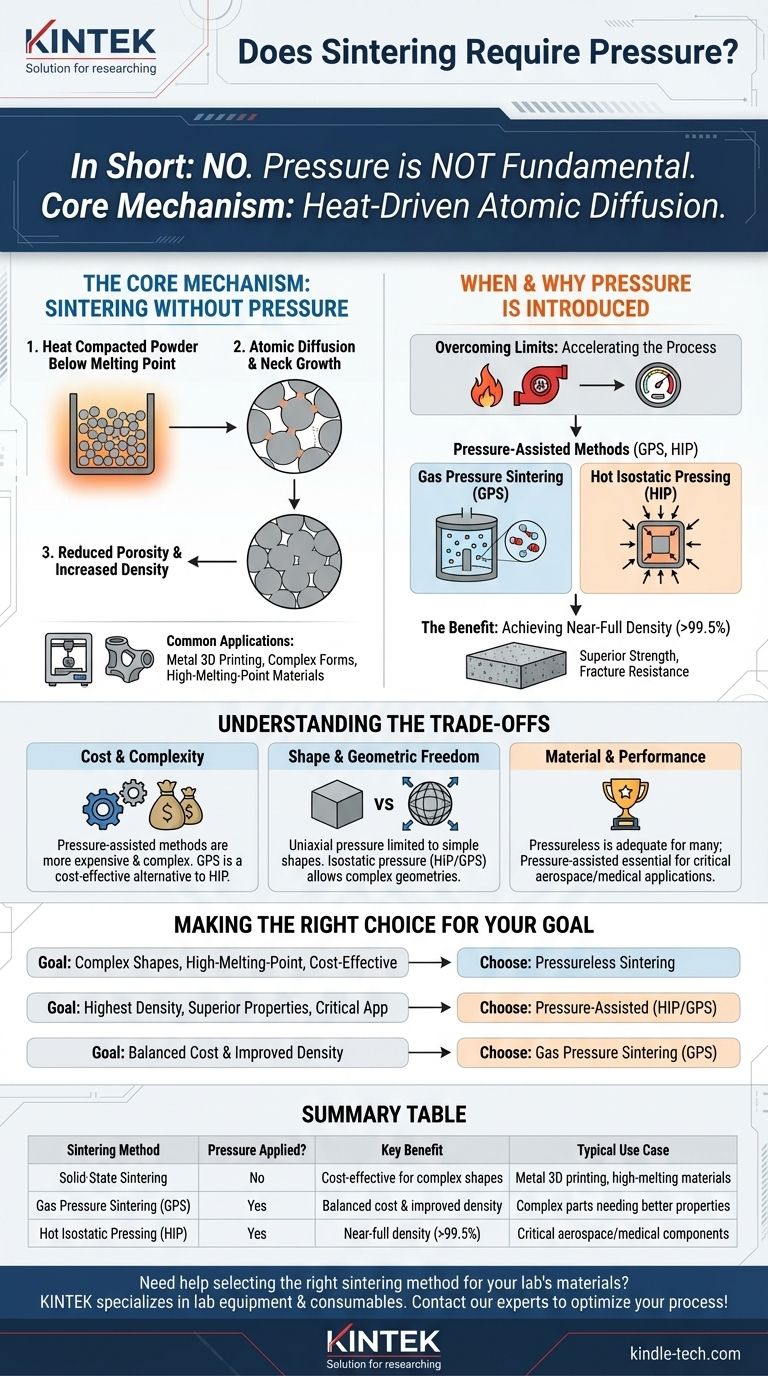
In short, no—pressure is not a fundamental requirement for every sintering process. The core mechanism of sintering relies on heat to bond particles together below their melting point. However, adding pressure is a common and powerful technique used in specific methods to achieve higher density and superior material properties.
Sintering is fundamentally a thermal process where heat drives atomic diffusion to fuse particles. Think of heat as the engine that makes sintering possible, while pressure acts as a turbocharger—it is not always required, but it is added to significantly accelerate the process and enhance the final outcome.

