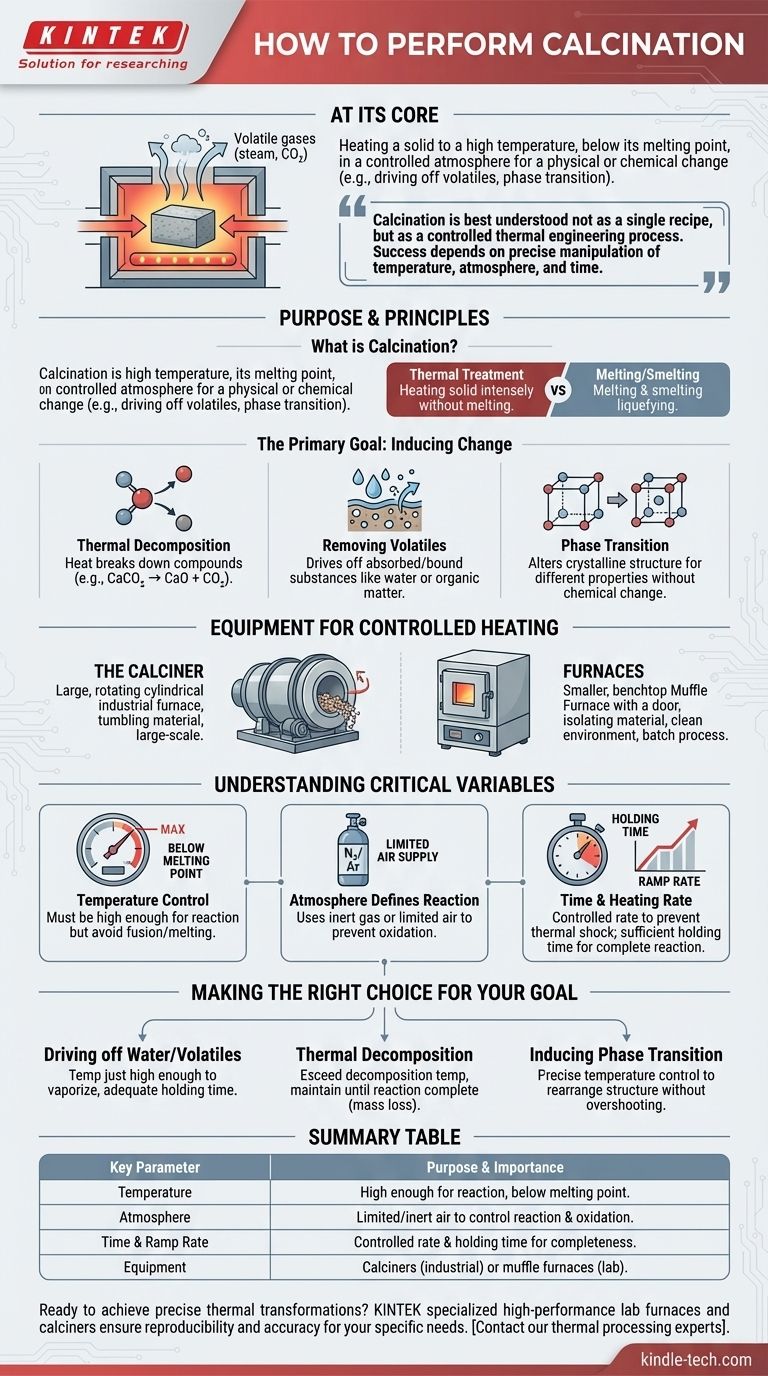
At its core, performing calcination involves heating a solid material to a high temperature, but below its melting point, in a controlled atmosphere. This process is not merely heating; it is a precise thermal treatment designed to cause a physical or chemical change, such as driving off volatile substances like water and carbon dioxide, or inducing a phase transition in the material's crystal structure.
Calcination is best understood not as a single recipe, but as a controlled thermal engineering process. Success depends entirely on the precise manipulation of temperature, atmosphere, and time to achieve a specific, predictable transformation in a solid material.

The Purpose and Principles of Calcination
Calcination is a fundamental process in materials science and metallurgy. Understanding its goals is key to executing it correctly.
What is Calcination?
