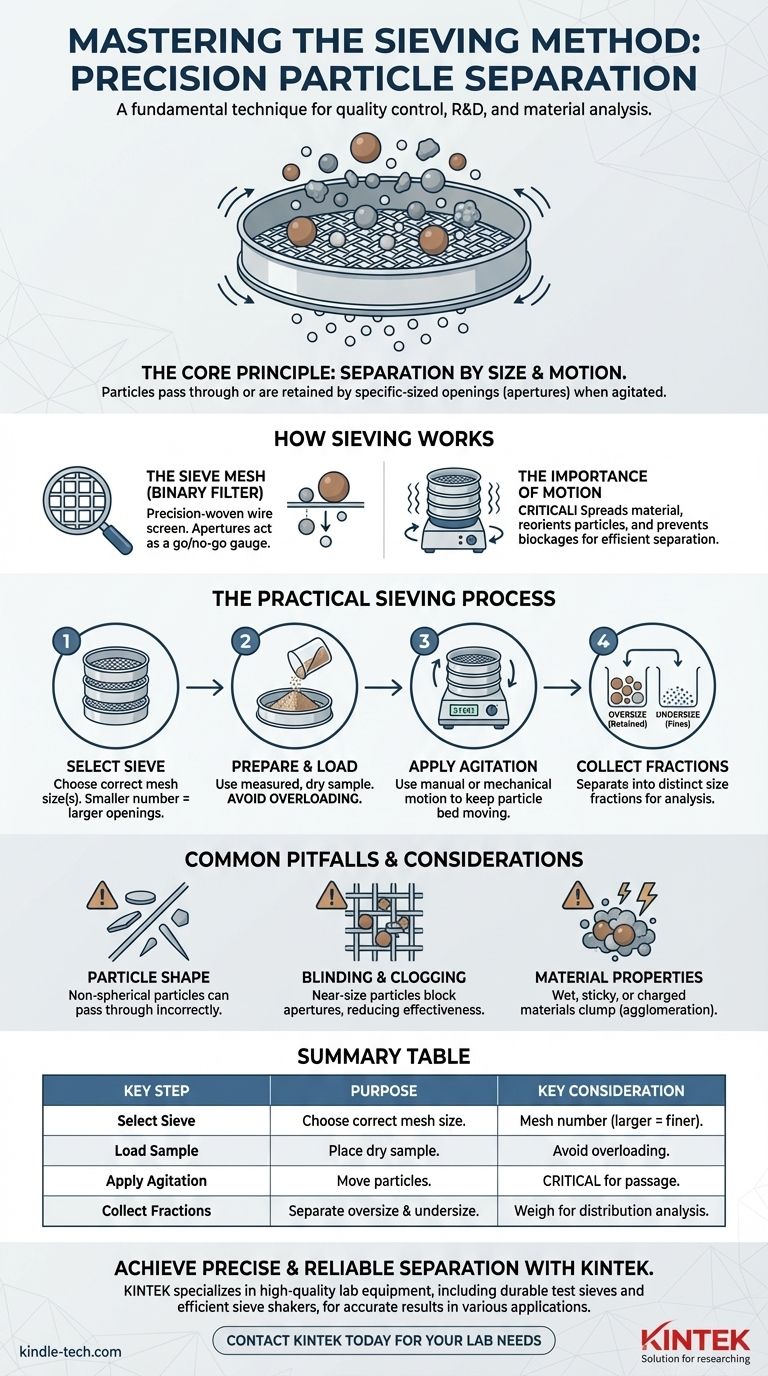
At its core, the sieving method separates a mixture of particles based on their size. You achieve this by passing the material over or through a surface with specific-sized openings, known as a sieve or screen, and applying motion to allow smaller particles to pass through while retaining the larger ones.
Sieving is a straightforward mechanical process that leverages a single physical property: particle size. The method's success depends entirely on the relative movement between the particles and the sieve, ensuring each particle has an opportunity to either pass through a mesh opening or be retained.

The Core Principle: How Sieving Works
Sieving operates on a simple, yet powerful, mechanical sorting principle. It doesn't involve complex chemistry or physics, but rather the interaction between a particle and a physical barrier.
The Role of the Sieve Mesh
The heart of the method is the sieve mesh, a screen typically made of woven wire with precisely sized and spaced openings, called apertures.
