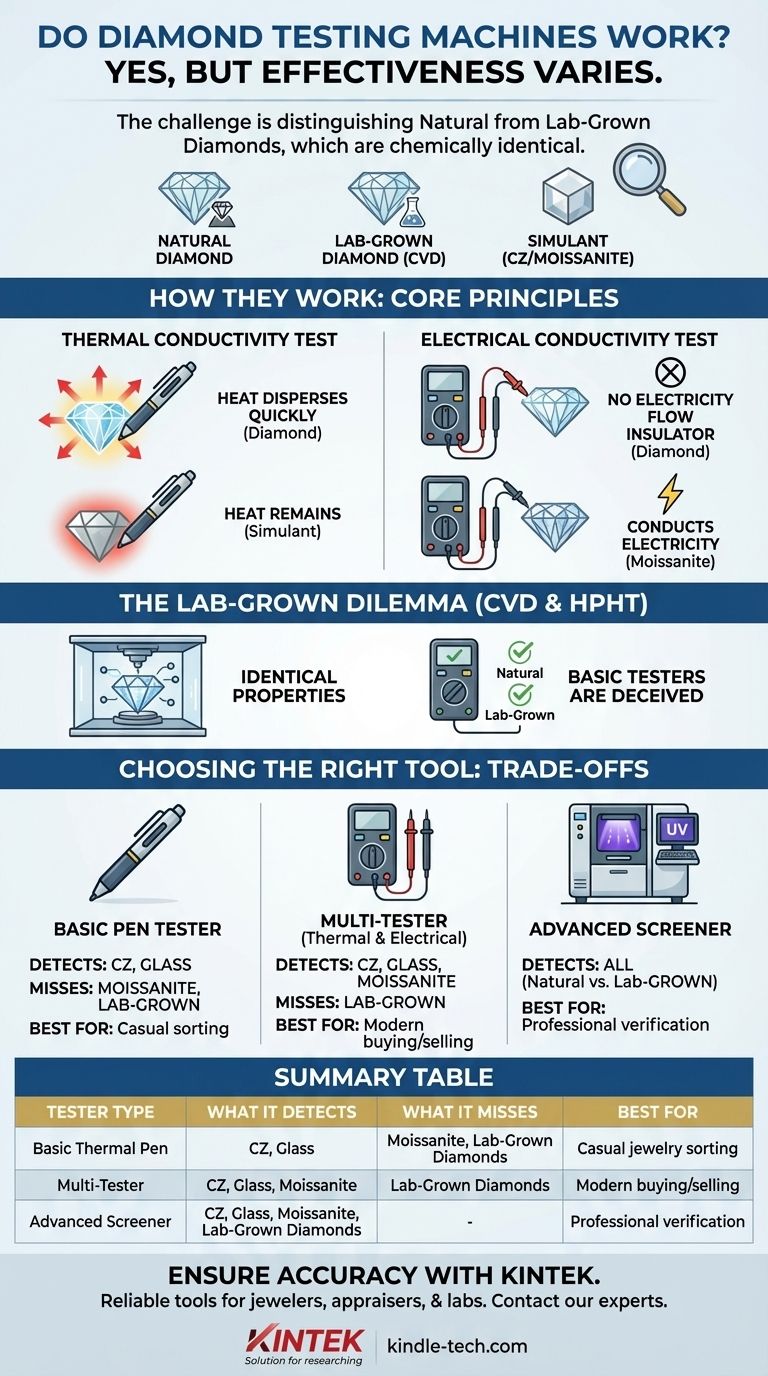
Yes, diamond testing machines absolutely work, but their effectiveness depends entirely on the type of tester and what you are trying to identify. While basic testers can easily spot simple fakes, they are often fooled by more sophisticated synthetics, requiring advanced tools to get a definitive answer.
The central challenge is no longer just distinguishing diamonds from fakes like cubic zirconia, but differentiating natural diamonds from lab-grown diamonds, which are physically and chemically identical. Your choice of tester must match the sophistication of the potential counterfeit.

How Diamond Testers Work: The Core Principles
Diamond testers operate by measuring specific physical properties that are unique to diamonds. The two most common methods are testing for thermal and electrical conductivity.
