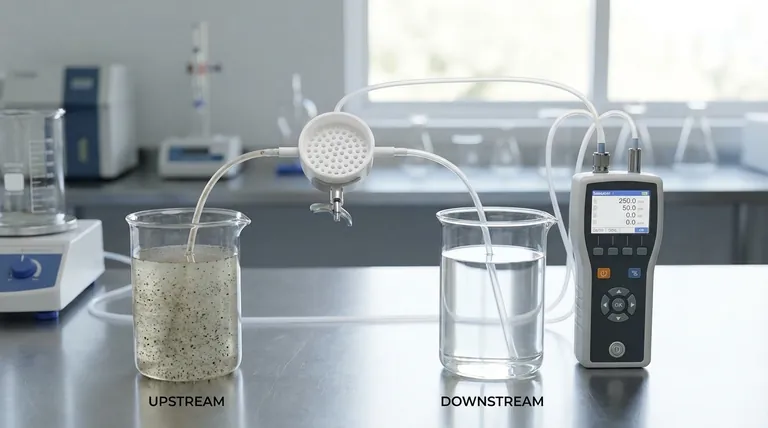
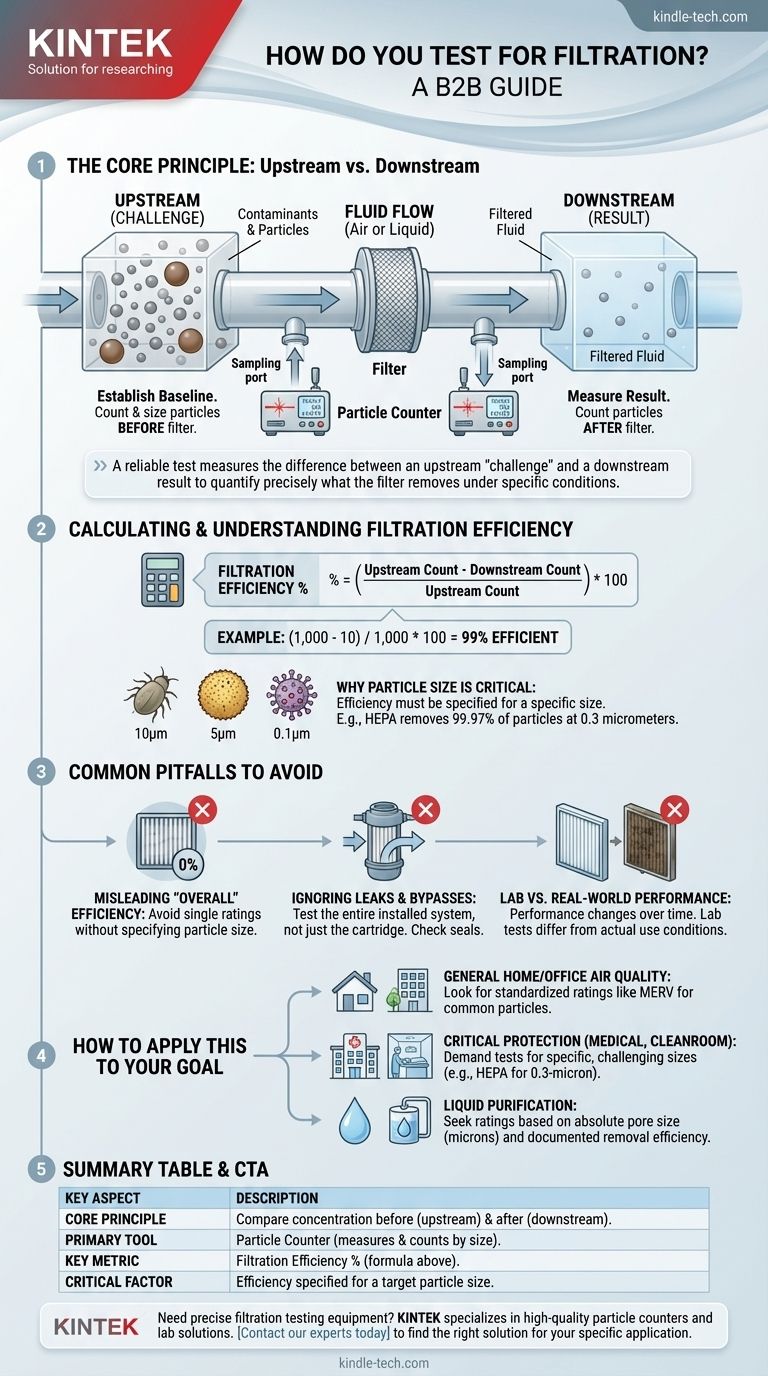
At its core, testing for filtration involves comparing the concentration of particles in a fluid (like air or a liquid) before it passes through a filter to the concentration of particles after it has been filtered. This measurement is typically performed with a device called a particle counter, and the result is expressed as the filter's efficiency.
