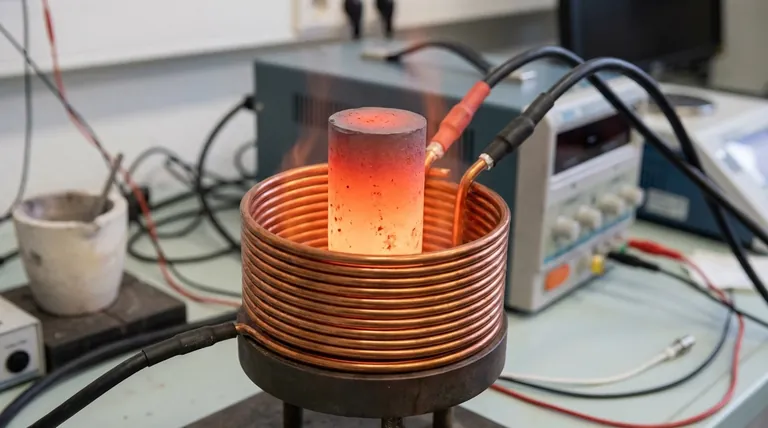
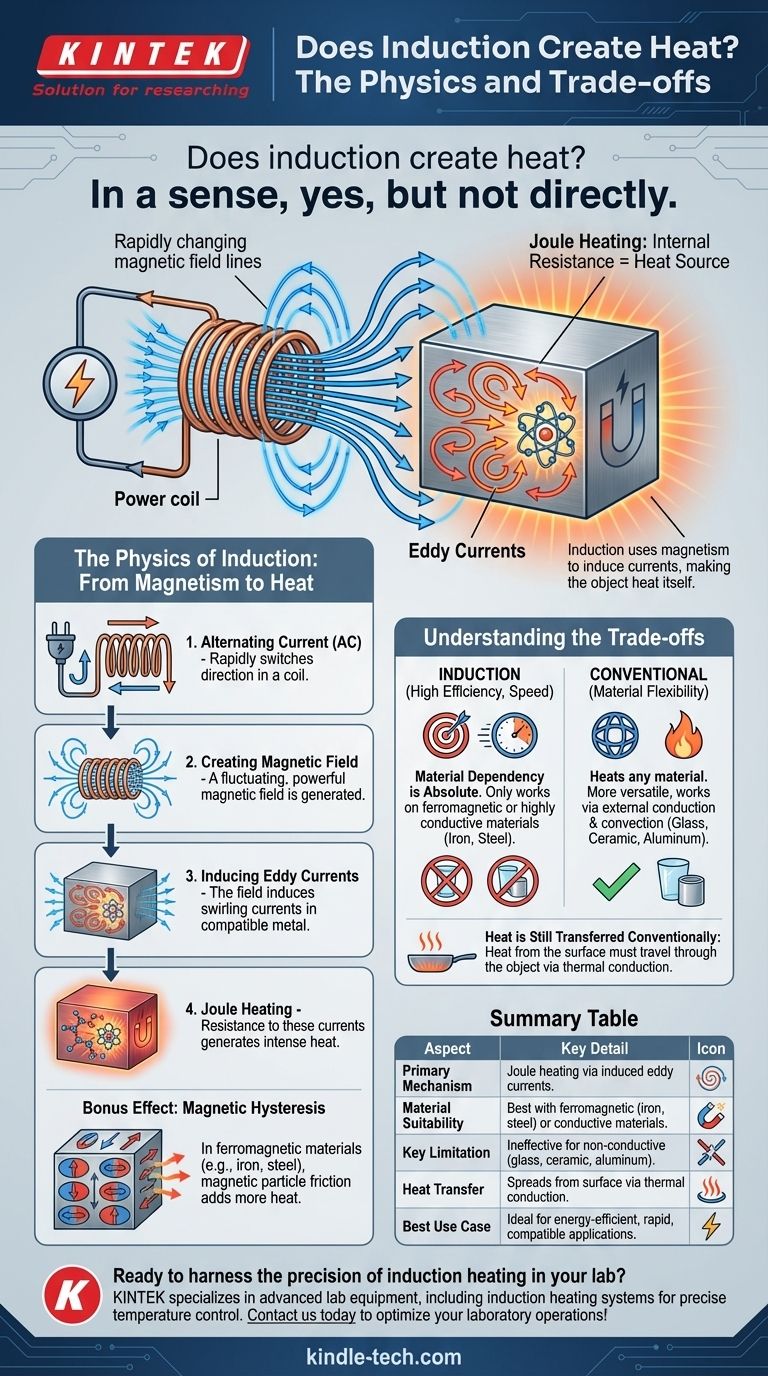
In a sense, yes, but not directly. Induction itself does not create heat. Instead, it is a process that uses a rapidly changing magnetic field to cause electrical currents to flow within a metal object. It is the resistance to these currents inside the object that generates the heat, effectively turning the object into its own heat source.