This mesh acts as a binary filter. If a particle is smaller than the aperture in all its dimensions, it has the potential to pass through. If it is larger, it will be retained on the sieve's surface.
The Importance of Motion
Simply placing material on a sieve is not enough. Motion is critical to ensure an effective separation.
This motion, whether it's a vertical tap, a horizontal shake, or a machine-driven vibration, serves two key purposes. First, it spreads the material across the entire sieve surface. Second, it continually reorients the particles, giving each one multiple opportunities to approach an aperture and pass through if it is small enough. This agitation prevents particles from piling up and blocking each other.
The Practical Sieving Process
Whether you are in a lab, a kitchen, or an industrial plant, the fundamental steps of sieving are universal.
Step 1: Select Your Sieve
The most critical decision is choosing a sieve with the correct mesh size for your goal. A smaller mesh number corresponds to larger openings, while a larger mesh number means smaller, finer openings. For analytical work, a stack of sieves with progressively finer mesh sizes is often used.
Step 2: Prepare and Load the Sample
Place a measured amount of your dry, granular material onto the top sieve. Do not overload the sieve, as this will hinder particle movement and lead to poor separation efficiency.
Step 3: Apply Agitation
Begin the agitation process. This can be done manually by shaking and tapping the sieve or by placing it in a mechanical sieve shaker for a set duration. The goal is to keep the particle bed moving.
Step 4: Collect the Fractions
Once the process is complete, you are left with two or more fractions. The particles that were retained on the sieve surface are called the oversize fraction. The particles that passed through the mesh are the undersize or "fines" fraction.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While the principle is simple, several factors can affect the accuracy and efficiency of sieving.
Particle Shape Can Be Deceiving
Sieving is most effective for particles that are roughly spherical. Long, needle-like, or flat, flaky particles can pass through the mesh end-on or diagonally, even if their total volume or mass is much larger than a spherical particle that would be retained.
The Risk of Blinding and Clogging
Blinding occurs when particles that are very close in size to the mesh openings become lodged in the apertures, blocking other particles from passing through. This significantly reduces the sieve's effectiveness over time.
Material Properties Matter
Sieving works best with dry, free-flowing materials. Wet, sticky, or electrostatically charged particles tend to clump together, a process called agglomeration. These clumps behave like larger particles and will not separate correctly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
You can apply the sieving method for vastly different purposes, from simple sorting to precise particle size analysis.
- If your primary focus is basic separation: Use a single sieve with a mesh size that cleanly divides the components you want to keep from those you want to discard.
- If your primary focus is quality control or analysis: Use a calibrated stack of sieves with varying mesh sizes and a mechanical shaker to determine the particle size distribution within a sample.
- If your primary focus is industrial processing: Use large-scale screening equipment designed for high throughput and resistance to blinding to continuously classify or scalp material.
By understanding these principles, you can use sieving as a precise and predictable tool for managing and analyzing particulate materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Sieving Step | Purpose | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Select Sieve | Choose correct mesh size for separation goal. | Mesh number (larger = finer openings). |
| Load Sample | Place a measured, dry sample onto the sieve. | Avoid overloading for efficient separation. |
| Apply Agitation | Shake or use a sieve shaker to move particles. | Critical for giving particles a chance to pass through. |
| Collect Fractions | Separate oversize (retained) and undersize (passed) particles. | Weigh fractions for particle size distribution analysis. |
Achieve precise and reliable particle separation in your laboratory.
The sieving method is fundamental for quality control, R&D, and material analysis. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment, including durable test sieves and efficient sieve shakers, designed to deliver accurate and repeatable results for your specific application—from pharmaceuticals and chemicals to construction materials.
Let our experts help you select the perfect sieving equipment for your needs. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory requirements and enhance your particle analysis workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of sieving machine? Achieve Accurate Particle Size Separation
- Which Cannot be separated by sieving? Understanding the Limits of Particle Size Separation
- What size are test sieves? A Guide to Frame Diameters and Mesh Sizes
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of sieve analysis? A Guide to Cost-Effective Particle Sizing
- Can sieving be used to separate a solid substance from a liquid substance? Learn the Right Technique for Your Mixture



















