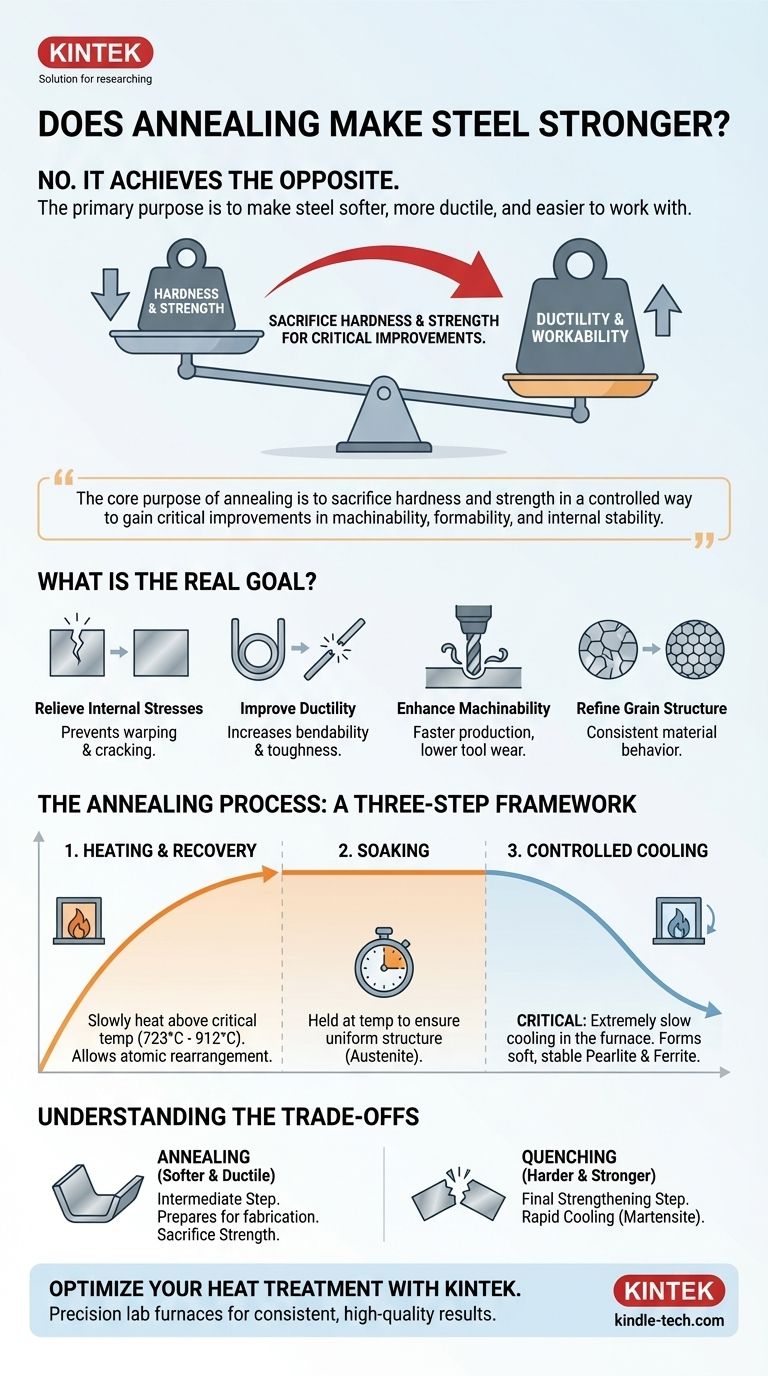
Contrary to a common misconception, annealing does not make steel stronger. In fact, it achieves the opposite. The primary purpose of annealing is to make steel softer, more ductile, and easier to work with by relieving internal stresses and refining its grain structure. It is a preparatory process, not a strengthening one.
The core purpose of annealing is to sacrifice hardness and strength in a controlled way. This trade-off is made to gain critical improvements in machinability, formability, and internal stability, preparing the steel for subsequent manufacturing steps.

What is the Real Goal of Annealing?
Understanding annealing requires a shift in perspective. Instead of viewing it as a strengthening process, see it as a "reset" button that makes the material more cooperative for fabrication.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Processes like welding, casting, heavy machining, or cold working (like bending) create significant stress within the steel's crystal structure. These stresses can lead to warping, cracking, or premature failure. Annealing heats the metal enough to allow its atoms to rearrange into a more stable, stress-free state.
Improving Ductility and Toughness
Ductility is a material's ability to be stretched or bent without breaking. Annealing significantly increases ductility, which is essential for manufacturing processes like deep drawing (forming a cup shape) or wire drawing. This makes the steel tougher and less brittle.
