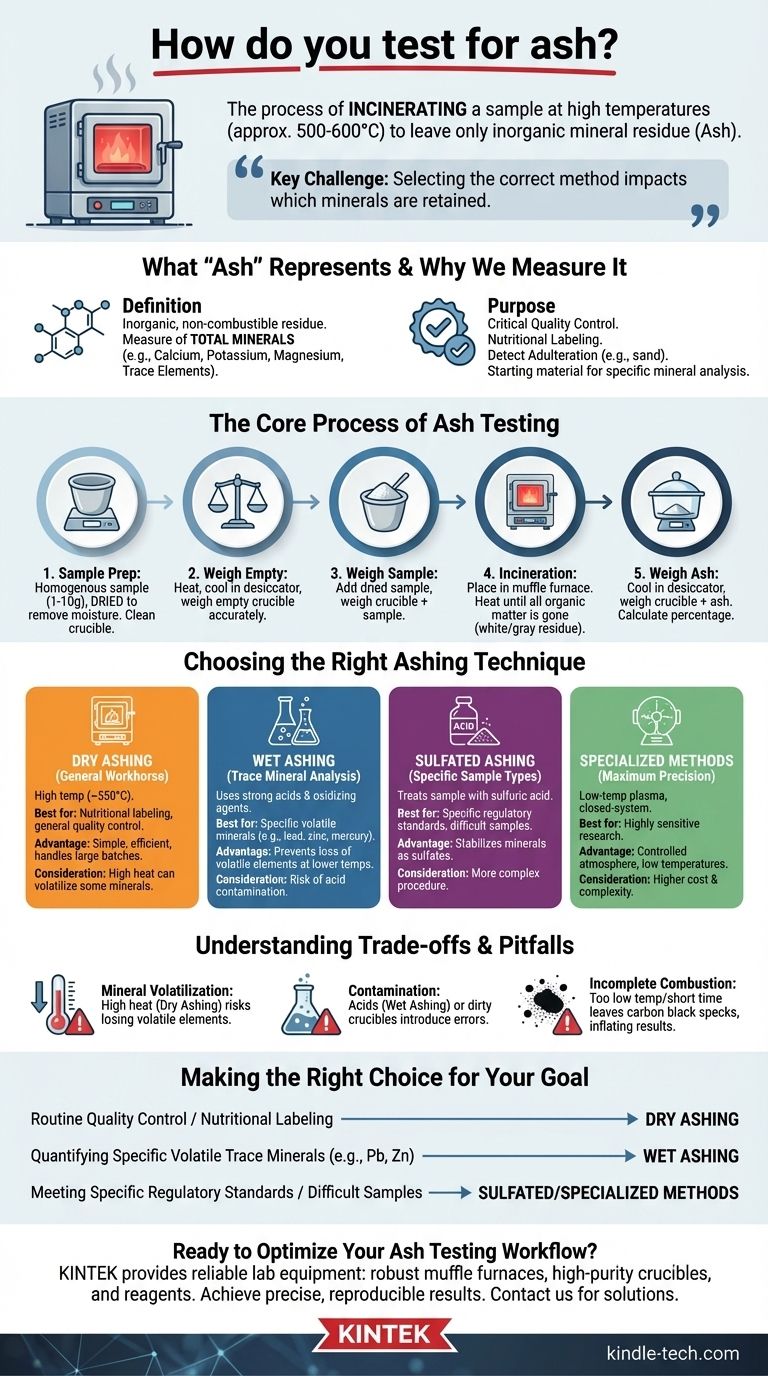
In practice, testing for ash involves incinerating a pre-weighed sample at high temperatures until only inorganic mineral residue remains. The sample is heated in a specialized furnace, typically around 500-600°C, which burns off all organic matter like protein, fat, and carbohydrates. The remaining non-combustible material, known as ash, is then cooled and weighed to determine the total mineral content of the original sample.
The core challenge of ash testing is not the procedure itself, but selecting the correct method. Your choice of technique directly impacts which minerals are retained and measured, meaning the method must align precisely with your analytical goal, whether it's for general nutritional labeling or specific trace element detection.
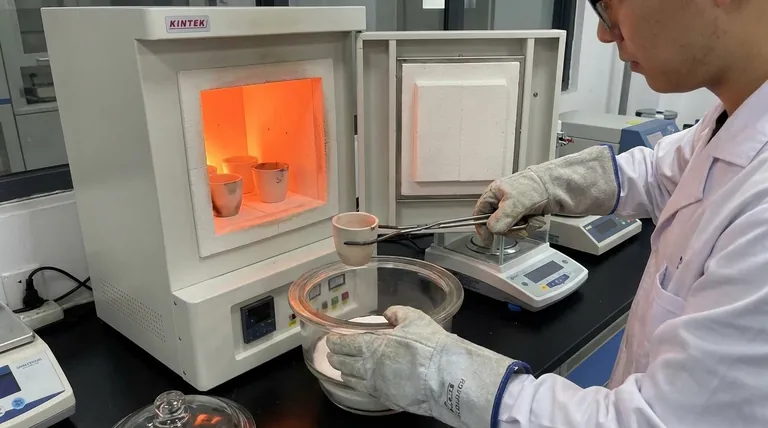

What "Ash" Represents and Why We Measure It
The Definition of Ash
In food science and chemistry, ash is the inorganic, non-combustible residue left after a sample is completely burned. It is a measure of the total amount of minerals present within a food or other organic material.
