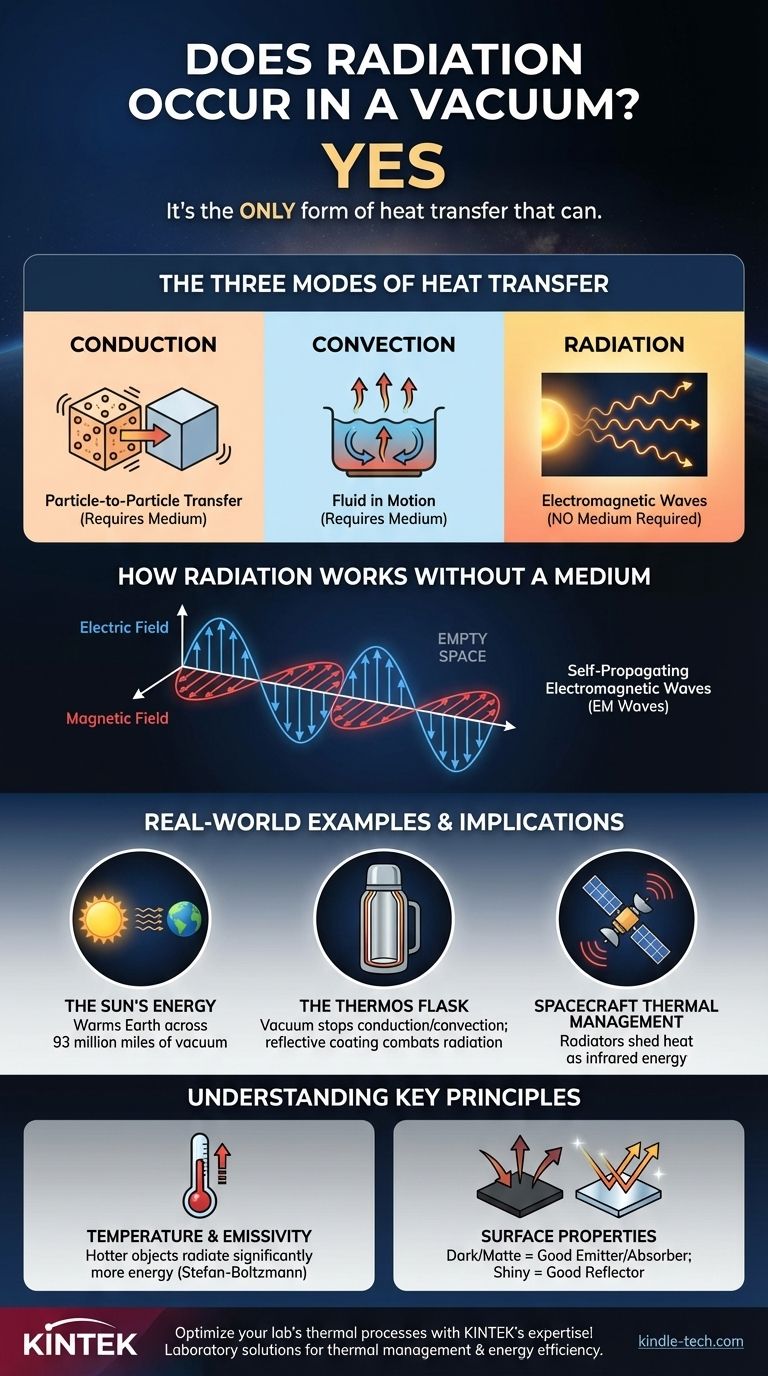
Yes, radiation not only occurs in a vacuum, but it is the only form of heat transfer that can. Unlike conduction or convection, which require a medium of particles to transfer energy, radiation travels as electromagnetic waves. These waves can propagate through the complete emptiness of space, which is precisely how the sun’s energy reaches Earth.
While conduction and convection depend on the interaction and movement of matter, radiation is fundamentally different. It is the transfer of energy via self-propagating electromagnetic waves that require no medium, making the vacuum of space their ideal environment for travel.

The Three Modes of Heat Transfer
To understand why radiation is unique, it's helpful to compare it to the other two forms of heat transfer.
Conduction: The Particle-to-Particle Transfer
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact. When you touch a hot stove, heat is transferred from the burner to your hand through the vibration of particles. This process requires a medium—be it solid, liquid, or gas—and cannot happen across a vacuum.
Convection: The Fluid in Motion
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids (liquids or gases). As a fluid is heated, it becomes less dense and rises, carrying thermal energy with it. Cooler, denser fluid then moves in to take its place, creating a convection current. This is how a furnace heats a room or water boils in a pot. It fundamentally requires a fluid medium.
Radiation: The Exception to the Rule
Radiation is the transfer of energy via electromagnetic waves. It does not require any particles or a medium. This makes it entirely distinct from conduction and convection and allows it to be the sole method of heat transfer in a vacuum.
