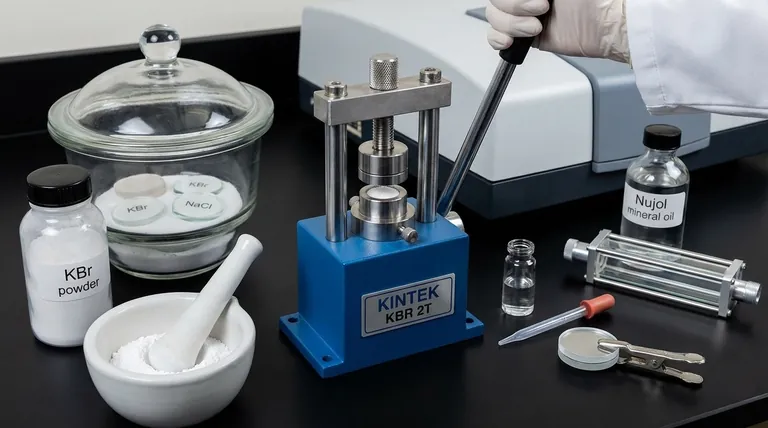
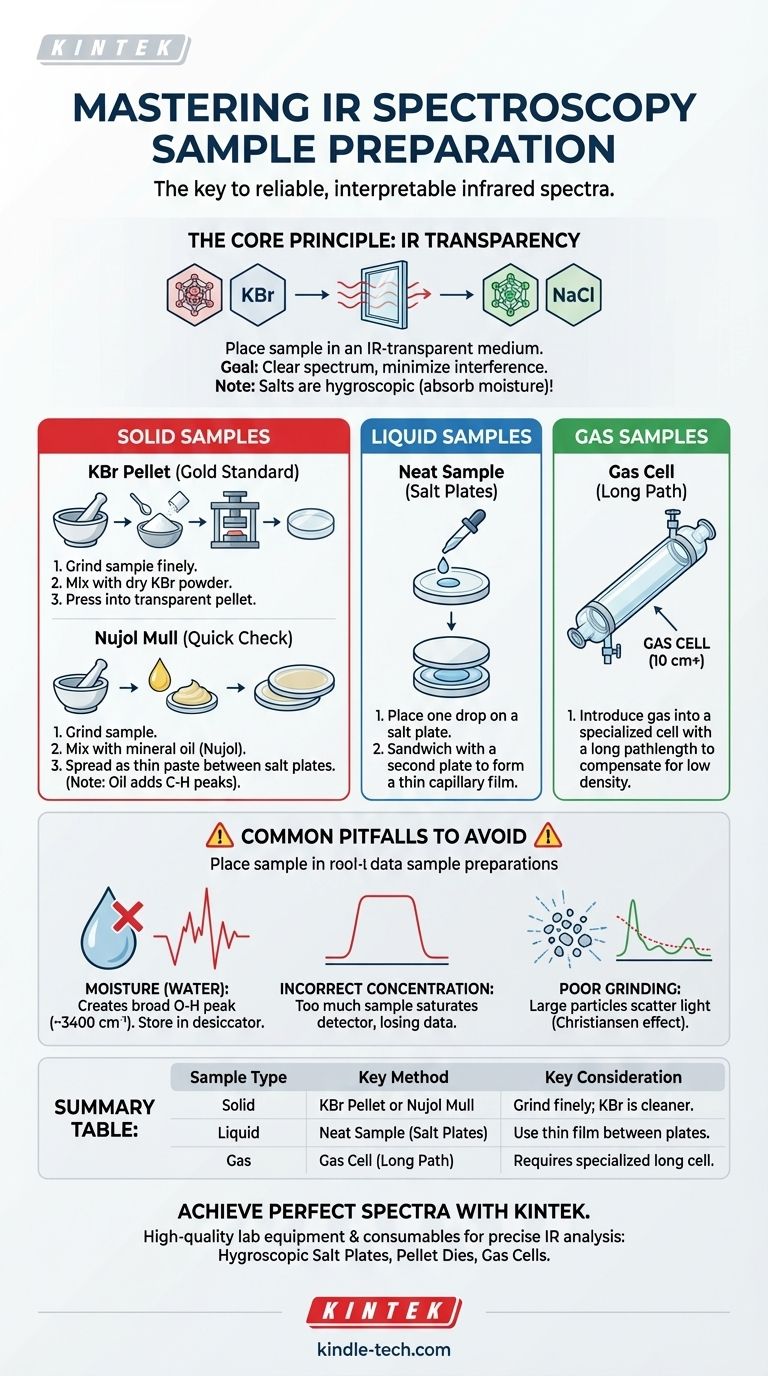
To prepare a sample for infrared (IR) spectroscopy, you must place it in a medium that is transparent to infrared light. The specific method depends entirely on whether your sample is a solid, liquid, or gas, but the goal is always to achieve a concentration that produces a clear, well-defined spectrum without overwhelming the detector. Common IR-transparent materials used for this purpose are salts like potassium bromide (KBr) and sodium chloride (NaCl).
The core principle of IR sample preparation is not just to hold the sample, but to present it to the instrument in a way that maximizes the signal from your compound while minimizing interference from light scattering, the sample holder, or atmospheric contaminants like water.

