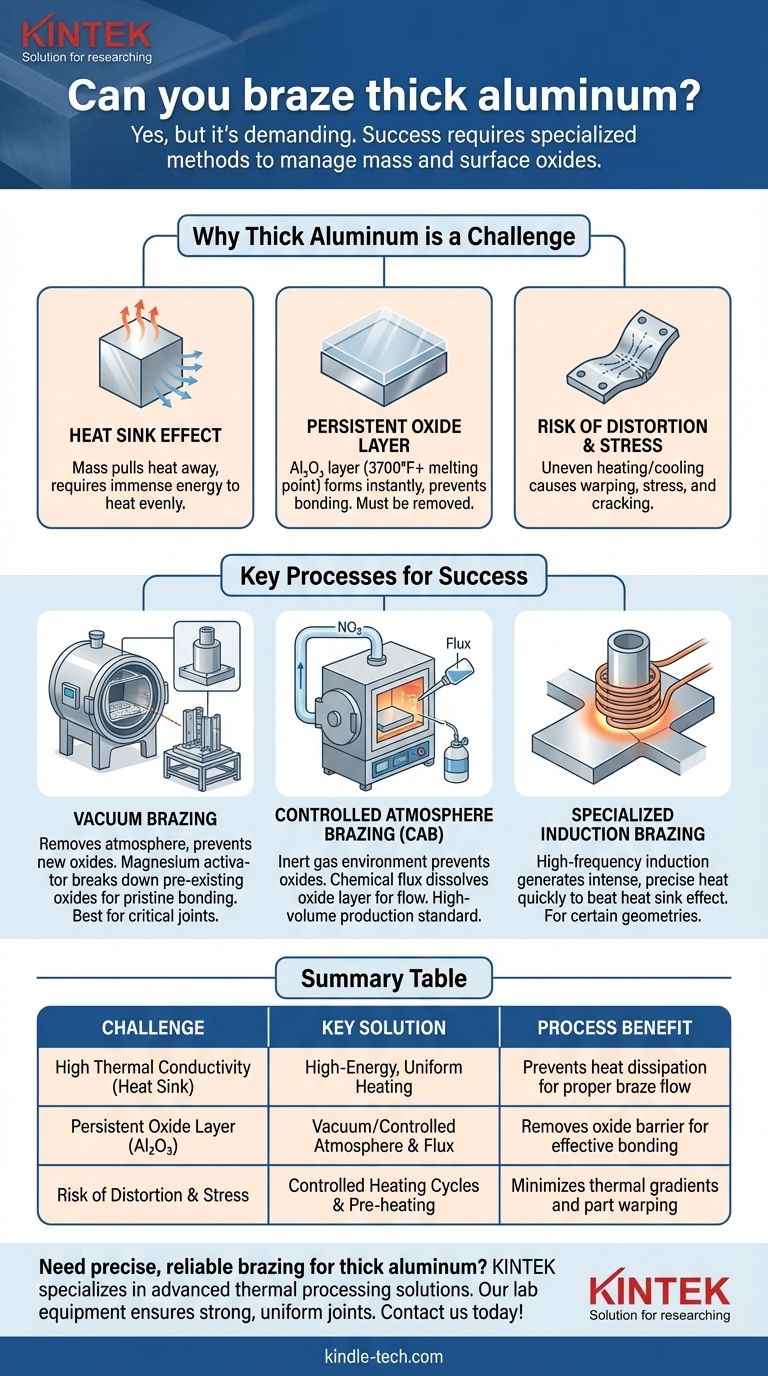
Yes, you can braze thick aluminum, but the process is fundamentally different and more demanding than brazing thin sheets. The material's mass acts as a powerful heat sink, requiring specialized methods like vacuum or controlled atmosphere brazing to deliver sufficient, uniform heat and manage the persistent surface oxide layer that prevents a good bond.
The core challenge in brazing thick aluminum is not the joining itself, but overcoming the material's high thermal conductivity. Your success hinges entirely on the ability to heat the entire joint area to a uniform brazing temperature before the heat dissipates into the rest of the component.
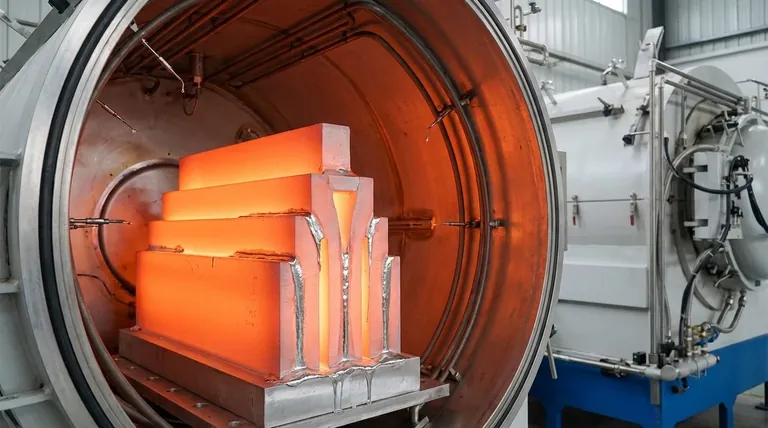

Why Thick Aluminum Presents a Unique Brazing Challenge
Successfully joining thick aluminum sections requires a deep understanding of its material properties. The very characteristics that make aluminum useful—its light weight and thermal conductivity—become obstacles during the brazing process.
