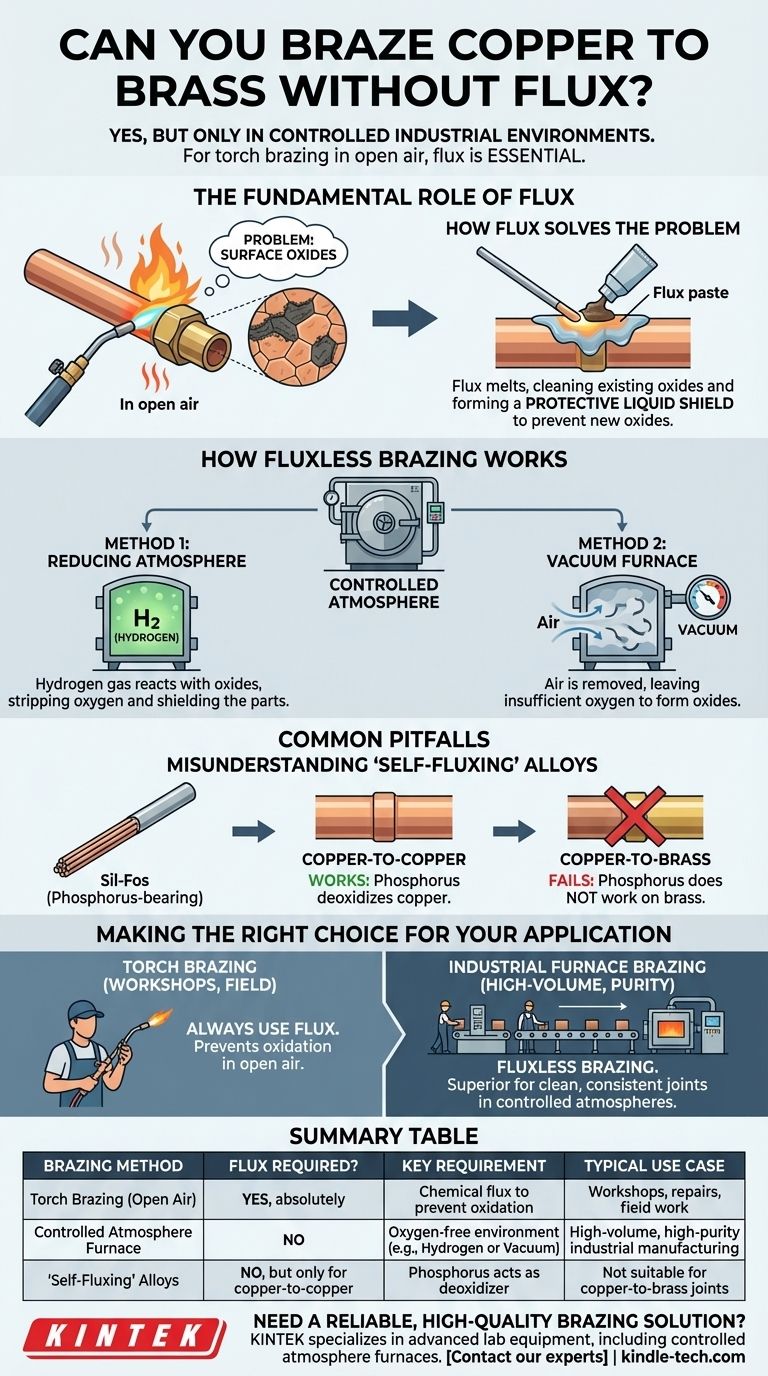
Yes, it is technically possible to braze copper to brass without flux, but only under highly specific industrial conditions. For any standard brazing operation using a torch in open air, flux is absolutely essential. The absence of flux in a normal environment will result in a failed joint due to the rapid formation of surface oxides when the metals are heated.
The core principle of brazing is that the filler metal must bond directly with a pure, clean base metal. The primary role of flux is to prevent oxygen from contaminating the joint area during heating. If you can remove the oxygen from the environment itself, you can eliminate the need for flux.

