of high-quality and pure metals and alloys. Their ability to melt metals in a vacuum environment, control impurities, and tailor properties makes them an essential tool in various industries. As technology continues to evolve, VIM furnaces will play an increasingly significant role in the production of advanced materials for cutting-edge applications.
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
Related Articles
- How Vacuum Induction Melting Powers Superior Material Performance in Critical Industries
- How Vacuum Induction Melting Outperforms Traditional Methods in Advanced Alloy Production
- How Vacuum Induction Melting Prevents Catastrophic Material Failures in Critical Components
- Melting process and maintenance of vacuum induction melting furnace
- Vacuum Melting Furnace: A Comprehensive Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting
