The Heat Sink Effect
Thick aluminum is exceptionally effective at pulling heat away from the joint. This "heat sink" effect means an enormous amount of energy is required to reach and maintain the necessary brazing temperature across the entire joint interface. Applying heat too slowly or with insufficient power will result in the heat dissipating into the body of the part faster than it can build up at the joint.
The Persistent Oxide Layer
Aluminum instantly forms a tough, transparent layer of aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) when exposed to air. This oxide has a melting point of over 3700°F (2072°C), far higher than the aluminum base metal itself. For a braze to succeed, this oxide layer must be chemically or mechanically removed so the filler metal can wet and bond with the raw aluminum beneath. The longer heating times required for thick sections give this oxide more opportunity to form and reform, complicating the process.
Risk of Distortion and Stress
Pouring immense heat into one area of a large, thick component while the rest remains cool creates significant thermal gradients. This uneven expansion and contraction can lead to warping, distortion, and the introduction of residual stress, potentially causing the part to crack as it cools.
Key Processes for Brazing Thick Sections
Standard torch brazing is often insufficient for thick aluminum. Industrial processes overcome these challenges by controlling both the heat and the atmosphere.
Vacuum Brazing
This is a highly effective method for critical components. The parts are assembled with the filler metal and placed in a vacuum furnace. Removing the atmosphere prevents the formation of new oxides. Small amounts of a metal activator, such as magnesium (Mg), are often included in the filler alloy. In the vacuum, this magnesium vaporizes and aggressively breaks down any pre-existing oxides, ensuring a pristine surface for the braze to bond to.
Controlled Atmosphere Brazing (CAB)
CAB is a common high-volume production method. Parts are passed through a furnace filled with an inert gas, typically nitrogen. This oxygen-free atmosphere prevents oxide formation during heating. A chemical flux is applied to the joint before heating, which melts and aggressively dissolves the oxide layer, allowing the molten filler metal to flow into the joint via capillary action.
Specialized Induction Brazing
For certain geometries, high-frequency induction heating can be a viable option. This method uses a magnetic field to generate intense heat very quickly and precisely within the metal itself. If the power is sufficient, it can heat the joint area faster than the heat can conduct away, allowing the braze to be completed in a very short time. This requires precise coil design and careful process control.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Even with the right process, success is not guaranteed. Careful attention to detail is essential for a sound joint.
Choosing the Right Filler Metal
The filler metal must have a melting point lower than the base aluminum alloy. For thick sections, selecting a filler with a slightly wider melting range (the gap between when it starts to melt and when it becomes fully liquid) can be advantageous. This "slushy" state can help fill larger joint gaps that may result from the thermal expansion of heavy parts.
The Importance of Joint Design
Brazing relies on capillary action to draw the molten filler metal into the space between the two parts. The gap, or joint clearance, is critical. If it's too tight, the filler can't penetrate. If it's too wide, capillary force is lost. For thick sections, these clearances must be precisely engineered to account for thermal expansion during the heating cycle.
The Need for Pre-heating
To minimize thermal shock and distortion, pre-heating the entire assembly to an intermediate temperature is often necessary. This reduces the temperature difference between the joint and the rest of the part, making it easier to reach the final brazing temperature uniformly and preventing stress-related cracking during cooling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of brazing method should be dictated by your project's specific requirements for quality, volume, and cost.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint integrity and complex shapes: Vacuum brazing is the superior choice, offering the cleanest, strongest, and most reliable bonds for critical applications.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and repeatability: Controlled Atmosphere Brazing (CAB) is the industry standard, providing an efficient and cost-effective solution for manufacturing at scale.
- If your primary focus is a simple, accessible joint on a moderately thick part: High-power induction brazing may be a fast and effective option, provided you can develop a highly controlled and repeatable process.
By properly managing heat and controlling the atmosphere, you can create strong, reliable brazed joints in even the most challenging thick-section aluminum components.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Key Solution | Process Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| High Thermal Conductivity (Heat Sink) | High-Energy, Uniform Heating | Prevents heat dissipation for proper braze flow |
| Persistent Oxide Layer (Al₂O₃) | Vacuum/Controlled Atmosphere & Flux | Removes oxide barrier for effective bonding |
| Risk of Distortion & Stress | Controlled Heating Cycles & Pre-heating | Minimizes thermal gradients and part warping |
Need to braze thick aluminum components with precision and reliability? KINTEK specializes in advanced thermal processing solutions, including vacuum and controlled atmosphere brazing systems. Our lab equipment and consumables are designed to meet the demanding needs of laboratory and industrial applications, ensuring strong, uniform joints in challenging materials. Let our experts help you achieve superior results—contact us today to discuss your specific brazing requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- Does brazing require heat? Yes, it's the catalyst for creating strong, permanent bonds.
- What is the basic of brazing? A Guide to Strong, Low-Heat Metal Joining
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy



















