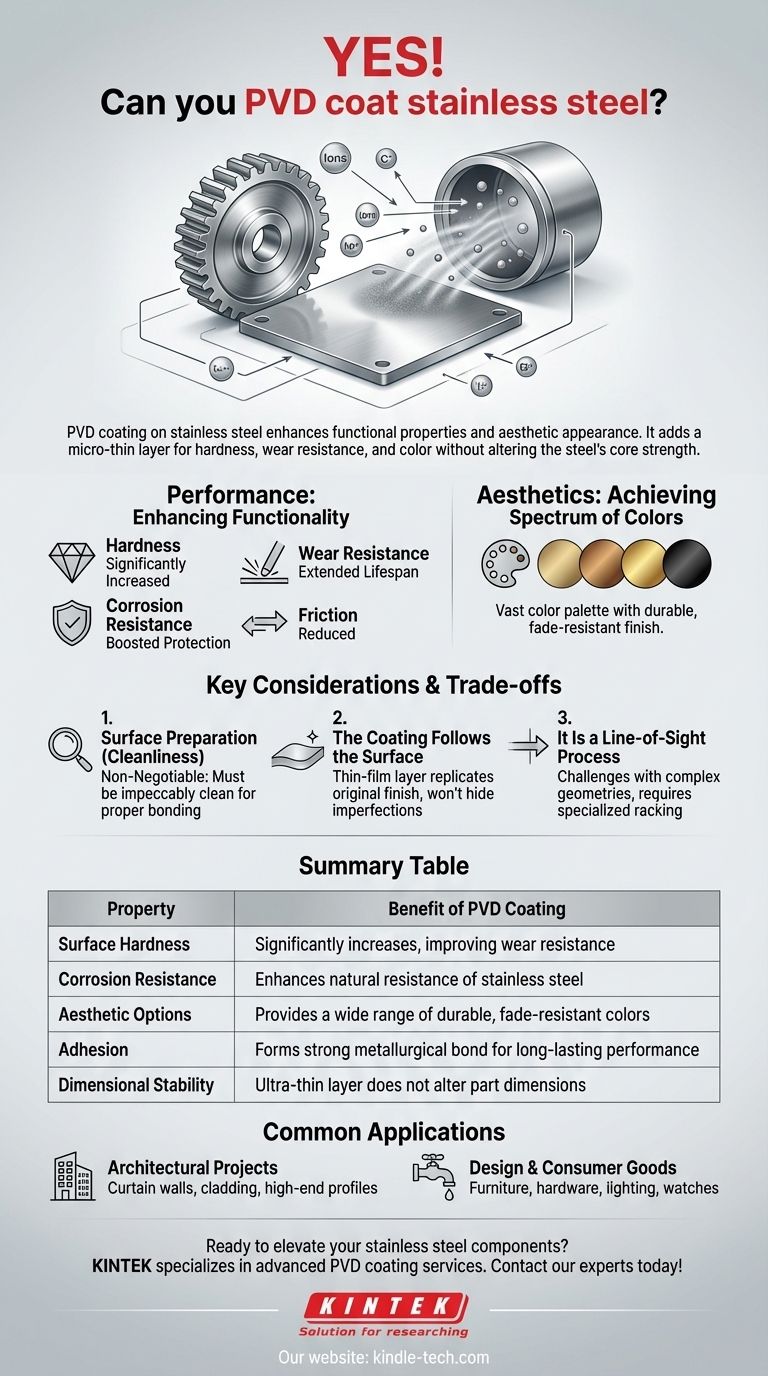
Yes, you can PVD coat stainless steel. In fact, stainless steel is an excellent substrate for Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating. The process is widely used to significantly enhance both the functional properties and the aesthetic appearance of stainless steel parts and products.
The core value of PVD coating on stainless steel is its ability to add a micro-thin layer that dramatically improves hardness, wear resistance, and appearance without altering the steel's fundamental strength and corrosion resistance.