The Core Mechanism: Sintering Without Pressure
Heat-Driven Atomic Diffusion
At its most basic level, sintering works by heating a compacted powder to a high temperature, but one that remains below the material's melting point.
At this elevated temperature, the atoms at the contact points of individual particles become highly mobile. They begin to diffuse across the boundaries, forming and growing solid "necks" between particles that fuse them into a single, coherent mass.
The Goal of Reducing Porosity
This process of atomic migration naturally fills the voids (or pores) that exist between the loose particles.
As the necks grow and the particles pull closer together, the overall porosity of the object decreases, and its density and mechanical strength increase. This is a primary goal of sintering.
Common Applications
This pressureless method, often called solid-state sintering, is widely used. It's common in applications like metal 3D printing to create complex custom forms and for materials with extremely high melting points where melting is impractical.
When and Why Pressure Is Introduced
Overcoming the Limits of Heat Alone
While effective, relying on heat alone can be a slow process. It may also leave behind residual porosity, preventing the part from reaching its full theoretical density and optimal strength.
To overcome these limitations, pressure can be applied simultaneously with heat.
Pressure-Assisted Sintering Methods
Methods like Gas Pressure Sintering (GPS) and Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) use external pressure to physically force the particles into closer contact.
This applied force dramatically accelerates the diffusion process and is much more effective at collapsing and eliminating the internal pores within the material.
The Benefit: Achieving Near-Full Density
The combination of high heat and high pressure allows manufacturers to create parts that are almost completely dense (often >99.5%). These parts exhibit significantly improved mechanical properties, such as strength and fracture resistance, compared to their pressureless-sintered counterparts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Cost and Complexity
The primary trade-off is cost. Equipment for pressure-assisted sintering, especially Hot Isostatic Pressing, is significantly more expensive and complex to operate than a standard furnace used for pressureless sintering.
As the references note, GPS can be a more cost-effective alternative to the more demanding HIP process for certain applications.
Shape and Geometric Freedom
Some pressure-assisted techniques can have limitations. For example, uniaxial hot pressing (applying pressure from one direction) is limited to simple shapes.
However, methods like GPS and HIP, which apply pressure uniformly from all directions (isostatically), have virtually no shape limitations and are excellent for complex geometries.
Material and Performance Requirements
The choice always comes down to the end-use requirements. For many components, the properties achieved via pressureless sintering are perfectly adequate. For high-performance, critical applications in aerospace or medical implants, the superior density from pressure-assisted sintering is non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the decision to use pressure depends entirely on the desired outcome for your part.
- If your primary focus is creating complex shapes or working with high-melting-point metals without needing maximum performance: Pressureless sintering is often the most direct and cost-effective path.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible density and superior mechanical properties for a critical application: A pressure-assisted method like HIP or GPS is the necessary choice.
- If your primary focus is balancing cost with improved density for complex parts: Gas Pressure Sintering (GPS) presents a strong middle-ground solution.
Understanding this distinction between heat-driven fusion and pressure-assisted densification allows you to select the precise manufacturing path for your specific material and performance goals.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Method | Pressure Applied? | Key Benefit | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid-State Sintering | No | Cost-effective for complex shapes | Metal 3D printing, high-melting-point materials |
| Gas Pressure Sintering (GPS) | Yes | Balanced cost & improved density | Complex parts needing better properties |
| Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) | Yes | Near-full density (>99.5%) | Critical aerospace/medical components |
Need help selecting the right sintering method for your lab's materials? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering solutions that balance cost, complexity, and performance—whether you require pressure-assisted sintering for maximum density or standard furnaces for complex shapes. Contact our experts today to optimize your sintering process and achieve your material goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the pressure for vacuum sintering? Achieve Optimal Material Purity and Density
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Superior Density for Nanocrystalline Fe3Al
- What is the primary function of a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Expert Guide for Ti-22Al-25Nb Fabrication
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics



