The Fundamental Role of Flux in Brazing
To understand when you can omit flux, you must first understand why it's required in the first place. The entire process hinges on preventing one chemical reaction: oxidation.
The Problem: Surface Oxides
When you heat metals like copper and brass in the presence of air, the metal surfaces react with oxygen to form a thin, hard layer of metal oxides.
This oxide layer acts as a barrier. Molten brazing alloy cannot wet or flow over an oxidized surface, and it cannot form a strong metallurgical bond with the base metals underneath.
How Flux Solves the Problem
Brazing flux is a chemical compound that performs two critical jobs when heated.
First, it cleans and dissolves any minor surface oxides that are already present. Second, and more importantly, it melts to form a protective liquid shield over the joint area, preventing oxygen from reaching the hot base metals and creating new oxides.
Why This is Critical for Copper-to-Brass
Both copper and the zinc within brass oxidize very quickly at brazing temperatures. Without a protective layer of flux, the joint area would become heavily oxidized long before the brazing alloy could melt and flow, guaranteeing a weak or nonexistent bond.
How Fluxless Brazing Works
Fluxless brazing is possible only when you replace the protective function of flux with another method of oxygen control.
The Core Principle: A Controlled Atmosphere
The only way to braze without flux is to perform the heating process inside a sealed environment where oxygen has been removed and replaced with a specific gas or a vacuum.
This is known as controlled atmosphere brazing and is typically done in an industrial furnace.
Method 1: Reducing Atmosphere Furnace
As noted in specialized processes, a furnace can be filled with a reducing gas like hydrogen.
At brazing temperatures, the hydrogen actively reacts with any metal oxides on the parts, stripping the oxygen away and converting the oxides back into pure metal. The hydrogen gas itself acts as the flux, both cleaning the parts and shielding them from any trace oxygen.
Method 2: Vacuum Furnace
Another common industrial method is brazing in a vacuum furnace. By pumping nearly all the air out of the heating chamber, there is simply not enough oxygen present to form detrimental oxide layers on the parts.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
It is crucial to distinguish industrial furnace brazing from common torch brazing. A frequent point of confusion arises with certain filler metals.
Misunderstanding "Self-Fluxing" Alloys
Some phosphorus-bearing brazing alloys (like Sil-Fos) are described as "self-fluxing" when joining copper to copper.
In this specific case, the phosphorus in the alloy acts as a deoxidizing agent, performing the function of flux. However, this effect only works on pure copper. It is not effective on brass, bronze, or steel. Attempting to braze copper to brass with a self-fluxing alloy and no separate flux will result in a failed joint.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your need for flux is determined entirely by your brazing environment, not just the metals you are joining.
- If your primary focus is brazing with a torch in a workshop or field setting: You must always use a suitable brazing flux designed for copper and brass.
- If your primary focus is designing a high-volume, high-purity industrial manufacturing process: Fluxless furnace brazing in a controlled atmosphere is often the superior method for creating clean, consistent, and residue-free joints.
Ultimately, mastering the brazing process comes down to controlling oxidation.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Method | Flux Required? | Key Requirement | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Torch Brazing (Open Air) | Yes, absolutely | Chemical flux to prevent oxidation | Workshops, repairs, field work |
| Controlled Atmosphere Furnace | No | Oxygen-free environment (e.g., Hydrogen or Vacuum) | High-volume, high-purity industrial manufacturing |
| "Self-Fluxing" Alloys | No, but only for copper-to-copper | Phosphorus content acts as a deoxidizer | Not suitable for copper-to-brass joints |
Need a reliable, high-quality brazing solution for your laboratory or production line?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment, including the controlled atmosphere furnaces that make fluxless brazing possible. Our expertise ensures clean, strong, and consistent joints for your copper, brass, and other metal assemblies.
Let us help you select the right equipment for your specific brazing application. Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover the KINTEK difference.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- What is nitrogen atmosphere for annealing? Achieve Oxidation-Free Heat Treatment
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- What is the role of nitrogen in annealing process? Creating a Controlled, Protective Atmosphere
- What are the functions of nitrogen (N2) in controlled furnace atmospheres? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment Results



