The fundamental principle of filtration testing is not just about the filter itself, but about the entire system. A reliable test measures the difference between an upstream "challenge" and a downstream result to quantify precisely what the filter removes under specific conditions.

The Core Principle: Upstream vs. Downstream
The most reliable way to test filtration is to create a controlled environment where you can measure what goes in and what comes out. This is known as upstream and downstream sampling.
Establishing a Baseline (Upstream)
Before the fluid enters the filter, a sample is taken to count the number and size of particles present. This is the "upstream" measurement, or the "challenge."
This initial count establishes a baseline, giving you a precise understanding of the contaminant load the filter is being subjected to.
Measuring the Result (Downstream)
After the fluid has passed through the filter, a second sample is taken. This "downstream" measurement counts the particles that successfully penetrated the filter media.
The Role of the Particle Counter
A particle counter is the instrument used for both measurements. It draws in a specific volume of air or liquid and uses a light source (typically a laser) to detect and count individual particles, often sorting them by size.
Calculating and Understanding Filtration Efficiency
The data from the particle counter is used to calculate a simple but powerful metric: filtration efficiency. This tells you how effectively the filter is performing its job.
The Basic Efficiency Formula
Filtration efficiency is a percentage calculated by a straightforward formula:
(Upstream Particle Count - Downstream Particle Count) / Upstream Particle Count * 100
For example, if the upstream count is 1,000 particles and the downstream count is 10, the filter is 99% efficient for that particle size.
Why Particle Size is Critical
A single efficiency number is meaningless without context. A filter might be highly effective at removing large dust particles but perform poorly against microscopic viruses or smoke.
Therefore, professional tests always report efficiency at a specific particle size. For example, a HEPA filter is defined by its ability to remove 99.97% of particles at 0.3 micrometers in size.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
A flawed test can be worse than no test at all, providing a false sense of security. Understanding common failure points is crucial for interpreting results correctly.
Misleading "Overall" Efficiency
Be wary of any single efficiency rating that does not specify the particle size being tested. An "80% efficient" filter could be removing large, harmless particles while allowing the most dangerous microscopic ones to pass through unhindered.
Ignoring Leaks and Bypasses
The most efficient filter media is useless if the air or liquid can simply go around it. A proper test evaluates the entire installed system, not just the filter cartridge in isolation. Leaks in the housing or seal are a common cause of system failure.
Lab Conditions vs. Real-World Performance
Filter performance can change over time as it becomes loaded with contaminants. A test on a brand-new filter in a lab does not always reflect its performance after months of real-world use with varying humidity, flow rates, and contaminant types.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The right test depends entirely on what you are trying to achieve. Use your end goal to determine what efficiency rating truly matters.
- If your primary focus is general home or office air quality: Look for standardized ratings like MERV, which provides a clear scale of effectiveness against a range of common particles like pollen, dust, and mold spores.
- If your primary focus is critical protection (e.g., medical, cleanroom): Demand tests that certify efficiency at a specific, challenging particle size, such as the HEPA standard for 0.3-micron particles.
- If your primary focus is liquid purification: Seek filter ratings based on absolute pore size (e.g., in microns) and documented removal efficiency for the specific contaminants you need to control.
Ultimately, understanding how filtration is tested empowers you to look beyond marketing claims and evaluate a filter's true performance for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Compare particle concentration before (upstream) and after (downstream) the filter. |
| Primary Tool | Particle Counter (measures & counts particles by size). |
| Key Metric | Filtration Efficiency % = [(Upstream - Downstream) / Upstream] x 100. |
| Critical Factor | Efficiency must be specified for a target particle size (e.g., 0.3 microns). |
Need precise filtration testing equipment for your laboratory? KINTEK specializes in high-quality particle counters and lab equipment to ensure your filtration systems meet critical standards for air and liquid purification. Contact our experts today to find the right solution for your specific application and achieve reliable, verifiable results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Buchner Funnel and Triangular Funnel
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
People Also Ask
- Why are PTFE laboratory consumables required when testing stainless steel against organic acids? Ensure Data Integrity
- What are the advantages of using PTFE molds for epoxy resin flame retardant samples? Ensure High-Purity Material Testing
- What is the difference between PPF and coating? Armor vs. Slick Shell for Your Car
- What are alloys in simple words? Unlock the Power of Engineered Materials
- What are the four main types of sensors? A Guide to Power Source and Signal Type
















