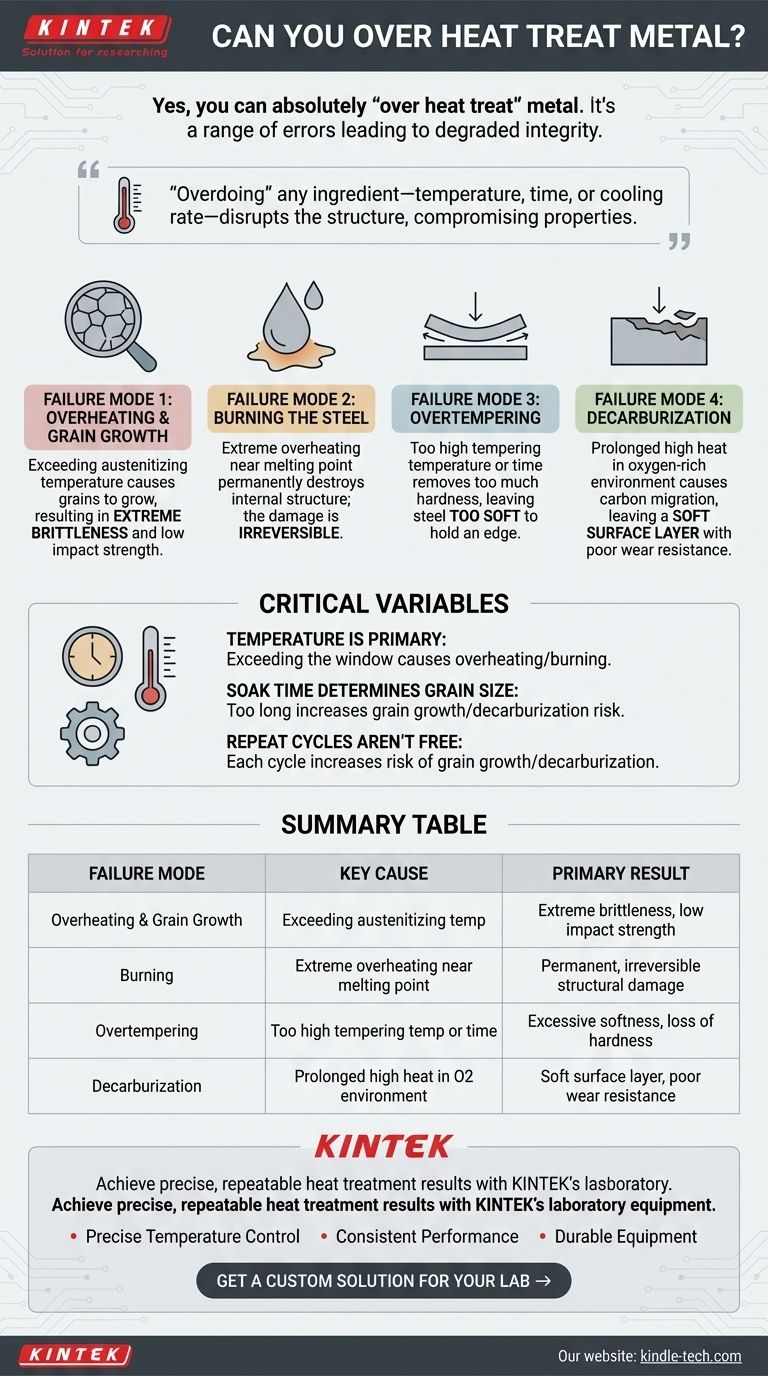
Yes, you can absolutely "over heat treat" metal. The term doesn't refer to a single mistake, but a range of errors where excessive heat or time is applied during the process. These mistakes degrade the metal's structural integrity, leading to outcomes like extreme brittleness, softness, or a ruined surface, often rendering the part useless.
Heat treatment is a precise recipe where temperature, time, and cooling rate are the key ingredients. "Overdoing" any of them—heating too high, holding for too long, or even tempering too hot—disrupts the carefully controlled crystalline structure, compromising the very properties you aim to achieve.

What "Over Heat Treating" Actually Means
The phrase "over heat treated" is a general term for several distinct failure modes. Understanding which one occurred is the key to diagnosing and preventing the problem.
Failure Mode 1: Overheating and Grain Growth
During the hardening phase, steel is heated to a critical temperature (the austenitizing temperature) to transform its internal crystal structure. If you exceed this temperature significantly, the microscopic "grains" of the steel begin to grow and coarsen.