The Fundamental Principle: IR Transparency
The first rule of IR spectroscopy is that anything you place in the instrument's beam path, other than your sample, must be invisible to infrared light. This is why materials like glass and quartz, common in UV-Vis spectroscopy, cannot be used; their silica bonds strongly absorb IR radiation, obscuring the spectrum of your compound.
Why Salts are the Standard
Materials like sodium chloride (NaCl) and potassium bromide (KBr) are the workhorses of IR spectroscopy. Their simple ionic lattices do not have covalent bonds that vibrate in the mid-infrared region, making them effectively transparent.
These salts are typically pressed into clear windows or discs that serve as sample holders. They are excellent for this role but have one major weakness: they are hygroscopic, meaning they readily absorb moisture from the air.
Preparing Different Sample Types
Your approach will change based on the physical state of your sample. The goal is always to get a thin, uniform layer of the compound into the IR beam.
Method 1: Preparing Solid Samples
Solids present the biggest challenge because they scatter light, which can distort the spectrum. The sample must be ground into a very fine powder, smaller than the wavelength of the IR light, to minimize this scattering.
- KBr Pellet: This is the gold standard for high-quality spectra. A small amount of the finely ground sample (about 1-2 mg) is mixed with about 100-200 mg of dry KBr powder. The mixture is then compressed under high pressure in a die to form a small, transparent pellet that can be placed directly in the sample holder.
- Nujol Mull: This is a faster alternative. The solid is ground into a fine powder and then mixed with a drop or two of mineral oil (Nujol) to create a thick paste or "mull." This paste is then spread thinly between two salt plates. The oil helps reduce light scattering, but it also adds its own C-H bond signals to the spectrum, which you must mentally subtract.
Method 2: Preparing Liquid Samples
Preparing a pure liquid is the most straightforward method.
- Neat Sample (Salt Plates): A single drop of the liquid is placed on the face of one polished salt plate. A second plate is carefully placed on top, creating a very thin capillary film of the liquid "sandwiched" between them. The plates are then mounted and placed in the spectrometer.
Method 3: Preparing Gas Samples
Gases have a very low density, so a much longer path is needed for the IR beam to interact with enough molecules to produce a signal.
- Gas Cell: Samples are introduced into a specialized gas cell, which is a long tube (often 10 cm or more) sealed at both ends with IR-transparent windows (like KBr or NaCl). The long pathlength compensates for the low concentration of the gas.
Understanding the Common Pitfalls
Proper technique is critical. A poorly prepared sample is the most common source of a bad IR spectrum.
The Problem of Water
Because KBr and NaCl absorb moisture, any exposure to humid air will introduce a broad, prominent O-H peak around 3400 cm⁻¹. This can easily obscure important N-H or O-H signals from your actual sample. Always store salt plates and KBr powder in a desiccator.
Incorrect Sample Concentration
Too much sample is as bad as too little. If the film or pellet is too concentrated, the strongest absorption bands will be completely "flat-topped" or saturated. This means the detector receives no light at those frequencies, and you lose all quantitative information for those peaks.
Inadequate Grinding of Solids
If a solid sample is not ground into a fine, uniform powder, particles will scatter the IR light. This results in a distorted spectrum with a sloping baseline and poor peak shapes, an artifact known as the Christiansen effect.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your preparation method based on your sample type and analytical needs.
- If you have a solid sample and need high quality: Use the KBr pellet method for a clean spectrum with no interference.
- If you have a solid sample and need a quick check: Use the Nujol mull method, but be prepared to disregard the C-H peaks from the mineral oil.
- If you have a pure liquid sample: Use the "sandwich" method with two salt plates, as this is the simplest and most direct technique.
- If you have a gas sample: You must use a dedicated gas cell with a long pathlength to obtain a usable signal.
Ultimately, mastering sample preparation is the single most important skill for acquiring reliable and interpretable infrared spectra.
Summary Table:
| Sample Type | Key Preparation Method | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Solid | KBr Pellet or Nujol Mull | Grind finely to avoid scattering; KBr provides cleaner spectra. |
| Liquid | Neat Sample (Salt Plates) | Use a thin capillary film between two plates for optimal signal. |
| Gas | Gas Cell with Long Pathlength | Requires a specialized cell to compensate for low density. |
Achieve perfect IR spectra every time with KINTEK.
Proper sample preparation is the foundation of reliable infrared spectroscopy. Whether you're working with solids, liquids, or gases, using the right equipment and consumables is essential for clear, interpretable results.
KINTEK specializes in supplying the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need for precise IR analysis, including:
- Hygroscopic Salt Plates (KBr, NaCl): Stored and shipped correctly to minimize moisture contamination.
- Pellet Dies and Presses: For creating uniform KBr pellets for solid samples.
- Durable Gas Cells: With the correct pathlength for effective gas analysis.
Let our expertise support your laboratory's success. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific IR spectroscopy needs and ensure your sample preparation is flawless.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- kbr pellet press 2t
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- How much sample is needed for IR? Optimize Your Analysis with Minimal Material
- What is a KBr pellet? A Guide to Preparing Solid Samples for IR Spectroscopy
- What are the safety precautions for KBr? Achieve Flawless FTIR Pellet Preparation and Data Accuracy
- What is KBr disc method in IR spectroscopy? A Guide to Solid Sample Analysis
- Why do we use KBr in IR spectroscopy? Achieve Clear, High-Quality Solid Sample Analysis



















