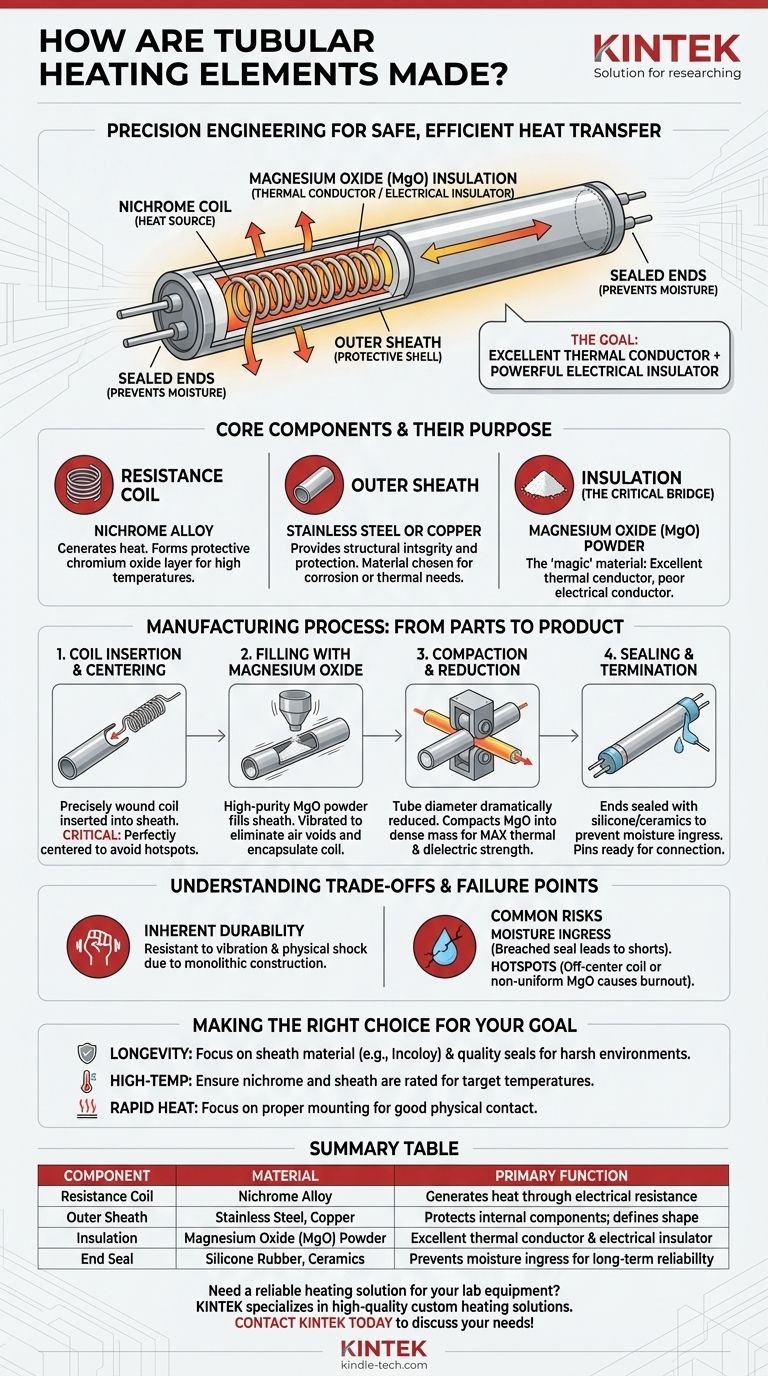
The construction of a tubular heating element is a precise engineering process designed to safely encase a live electrical coil while maximizing its ability to transfer heat. At its core, a nichrome resistance wire coil is positioned inside a metal tube, which is then filled with magnesium oxide powder. The entire assembly is then mechanically compacted to densify the powder, ensuring excellent thermal conductivity and dielectric strength before the ends are sealed.
The entire manufacturing process is engineered to solve a fundamental challenge: creating an element that is an excellent thermal conductor but also a powerful electrical insulator. This dual characteristic is what makes the tubular element so safe, durable, and widely used.

The Core Components and Their Purpose
To understand how a tubular element is made, we must first understand the function of each raw material. Each component is chosen for its specific properties.
The Resistance Coil (The Heat Source)
The heart of the element is a coil of nichrome (nickel-chromium) alloy wire. This material is the industry standard for resistance heating.
Its primary advantage is that it forms a protective layer of chromium oxide when heated, which prevents further oxidation. This allows it to operate at very high temperatures for long periods without degrading.
The Outer Sheath (The Protective Shell)
The outer tube, or sheath, provides structural integrity and protection from the operating environment.