Fine, small grains create a tough, strong material. Large, coarse grains create pathways for cracks to travel easily, resulting in extreme brittleness and low impact strength. A part that has suffered from grain growth may be very hard, but it will shatter like glass under stress.
Failure Mode 2: Burning the Steel
This is the most extreme form of overheating. If the temperature gets far too high, approaching the metal's melting point, the boundaries between the grains can begin to melt and oxidize.
This damage is permanent and irreversible. The steel's internal structure is fundamentally destroyed, and it cannot be recovered through subsequent heat treatment cycles. The metal is scrap.
Failure Mode 3: Overtempering
After a steel part is hardened (quenched), it is extremely hard but also very brittle. Tempering is a subsequent, lower-temperature heating process designed to reduce that brittleness and increase toughness.
Overtempering occurs when you either use too high a temperature for the tempering step or hold it at that temperature for too long. This process removes too much hardness, leaving the steel too soft to hold an edge or resist wear.
Failure Mode 4: Decarburization
This failure is a function of both time and atmosphere. When steel is held at high temperatures for extended periods in an oxygen-rich environment, carbon atoms can migrate out of the surface.
This leaves a soft, low-carbon "skin" on the part. A blade with a decarburized edge will never hold its sharpness, and a bearing surface with a decarburized layer will wear out almost instantly.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Variables
Avoiding these failures requires precise control over the core variables of heat treatment. Small deviations can have major consequences.
Temperature is the Primary Factor
For any given steel alloy, there is a specific and often narrow temperature window for hardening. Exceeding this window is the direct cause of overheating, grain growth, and burning. Using a calibrated thermometer or temperature controller is non-negotiable for consistent results.
Soak Time Determines Grain Size
Soak time is the duration a part is held at the target temperature. Even if the temperature is correct, holding it for too long will cause grain growth and increase the risk of decarburization. The goal is to hold it just long enough for the entire cross-section to reach a uniform temperature and complete its transformation, but no longer.
Repeat Cycles Aren't a Free Pass
While it's sometimes possible to fix a mistake by re-heat treating (e.g., re-hardening an overtempered part), every heating cycle carries risk. Each cycle is another opportunity for grain growth or decarburization to occur if not performed with precision. It is not a process that can be repeated indefinitely without consequences.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your goal determines which variables you must watch most closely. Use this framework to guide your process.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness for wear resistance: Prioritize a precise austenitizing temperature and a fast, effective quench; overheating will only make the steel brittle, not harder.
- If your primary focus is toughness and impact strength: Avoid grain growth at all costs by never exceeding the recommended temperature and minimizing your soak time.
- If you suspect you've made a mistake: First diagnose the failure—is the part too brittle (likely overheated) or too soft (likely overtempered or decarburized)? This tells you which step of the recipe went wrong.
- If you are aiming for a specific balance of properties: Follow the alloy manufacturer's heat treatment data sheet exactly, as it is the "recipe" designed to achieve that balance.
Understanding these failure modes transforms heat treatment from a risk into a reliable, controllable process.
Summary Table:
| Failure Mode | Key Cause | Primary Result |
|---|---|---|
| Overheating & Grain Growth | Exceeding austenitizing temperature | Extreme brittleness, low impact strength |
| Burning | Extreme overheating near melting point | Permanent, irreversible structural damage |
| Overtempering | Too high tempering temperature or time | Excessive softness, loss of hardness |
| Decarburization | Prolonged high heat in oxygen-rich environment | Soft surface layer, poor wear resistance |
Achieve precise, repeatable heat treatment results with KINTEK's laboratory equipment.
Whether you're working on R&D, quality control, or production, our furnaces, temperature controllers, and consumables provide the accuracy and reliability needed to avoid overheating, grain growth, and decarburization.
We serve laboratories and manufacturers who demand:
- Precise Temperature Control: Eliminate the risk of overheating and burning.
- Consistent Performance: Ensure uniform results batch after batch.
- Durable Equipment: Built for the rigors of daily metal heat treating.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and let our experts help you select the right equipment for your needs.
Get a Custom Solution for Your Lab →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the leak rate for a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Purity and Repeatability
- How does argon and nitrogen cooling compare in vacuum furnaces? A Guide to Faster, Cheaper Quenching
- What is the vacuum heat treatment cycle? Achieve Superior Material Purity and Precision
- What are the advantages of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Purity and Control in Heat Treatment
- How to vacuum out a furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe DIY Maintenance



