The Thermal Conductivity Test
A diamond is an exceptional thermal conductor, meaning it disperses heat incredibly quickly. Basic diamond "pen" testers have a small, heated metal tip. When this tip touches a real diamond, the heat is rapidly pulled away, and the device signals "diamond."
Most common simulants, like cubic zirconia (CZ) or glass, are thermal insulators. They do not conduct heat well, so when the tester's tip touches them, the heat remains, and the device indicates it is not a diamond.
The Electrical Conductivity Test
Most diamonds are electrical insulators (dielectrics), meaning they do not conduct electricity. However, a very popular and convincing diamond simulant, moissanite, is an electrical conductor.
This difference allows more advanced "multi-testers" to distinguish between a diamond and moissanite. After a positive thermal test, the device will also check electrical conductivity. If it detects conductivity, it will identify the stone as moissanite.
The Challenge of Lab-Grown Diamonds
The game has changed with the rise of high-quality, lab-grown diamonds. These are not fakes or simulants; they are real diamonds, simply created in a laboratory instead of deep within the Earth.
What is a CVD Diamond?
A CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) diamond is grown in a lab using a process that "builds" the diamond's crystal structure atom by atom. The result is a stone with the exact same chemical composition and physical properties as a natural, mined diamond.
Why Basic Testers Are Deceived
Because a lab-grown diamond is physically a diamond, it has the same exceptional thermal conductivity as a natural one. A basic thermal tester will heat the stone, see the heat dissipate rapidly, and correctly identify it as "diamond."
The tester cannot, however, tell you if that diamond came from the earth or from a lab. For most buyers and sellers, this distinction is critical for valuation.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Choosing the Right Tool
Not all testers are created equal. The tool you need depends on the certainty you require.
The Basic Pen Tester: Strengths and Limitations
These devices only test for thermal conductivity. They are affordable and effective at weeding out obvious fakes like glass and CZ. However, they will be fooled by both moissanite and lab-grown diamonds, reading both as "diamond."
The Multi-Tester: A Necessary Upgrade
A multi-tester combines both thermal and electrical conductivity tests. This is the minimum standard for anyone buying or selling gems today, as it reliably separates diamond from the very common simulant, moissanite. It still cannot distinguish a natural diamond from a lab-grown one.
Advanced Screeners: The Professional Standard
To differentiate between natural and lab-grown diamonds, you need a professional-grade screening device. These tools use more advanced methods, such as observing the stone's reaction to shortwave UV light, to identify the subtle differences in growth structure between natural and synthetic diamonds (both CVD and HPHT). These devices are significantly more expensive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the "best" tester is the one that aligns with your specific needs and risk tolerance.
- If your primary focus is sorting casual jewelry or heirlooms: A basic thermal tester is often sufficient to identify obvious non-diamond pieces.
- If your primary focus is buying or selling in a modern market: A multi-tester that detects moissanite is the absolute minimum requirement to avoid costly mistakes.
- If your primary focus is verifying the origin of a high-value diamond: The only definitive options are a professional-grade screening device or, more practically, submitting the stone to a reputable gemological laboratory (like GIA or IGI) for a full grading report.
Choosing the right tool is about matching your level of investment to the level of certainty you require.
Summary Table:
| Tester Type | What It Detects | What It Misses | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Thermal Pen | Cubic Zirconia, Glass | Moissanite, Lab-Grown Diamonds | Casual jewelry sorting |
| Multi-Tester (Thermal & Electrical) | CZ, Glass, Moissanite | Lab-Grown Diamonds | Modern buying/selling |
| Advanced Screener | CZ, Glass, Moissanite, Lab-Grown Diamonds | - | Professional verification |
Ensure the accuracy and value of your gemological work with the right equipment from KINTEK.
Whether you are a jeweler, appraiser, or lab professional, having reliable testing tools is essential in today's market. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to meet the precise needs of the gemological and laboratory industries.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements. We can help you select the perfect diamond testing solution to protect your investments and build trust with your clients.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What are the factors affecting sieving performance and efficiency? Optimize Your Particle Separation Process
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification
- What is the function of sieving equipment in CuAlMn alloys? Master Pore Size Precision
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide



