Enhancing Machinability
Hard, strong steel is difficult to cut, drill, or shape. This resistance causes rapid wear on cutting tools and requires more energy. By making the steel softer, annealing dramatically improves its machinability, leading to faster production, lower costs, and a better surface finish.
Refining the Grain Structure
On a microscopic level, steel is made of crystalline grains. The size and uniformity of these grains dictate its properties. Annealing produces a more uniform and refined grain structure, which results in more predictable and consistent mechanical behavior throughout the workpiece.
The Annealing Process: A Three-Step Framework
The defining characteristic of annealing is its extremely slow and controlled cooling rate. This is what allows the desired soft and stable microstructure to form.
Step 1: Heating and Recovery
The steel is slowly and uniformly heated to a specific temperature, typically above its upper critical temperature (around 723°C to 912°C, depending on the carbon content). This provides the thermal energy needed for the atomic structure to change.
Step 2: Soaking
The steel is held at this high temperature for a predetermined amount of time. This "soaking" period ensures that the entire volume of the material reaches a consistent temperature and completes its structural transformation into a phase called austenite.
Step 3: Controlled Cooling
This is the most critical step. The steel is cooled down very slowly, often by simply turning off the furnace and allowing it to cool with the furnace itself over many hours or even days. This slow cooling rate allows the grains to form into a soft, coarse structure known as pearlite and ferrite.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Strength vs. Workability
In metallurgy, you rarely get something for nothing. Annealing is a perfect example of making a deliberate trade-off to achieve a specific manufacturing goal.
The Inverse Relationship
For most common heat treatments, hardness and strength are inversely related to ductility and toughness. When you increase one, you typically decrease the other. Annealing pushes the material to the soft and ductile end of the spectrum.
Why You Sacrifice Strength
Annealing is almost always an intermediate step. You temporarily sacrifice strength to make the steel easy to machine or form. Once the part is in its final shape, it can then undergo a different heat treatment, like hardening and tempering, to achieve the desired high strength for its final application.
Where Annealing Differs from Strengthening
The process that does make steel significantly stronger and harder is quenching. This involves heating the steel similarly to annealing but then cooling it extremely rapidly by plunging it into water, oil, or air. This rapid cooling traps the atoms in a hard, brittle structure called martensite, which is the opposite of the soft structure formed during annealing's slow cool.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heat treatment depends entirely on what you need to accomplish with the material at that specific stage of production.
- If your primary focus is maximum machinability and formability: Full annealing is the correct choice to achieve the softest, most ductile state possible before extensive cutting or shaping.
- If your primary focus is preparing steel for subsequent hardening: Annealing is a critical preliminary step to remove internal stresses and create a uniform grain structure, ensuring a more predictable outcome from the final quench and temper.
- If your primary focus is a high-strength final product: Annealing is the opposite of what you need for the final step. Your process should end with a hardening (quenching) and tempering cycle.
- If your primary focus is simply relieving stress from welding or cold work: A lower-temperature "stress-relief anneal" may be sufficient, which can remove internal stresses without significantly reducing the material's overall strength.
Ultimately, understanding that annealing is a strategic tool for workability, not final strength, is the key to mastering steel heat treatment.
Summary Table:
| Goal of Annealing | Effect on Steel | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Relieve Internal Stresses | Reduces risk of warping/cracking | Improves stability for fabrication |
| Increase Ductility | Makes steel easier to bend/form | Enhances toughness and workability |
| Improve Machinability | Softens steel for easier cutting | Lowers production costs and tool wear |
| Refine Grain Structure | Creates uniform microstructure | Ensures consistent material behavior |
Optimize Your Steel Heat Treatment Process with KINTEK
Understanding the precise role of annealing is crucial for efficient manufacturing. Whether you need to improve machinability, relieve stresses from welding, or prepare material for final hardening, having the right laboratory equipment is key to achieving consistent, high-quality results.
KINTEK specializes in precision lab furnaces and consumables that provide the exact temperature control required for reliable annealing cycles. Our solutions help metallurgy labs, R&D departments, and quality control teams ensure their materials are perfectly prepared for every stage of production.
Ready to enhance your heat treatment capabilities? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's equipment can support your specific annealing and material testing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Can you braze with natural gas? Unlock the Secrets to High-Temperature Brazing Success
- Why does copper-based porous foil as an interlayer in vacuum diffusion welding result in base-metal strength joints?
- What is the function of high vacuum furnaces for Inconel 718? Achieve Peak Superalloy Strength via Micro-Engineering
- How does a vacuum heater work? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the traditional sintering process? A Guide to Powder Metallurgy & Ceramic Fabrication
- What gas can be used for brazing? Select the Right Atmosphere for Metallurgical Success
- What material is used for melting furnace? It's a System of Specialized Components
- In what ways can you detect leaks in vacuum system? Master Leak Detection for Optimal Performance



