Calcination is a form of thermal treatment. Unlike melting or smelting, the goal is to heat the solid material intensely without liquefying it.
This process is conducted with a limited supply of air or in a completely inert atmosphere to prevent unwanted oxidation or combustion.
The Primary Goal: Inducing Change
The heat applied during calcination serves as the energy source for three main types of transformations.
1. Thermal Decomposition: This is the most common goal, where heat breaks down a compound into simpler substances. A classic example is heating limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) to produce quicklime (calcium oxide, CaO) and release carbon dioxide (CO₂).
2. Removing Volatiles: Calcination is highly effective at driving off volatile components absorbed or chemically bound within a material. This includes removing crystalline water from hydrates or residual organic matter.
3. Phase Transition: Heat can be used to change the crystalline structure of a material from one form (polymorph) to another, more desirable one. This alters the material's physical properties, such as density or reactivity, without changing its chemical composition.
The Equipment for Controlled Heating
Specialized equipment is required to maintain the precise conditions necessary for successful calcination.
The Calciner
The primary piece of equipment is a calciner, a type of industrial furnace or reactor. These are often large, rotating cylindrical vessels that tumble the material to ensure uniform heating.
Calciners are designed to provide excellent control over both temperature and the internal atmosphere, making them ideal for large-scale, continuous production.
Furnaces
For smaller-scale laboratory work or specialized batch processes, various types of high-temperature furnaces are used.
A muffle furnace is common, as its design separates the material being heated from the fuel and combustion byproducts, allowing for a clean and controlled atmospheric environment.
Understanding the Critical Variables
Executing calcination is a game of control. Simply heating a material is not enough; several parameters must be managed precisely.
Temperature Control is Paramount
The calcination temperature must be high enough to drive the desired reaction but remain below the material's melting point. Exceeding this can lead to fusion, sintering, or melting, which ruins the intended outcome.
Atmosphere Defines the Reaction
The process is defined by its use of an absent or limited supply of air. Using an inert gas like nitrogen or argon prevents oxidation. In other cases, a "limited supply" of a specific gas might be introduced to facilitate a particular reaction.
Time and Heating Rate
The holding time at the peak temperature and the rate of heating (ramp rate) are also critical. A slow ramp can prevent thermal shock, while the holding time ensures the reaction proceeds to completion throughout the entire volume of material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this process effectively, align your parameters with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is driving off water or volatiles: Use a temperature just high enough to vaporize the target substance and ensure adequate holding time for it to escape the material's pores.
- If your primary focus is thermal decomposition (e.g., carbonates): You must exceed the specific decomposition temperature of the compound and maintain it until the reaction is complete, often confirmed by mass loss.
- If your primary focus is inducing a phase transition: The key is precise temperature control, heating to the exact point where the crystal structure rearranges without overshooting into an unwanted phase or melting.
Mastering calcination means moving beyond simple heating and embracing the precise control of its core variables.
Summary Table:
| Key Parameter | Purpose & Importance |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Must be high enough for the reaction but below the material's melting point to prevent fusion. |
| Atmosphere | Limited or inert air supply (e.g., N₂) to prevent unwanted oxidation and control the chemical reaction. |
| Time & Ramp Rate | Controlled heating rate and holding time ensure complete reaction and prevent thermal shock. |
| Equipment | Calciners (industrial) or muffle furnaces (lab-scale) provide the necessary controlled environment. |
Ready to achieve precise thermal transformations in your lab? The right equipment is critical for successful calcination processes. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and calciners designed for exact temperature and atmosphere control. Whether you are decomposing carbonates, removing volatiles, or inducing phase transitions, our solutions ensure reproducibility and accuracy. Contact our thermal processing experts today to find the perfect furnace for your calcination needs and enhance your material synthesis capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- At what temperature does ceramic melt? A Guide to Ceramic Heat Resistance
- What is a muffle furnace used in determination of? Precise Ash Content and Material Composition
- Does ceramic break with heat? The Real Culprit is Thermal Shock
- What is the meaning of muffle furnace? The Key to Pure, High-Temperature Processing
- What are the environmental impacts of metal processing? A Guide to Sustainability and Solutions



