Induction is not a heat source; it is a mechanism. It uses magnetism to efficiently generate heat directly inside a compatible material, bypassing the need to heat it from an external source like a flame or a hot coil.

The Physics of Induction: From Magnetism to Heat
To understand induction, you must visualize a chain reaction. It’s not a single event but a sequence of physical principles working together with remarkable efficiency.
The Role of the Alternating Current
It all begins with a powerful alternating current (AC) flowing through a coil, typically made of copper wire. The key is "alternating," meaning the electricity rapidly switches direction.
Creating the Magnetic Field
This rapidly reversing flow of electricity in the coil generates a dynamic and powerful magnetic field around it. This field expands and collapses, and reverses its polarity, many thousands of times per second.
Inducing Eddy Currents
When a suitable material (like an iron pan) is placed within this magnetic field, the field penetrates the metal. This powerful, fluctuating field induces small, swirling electrical currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
Joule Heating: The Source of Heat
The metal has natural electrical resistance. As the induced eddy currents flow against this resistance, friction is created at a molecular level. This friction generates intense heat. This phenomenon is called Joule heating or resistive heating.
The Bonus Effect: Magnetic Hysteresis
In ferromagnetic materials like cast iron and many types of stainless steel, there is a secondary source of heat. The material's magnetic particles physically resist the rapid back-and-forth switching of the magnetic field. This internal friction, called magnetic hysteresis, also generates significant heat, adding to the overall efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly efficient, induction heating is not a universal solution. Its unique mechanism comes with specific limitations that are critical to understand.
Material Dependency is Absolute
This is the most significant trade-off. The process relies entirely on inducing currents within the target material. Therefore, induction only works on materials that are either ferromagnetic (like iron) or highly conductive.
Glass, ceramic, aluminum, and copper cookware will not heat up on a standard induction cooktop because the magnetic field cannot efficiently induce the necessary currents within them.
Heat is Still Transferred Conventionally
While heat is generated in the surface of the metal, it must still travel to the rest of the object (or its contents, like food in a pan) via thermal conduction. This is the same way heat spreads through the bottom of a pan on a gas stove.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the mechanism helps you decide when and why to use induction over other methods.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and speed: Induction is superior because it generates heat directly where it's needed, minimizing the energy wasted on heating the surrounding air or cooktop surface.
- If your primary focus is material flexibility: Conventional heating (gas, radiant electric) is more versatile, as it can heat any material through external conduction and convection without relying on magnetic properties.
By mastering the flow of energy, induction transforms the object being heated from a passive recipient into an active part of the heating process itself.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Mechanism | Generates heat via electrical resistance to induced eddy currents (Joule heating). |
| Material Suitability | Works best with ferromagnetic or highly conductive materials (e.g., iron, steel). |
| Key Limitation | Ineffective for non-conductive materials like glass, ceramic, or aluminum. |
| Heat Transfer | Heat spreads from the object's surface via thermal conduction. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for energy-efficient, rapid heating applications where material compatibility exists. |
Ready to harness the precision of induction heating in your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including induction heating systems, designed for efficiency and reliability. Whether you need precise temperature control for materials testing or efficient heating solutions for your processes, our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for your needs. Contact us today to learn how KINTEK can optimize your laboratory operations with tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- High Performance Laboratory Stirrers for Diverse Applications
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the specifications of the Platinum-Titanium Functional Electrode? Maximize Electrochemical Performance
- What is the most critical guideline for immersing a platinum sheet electrode in an electrolyte? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- What is the expected lifespan of a platinum sheet electrode? Maximize Your Electrode's Service Life
- What is the proper post-treatment procedure for a platinum sheet electrode? Ensure Long-Term Accuracy & Protect Your Investment
- What precautions should be taken when using a platinum sheet electrode? Ensure Accurate & Reproducible Electrochemical Data


