The Synergy Between PVD and Stainless Steel
Physical Vapor Deposition is not merely a decorative layer; it forms a strong metallurgical bond with the stainless steel surface. This creates a finish that is far superior to traditional plating or painting methods.
Superior Adhesion and Finish
PVD coating provides excellent adhesion to stainless steel. This is due to the high levels of metal ionization achieved during the deposition process, which creates a very strong bond.
The coating itself is extremely thin, allowing it to perfectly replicate the original surface finish of the steel, whether it's brushed, polished, or matte.
The Critical First Step: Cleanliness
The success of the entire process hinges on surface preparation. The stainless steel part must be impeccably clean before entering the PVD chamber to ensure the coating will bond correctly.
Any surface contamination will compromise the adhesion and quality of the final coat.
Dual Benefits: Performance and Aesthetics
PVD coating is chosen for two primary reasons: to improve the physical performance of a component or to achieve a specific, durable decorative finish. Often, it's for both.
Enhancing Functional Properties
For functional parts, PVD adds an extra layer of durability. It significantly improves surface hardness, reduces friction, and boosts resistance to corrosion and abrasion.
This extends the operational lifespan of stainless steel components and can be essential for their intended function in demanding environments.
Achieving a Spectrum of Colors
PVD is a highly versatile decorative process. By precisely controlling the vaporized metals and reactive gases in the chamber, a wide range of colors can be produced.
This allows stainless steel to take on the appearance of brass, bronze, gold, black, and other custom colors, combining the strength of steel with a premium aesthetic.
Common Applications Across Industries
The combination of durability and beauty makes PVD-coated stainless steel a preferred material in numerous fields.
Architectural Projects
PVD-coated stainless steel is frequently used for high-end architectural applications. You can see it on curtain walls, exterior cladding, and profiles for hotels, casinos, and luxury retail stores.
Design and Consumer Goods
On a smaller scale, the process is ideal for products where both aesthetics and wear resistance matter. This includes furniture, display cases, lighting fixtures, door handles, and faucets.
Key Considerations and Trade-offs
While the process is highly effective, it's important to understand its operational realities to ensure a successful outcome.
Surface Preparation is Non-Negotiable
This cannot be overstated. The most common cause of PVD coating failure is inadequate cleaning of the stainless steel substrate. Any oil, residue, or oxidation will prevent proper bonding.
The Coating Follows the Surface
PVD is a thin-film coating, not a thick paint or plating. It will not hide or fill in deep scratches, dents, or other imperfections in the underlying steel. The quality of the final finish is entirely dependent on the quality of the initial surface.
It Is a Line-of-Sight Process
The vaporized material travels in a straight line inside the vacuum chamber. This means that coating complex internal geometries or deeply recessed areas can be challenging and may require specialized racking and part rotation to achieve even coverage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
To determine if PVD is the right solution, consider your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is durability: PVD offers an excellent way to increase the surface hardness and wear resistance of functional stainless steel parts, extending their service life.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics: The process provides a vast color palette and a finish that is far more durable and resistant to discoloration than other coloring methods.
- If your primary focus is a combination of both: PVD is the ideal choice for high-end products that must look pristine while withstanding daily use, such as architectural hardware, watches, or premium fixtures.
Ultimately, PVD coating empowers you to elevate the performance and appearance of stainless steel far beyond its natural state.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit of PVD Coating |
|---|---|
| Surface Hardness | Significantly increases, improving wear resistance |
| Corrosion Resistance | Enhances the natural resistance of stainless steel |
| Aesthetic Options | Provides a wide range of durable, fade-resistant colors |
| Adhesion | Forms a strong metallurgical bond for long-lasting performance |
| Dimensional Stability | Ultra-thin layer does not alter part dimensions |
Ready to elevate your stainless steel components? KINTEK specializes in advanced PVD coating services for laboratory equipment, architectural hardware, and precision components. Our coatings deliver superior durability and stunning aesthetics, ensuring your products perform flawlessly and look exceptional. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can add value to your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