These minerals can include essential elements like calcium, potassium, and magnesium, as well as trace elements.
The Purpose of Ash Analysis
Measuring ash content is a critical quality control parameter. It serves as a quick indicator of the overall mineral content for nutritional labeling.
It can also be used to detect adulteration. For example, an unusually high ash content in a ground spice might indicate the presence of sand or other inorganic fillers. Finally, the resulting ash is often the starting material for analyzing individual specific minerals.
The Core Process of Ash Testing
The Critical First Step: Sample Preparation
Accurate results begin with meticulous preparation. The sample, typically between 1 and 10 grams, must be uniform and homogenous, which often requires grinding it into a fine powder.
Crucially, the sample must be dried in an oven to remove all moisture. This prevents spattering during incineration, which would lead to a loss of sample material and an inaccurate result. The crucible or dish holding the sample must also be perfectly clean to avoid contamination.
The Universal Steps of Incineration
Regardless of the specific technique, the fundamental process is the same:
- A clean, empty crucible is heated, cooled in a desiccator, and weighed accurately.
- The prepared, dried sample is placed in the crucible and weighed.
- The crucible and sample are placed in a muffle furnace and heated until all organic material is gone, leaving a white or gray residue.
- The crucible containing the ash is carefully removed, cooled in a moisture-free environment (a desiccator), and weighed again.
- The percentage of ash is calculated by dividing the weight of the ash by the original weight of the sample.
Choosing the Right Ashing Technique
The method you choose depends entirely on what you need to measure. A simple method for total minerals may cause a loss of specific, more volatile elements.
Dry Ashing: The General Workhorse
This is the most common method, using a muffle furnace at high temperatures, typically around 550°C. It's straightforward and effective for determining total mineral content for applications like nutritional labeling.
Its simplicity and ability to handle large batches of samples make it the standard for general quality assurance.
Wet Ashing: For Trace Mineral Analysis
Wet ashing, also known as acid digestion, uses strong acids and oxidizing agents to destroy the organic matrix at much lower temperatures than dry ashing.
This method is preferred when you need to analyze for specific, volatile minerals like lead, zinc, or mercury, which could be lost at the high temperatures of a muffle furnace.
Sulfated Ashing: For Specific Sample Types
This technique involves treating the sample with sulfuric acid before or during heating. The acid converts metal oxides and other minerals into more stable sulfate salts before they can be volatilized.
It is often required for specific materials where certain elements need to be stabilized to ensure they are fully accounted for in the final ash weight.
Specialized Methods: For Maximum Precision
For highly sensitive research, other methods exist. Low-temperature plasma ashing (around 200°C) is used for extremely volatile elements. Closed-system ashing uses sealed chambers to control the atmosphere precisely, preventing any potential contamination from the air.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
The Risk of Mineral Volatilization
The primary trade-off is between speed and accuracy for specific elements. The high heat of dry ashing is efficient but can cause volatile minerals to be lost, underrepresenting their presence in the final measurement.
The Danger of Contamination
Wet ashing avoids mineral loss but introduces a new risk: contamination from the acids themselves. High-purity, trace-metal-grade reagents are essential for accurate results. Likewise, any contaminant in the crucible will be incorrectly counted as ash.
Incomplete Combustion
If the ashing temperature is too low or the time is too short, small black specks of carbon will remain in the ash. This indicates incomplete combustion of the organic matter, which will artificially inflate the final ash weight and lead to an incorrect result.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct ash testing protocol is a decision based on your analytical needs.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control or nutritional labeling: Dry ashing is the most efficient and suitable method for determining total mineral content.
- If your primary focus is quantifying specific volatile trace minerals (e.g., lead, zinc): Wet ashing is the superior choice, as it prevents high-temperature losses and preserves these elements for analysis.
- If your primary focus is meeting a specific regulatory standard or working with difficult samples: Sulfated ashing or other specialized methods may be required to ensure stable and accurate results.
By matching the method to your objective, you ensure that your results are not just a number, but a true and actionable measure of quality.
Summary Table:
| Ashing Method | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry Ashing | Nutritional labeling, general quality control | Simple, efficient, handles large batches | High heat can volatilize some minerals |
| Wet Ashing | Trace mineral analysis (lead, zinc, mercury) | Prevents loss of volatile elements | Risk of acid contamination |
| Sulfated Ashing | Specific regulatory standards, difficult samples | Stabilizes minerals as sulfates | More complex procedure |
| Specialized Methods | Maximum precision for volatile elements | Controlled atmosphere, low temperatures | Higher cost and complexity |
Ready to Optimize Your Ash Testing Workflow?
Accurate mineral analysis starts with the right equipment and consumables. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment for all your ashing needs, from robust muffle furnaces for dry ashing to high-purity crucibles and trace-metal-grade reagents for wet ashing.
We help laboratories like yours:
- Achieve precise and reproducible ash content results
- Select the optimal ashing method for your specific application
- Maintain quality control with durable, contamination-free consumables
Contact us today to discuss your ash testing requirements and let our experts help you select the perfect solution. Get in touch via our contact form to get started!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between an oven and a muffle? Choose the Right Heating Tool for Your Lab
- What is a muffle furnace and its uses? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What are the safety precautions during heat treatment process? A Guide to Mitigating Thermal, Atmospheric, and Mechanical Hazards
- What is the use of muffle furnace in food lab? Essential for Accurate Ash Content Analysis
- What is the temperature accuracy of a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise and Uniform Heating



