How Radiation Works Without a Medium
The idea of energy moving through nothingness can feel counterintuitive. The mechanism lies in the nature of electromagnetic waves themselves.
The Nature of Electromagnetic Waves
All objects with a temperature above absolute zero (-273.15°C or 0 Kelvin) emit thermal radiation. This energy is released in the form of electromagnetic (EM) waves, which include everything from radio waves and microwaves to infrared, visible light, and X-rays.
A Self-Propagating System
An EM wave consists of an oscillating electric field and an oscillating magnetic field. These two fields are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of the wave's travel. Crucially, a changing electric field generates a magnetic field, and a changing magnetic field generates an electric field.
This interplay creates a self-sustaining wave that can travel indefinitely through a vacuum, carrying energy with it until it is absorbed by another object.
Real-World Examples and Implications
Understanding radiation in a vacuum isn't just a theoretical exercise; it has critical real-world applications.
The Sun's Energy
The most powerful example is our own sun. It continuously radiates an immense amount of energy into space. This energy travels approximately 93 million miles (150 million kilometers) across the vacuum of space to warm our planet, drive our weather, and enable life.
The Thermos Flask
A vacuum flask (or thermos) is a perfect everyday example. It has an inner chamber and an outer casing separated by a vacuum. This vacuum layer effectively stops heat transfer by both conduction and convection. To combat radiation, the inner chamber is coated with a reflective layer (like silver) to reflect thermal radiation back, keeping hot liquids hot and cold liquids cold.
Spacecraft Thermal Management
Engineers must account for radiation when designing spacecraft and satellites. Since space is a near-perfect vacuum, a spacecraft can only shed the heat generated by its electronics by radiating it away as infrared energy. Large panels called radiators, often with specialized coatings, are designed specifically for this purpose.
Understanding Key Principles and Trade-offs
Simply knowing that radiation occurs in a vacuum isn't enough. Its behavior is governed by specific principles.
Temperature Is a Decisive Factor
The amount of energy an object radiates is strongly dependent on its temperature. According to the Stefan-Boltzmann law, the total energy radiated is proportional to the fourth power of its absolute temperature. In simple terms, a slightly hotter object radiates significantly more energy than a cooler one.
Surface Properties Matter
An object's surface has a huge impact on how well it radiates and absorbs energy. A dark, matte surface is both a good emitter and a good absorber of radiation. Conversely, a light-colored, shiny surface is a poor emitter and a poor absorber (it is a good reflector). This is why emergency space blankets are shiny—to reflect thermal radiation and prevent heat loss.
Not All Radiation Is "Heat"
While we often associate radiation with heat (infrared radiation), it's important to remember that this is just one part of the broad electromagnetic spectrum. Visible light, radio waves, and microwaves are all forms of radiation that travel perfectly through a vacuum, each carrying energy.
Applying This Understanding
Understanding how radiation behaves is key to solving problems in fields ranging from astrophysics to materials science.
- If your primary focus is engineering or product design: Remember that in a vacuum, radiation is your only method for heat transfer, and surface properties (emissivity and reflectivity) are your primary means of control.
- If your primary focus is physics or astronomy: Recognize that electromagnetic radiation is your primary source of information about the universe, carrying data about distant stars and galaxies across the vast vacuum of space.
- If your primary focus is everyday understanding: Know that the warmth you feel from the sun on your skin is a direct result of radiation traveling through a vacuum, a process fundamentally different from touching a hot pan (conduction) or feeling warm air from a vent (convection).
By mastering the principles of radiation, you move from simply knowing that energy can travel through a vacuum to understanding how to control and utilize it.
Summary Table:
| Heat Transfer Method | Medium Required? | Key Mechanism | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radiation | No | Electromagnetic waves | Sun warming Earth, vacuum furnace operation |
| Conduction | Yes (solid, liquid, gas) | Direct particle contact | Touching a hot stove |
| Convection | Yes (fluid) | Movement of heated fluid | Boiling water, room heating |
Optimize your lab's thermal processes with KINTEK's expertise!
Whether you're working with vacuum furnaces, high-temperature materials testing, or specialized lab equipment, understanding radiation heat transfer is critical for achieving precise results. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with reliable solutions for thermal management and energy efficiency.
Let us help you:
- Select equipment with optimal emissivity and reflectivity coatings
- Design systems for effective heat transfer in vacuum environments
- Improve the accuracy and repeatability of your thermal processes
Contact our thermal engineering experts today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Control, Cleanliness, and Quality
- What are the advantages of vacuum hardening? Achieve Superior Precision and Cleanliness for Critical Components
- What is a vacuum furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- How does a vacuum heat treatment work? Achieve Superior Material Properties in a Pristine Environment
- What are the advantages of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Purity and Control in Heat Treatment



















