Yes, hydrogen is actively used in industrial furnaces, but its application is highly specialized and governed by strict safety protocols. It is not a simple drop-in replacement for other fuels but is instead employed as a process gas in applications like atmospheric brazing and metal heat treating, where its unique chemical and thermal properties are critical for achieving a specific result.
While hydrogen offers powerful process advantages—namely rapid temperature control and preventing metal oxidation—its use is fundamentally defined by the need to manage significant safety risks and material compatibility challenges through specialized furnace design and operation.
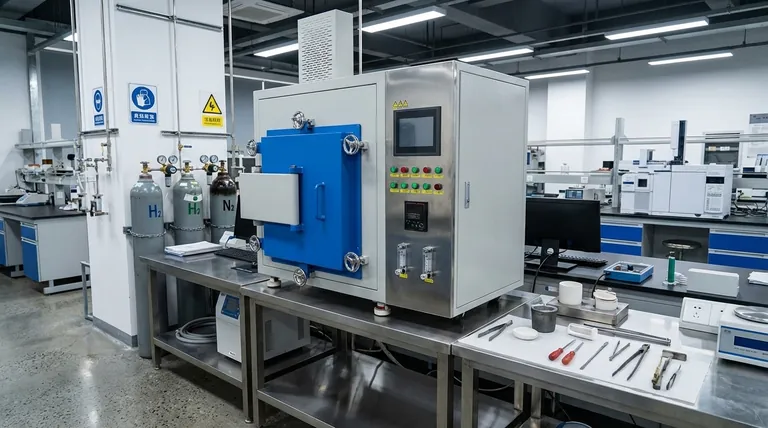

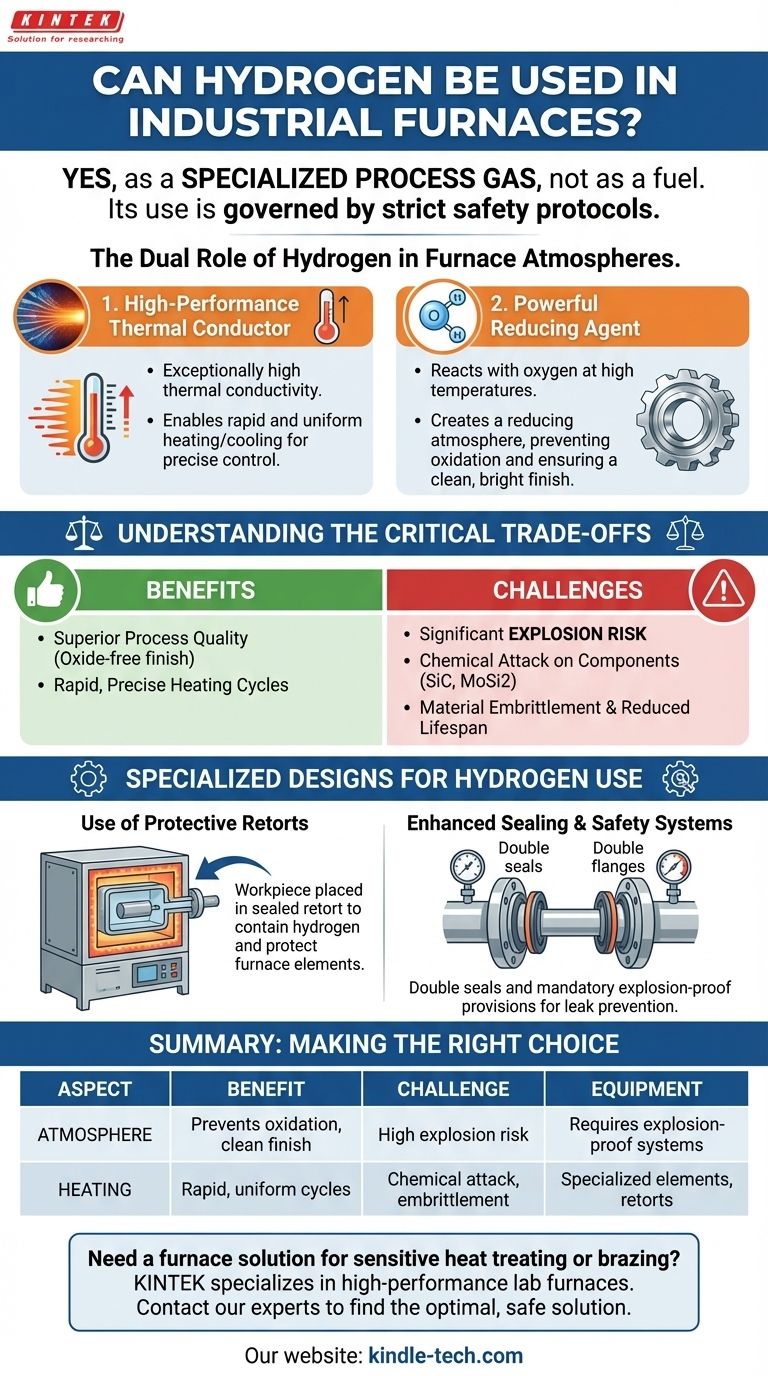
The Dual Role of Hydrogen in Furnace Atmospheres
Hydrogen is valued in furnace environments not as a primary fuel, but for its profound impact on the process and the product. It serves two distinct and critical functions.