Common materials include stainless steel alloys, chosen for their strength and corrosion resistance, or copper, used in applications like water heating where its thermal conductivity is an advantage.
The Insulation (The Critical Bridge)
The "magic" of the tubular element lies in the insulating material: magnesium oxide (MgO) powder.
MgO is the unsung hero of the design. It is one of the few materials that is an excellent thermal conductor (letting heat escape) but a very poor electrical conductor (preventing short circuits).
The Manufacturing Process: From Parts to Product
The assembly process methodically combines these components into a solid, robust unit. The key step is compaction, which fundamentally changes the properties of the powder-filled tube.
Step 1: Coil Insertion and Centering
A precisely wound nichrome coil, with terminal pins attached, is carefully inserted into the outer metal sheath.
It is critical that the coil remains perfectly centered within the tube. Any deviation can lead to "hotspots" where the coil is too close to the sheath, causing premature failure.
Step 2: Filling with Magnesium Oxide
The sheath is then filled with high-purity MgO powder. This is often done on a vertical filling machine that vibrates to ensure the powder flows evenly and settles around the coil.
The goal is to eliminate air voids and ensure the coil is completely encapsulated by the insulating powder.
Step 3: Compaction and Reduction
This is the most critical manufacturing step. The entire filled tube is passed through a rolling mill or a swaging machine.
This process dramatically reduces the diameter of the tube, compacting the MgO powder into a dense, solid mass. This compaction is vital for two reasons:
- It maximizes thermal conductivity by forcing the MgO grains into tight contact.
- It maximizes dielectric strength, ensuring the element can withstand high voltages without electrical arcing.
Step 4: Sealing and Termination
The ends of the element must be sealed to prevent moisture from being absorbed by the hygroscopic MgO. Contamination by moisture would ruin its insulating properties.
Materials like silicone rubber or ceramics are used to create a moisture-proof seal. Finally, the terminal pins are ready for electrical connection.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Failure Points
The design of a tubular element is exceptionally robust, but understanding its potential failure points is key to proper application and diagnosis.
Inherent Durability
The compacted, monolithic construction makes tubular elements highly resistant to vibration and physical shock, which is why they are used in everything from industrial equipment to household appliances.
The Enemy: Moisture Ingress
The most common cause of failure is a breached end seal. If moisture penetrates the element, it is absorbed by the MgO, creating a path for electrical current to short to the outer sheath.
The Risk of Hotspots
If the element is not manufactured with a perfectly centered coil or uniform MgO density, hotspots can develop. These localized areas of extreme temperature will cause the resistance wire to burn out, breaking the electrical circuit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this construction process allows you to better select and diagnose heating elements for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is longevity in harsh environments: Pay close attention to the sheath material (e.g., stainless steel or Incoloy alloys for corrosion resistance) and the quality of the end seals.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance: Ensure the nichrome alloy and the sheath material are rated for your target temperatures, as this is determined during initial component selection.
- If your primary focus is rapid and efficient heat transfer: Recognize that the compacted MgO is already optimized for this, so your focus should be on ensuring the element is properly mounted for good physical contact with whatever you are heating.
Ultimately, this meticulous manufacturing process is what transforms a few simple materials into the reliable and ubiquitous heating elements that power countless applications.
Summary Table:
| Component | Material | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance Coil | Nichrome Alloy | Generates heat through electrical resistance |
| Outer Sheath | Stainless Steel, Copper | Protects internal components; defines shape |
| Insulation | Magnesium Oxide (MgO) Powder | Excellent thermal conductor & electrical insulator |
| End Seal | Silicone Rubber, Ceramics | Prevents moisture ingress for long-term reliability |
Need a reliable heating solution for your lab equipment?
The meticulous manufacturing process described is key to creating durable, efficient, and safe heating elements. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including custom heating solutions built with these precise engineering principles.
Let our experts help you select or design the perfect heating element for your specific application, ensuring optimal performance, longevity, and safety. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory's heating needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Which is a disadvantage of electric resistance heating systems? High Operating Costs Explained
- What is the electrical resistivity of molybdenum disilicide? Unlocking its High-Temperature Heating Power
- What is a graphite heater? Achieve Superior Temperature Uniformity and Stability
- How do you control the temperature of a resistance? Master Voltage, Resistance, and PWM Methods
- Is graphite good heating element? Discover Its Superior Performance in High-Temperature Vacuum Furnaces
- Which high temperature furnace elements to be used in oxidizing atmosphere? MoSi2 or SiC for Superior Performance
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process
- What are heating elements with tungsten? Unlock Extreme Heat for Vacuum & Industrial Processes

