As a High-Performance Thermal Conductor
Hydrogen gas has exceptionally high thermal conductivity. This property allows for very rapid and uniform heating or cooling of the materials inside the furnace.
This rapid thermal response is crucial in heat treating processes where precise control over temperature gradients and cycle times directly impacts the final metallurgical properties of the component.
As a Powerful Reducing Agent
At high temperatures, hydrogen readily reacts with oxygen. This is a highly desirable effect inside a furnace, as it consumes any residual oxygen, creating what is known as a "reducing atmosphere."
By removing oxygen, hydrogen effectively prevents the formation of oxides (rust or scale) on the surface of metal parts. This ensures a clean, bright finish, which is essential for processes like brazing where surface quality is paramount.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
The benefits of hydrogen come with significant operational challenges that cannot be ignored. The decision to use it requires a clear understanding of the risks and necessary engineering controls.
The Inherent Explosion Risk
The most significant danger is the risk of a hydrogen explosion. Hydrogen gas is highly flammable and can be explosive over a wide range of concentrations in air.
Because of this, any furnace using hydrogen—or a "forming gas" mixture containing hydrogen—must be equipped with mandatory, explosion-proof safety provisions and specialized control software to ensure safe operation.
Chemical Attack on Furnace Components
Hydrogen is chemically reactive, especially at the high temperatures found in furnaces. This reactivity can degrade the furnace itself.
Heating elements made from common materials like silicon carbide (SiC) and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) can be chemically attacked and damaged by a hydrogen atmosphere.
Material Embrittlement and Reduced Lifespan
Even beyond direct chemical attack, the presence of hydrogen can cause components like electrical resistors to become brittle over time.
This embrittlement significantly shortens the operational life of critical furnace parts, increasing maintenance requirements and operational costs.
Specialized Designs for Hydrogen Use
Standard furnaces are not suitable for hydrogen atmospheres. The equipment must be purpose-built or extensively modified to handle the gas safely and effectively.
Use of Protective Retorts
To protect furnace components, high-temperature hydrogen furnaces often use an internal, sealed chamber called a retort.
The workpiece is placed inside the retort, which is then filled with the hydrogen atmosphere. This contains the hazardous gas and isolates it from the furnace's primary heating elements and insulation, preventing damage.
Enhanced Sealing and Safety Systems
Furnaces designed for hydrogen, especially vacuum furnaces, require enhanced safety measures. This includes features like double seals on all flanges to prevent any potential leaks of the flammable gas into the surrounding environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to use a hydrogen atmosphere depends entirely on whether its specific benefits outweigh the considerable safety and equipment costs.
- If your primary focus is process quality: Hydrogen is an exceptional choice for achieving an oxide-free surface finish and enabling rapid, precise heating or cooling cycles for sensitive metal parts.
- If your primary focus is operational simplicity and safety: The extensive engineering controls, specialized equipment, and material degradation issues mean hydrogen should only be adopted if its process benefits are absolutely essential.
- If your primary focus is high-volume brazing: A continuous belt furnace with a hydrogen atmosphere can be an economical solution for processing large quantities of small parts where a clean, flux-free joint is required.
Ultimately, integrating hydrogen into a furnace process is a strategic decision that balances clear metallurgical advantages against significant operational complexity and investment.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Benefit | Challenge |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Creates a powerful reducing atmosphere, preventing oxidation. | High explosion risk; requires explosion-proof safety systems. |
| Heating | High thermal conductivity enables rapid, uniform heating/cooling. | Can chemically attack and embrittle standard heating elements. |
| Equipment | Essential for achieving clean, bright finishes in brazing. | Requires specialized furnace design (e.g., retorts, double seals). |
Need a furnace solution for sensitive heat treating or brazing?
Hydrogen atmospheres offer superior results but demand expert engineering. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and thermal processing systems. Our team can help you determine if a hydrogen-compatible furnace is right for your application and provide the safe, reliable equipment you need.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific metal processing goals and find the optimal furnace solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why must a hydrogen-reducing atmosphere be maintained for tungsten annealing? Ensure Purity in High-Temp Processing
- What are hydrogen furnaces used for? Achieve Purity and Speed in High-Temperature Processing
- When would you need to use a controlled atmosphere? Prevent Contamination and Control Reactions
- Why is an industrial furnace with hydrogen atmosphere control necessary for the pre-sintering of Fe-Cr-Al materials?
- What are the primary benefits of using hydrogen firing for sintering parts? Achieve Peak Density & Corrosion Resistance



















