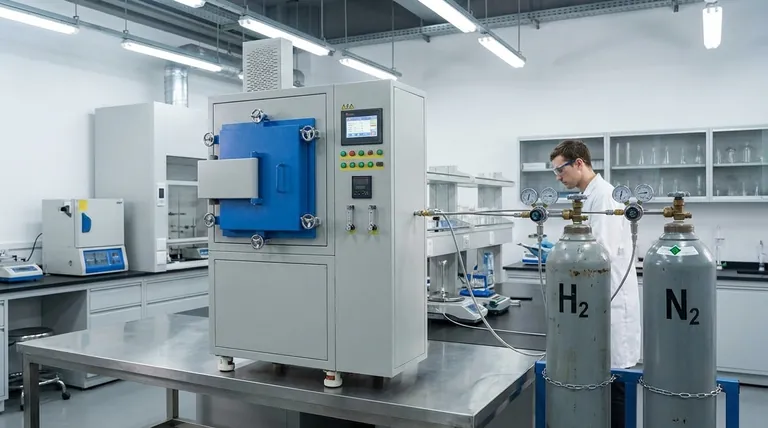
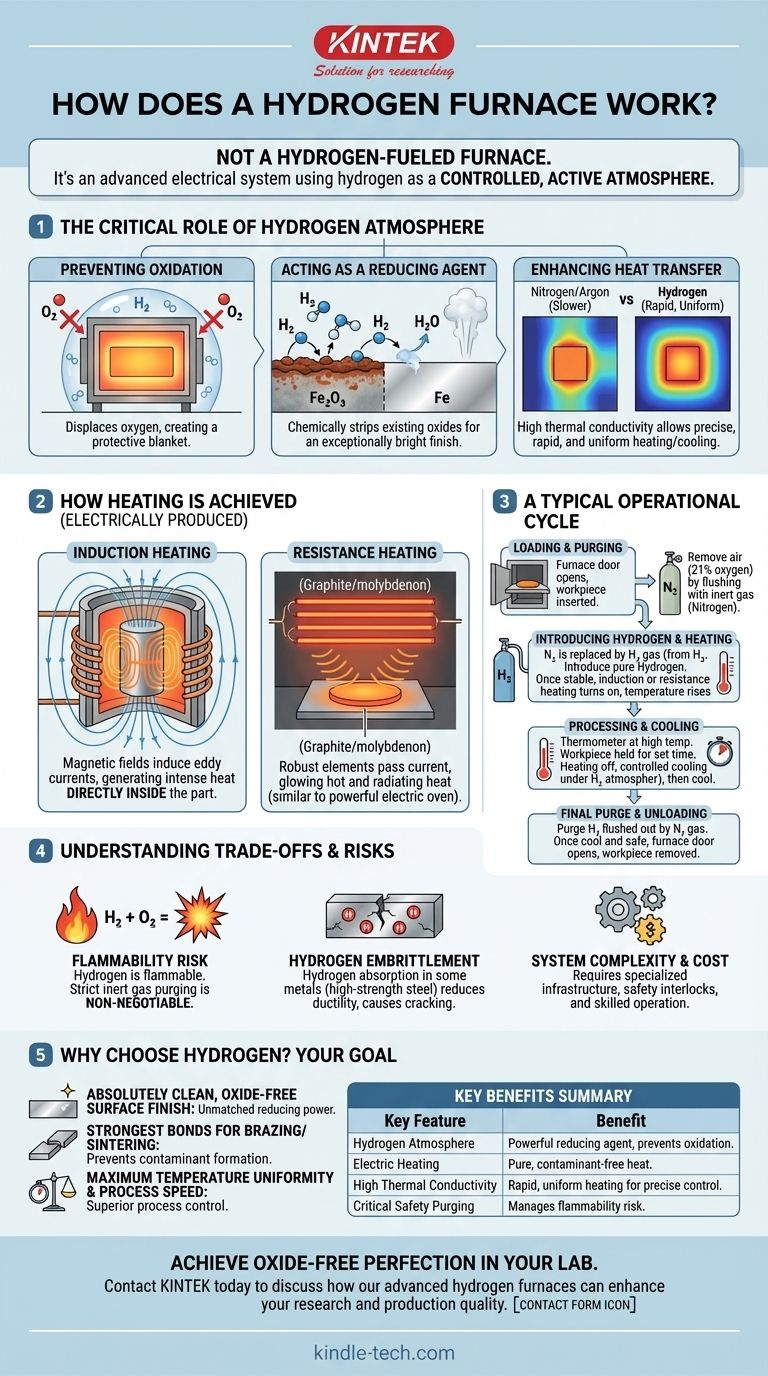
In essence, a hydrogen furnace is not a furnace that burns hydrogen for fuel. Instead, it is an advanced system that uses hydrogen gas to create a highly controlled, active atmosphere around a workpiece. The heat itself is generated electrically, allowing the unique chemical properties of hydrogen to treat materials at extreme temperatures without oxidation.
The core purpose of a hydrogen furnace is to leverage hydrogen as a powerful reducing agent and an excellent heat transfer medium. This creates an ultra-pure, oxygen-free environment that cleans material surfaces and ensures uniform heating for processes like annealing, brazing, and sintering.

The Critical Role of the Hydrogen Atmosphere
The decision to use a hydrogen atmosphere is deliberate and centers on its powerful chemical and physical properties at high temperatures.
Preventing Oxidation
At the high temperatures required for heat treatment, most metals will readily react with any oxygen present, forming a layer of oxide scale on the surface. A pure hydrogen atmosphere displaces all the oxygen, creating a protective blanket around the workpiece.
Acting as a Reducing Agent
Hydrogen goes a step beyond simple protection. It is an active reducing agent, meaning it chemically strips existing oxides from the material's surface. The hydrogen reacts with the metal oxides (e.g., iron oxide) to form water vapor (H₂O), which is then safely vented from the furnace. This leaves the part with an exceptionally bright, clean finish.
Enhancing Heat Transfer
Hydrogen has a very high thermal conductivity, far greater than nitrogen or argon. This property allows for rapid and extremely uniform heating and cooling of the workpiece, providing precise control over the final material properties.
How the Heating is Actually Achieved
The heat in a hydrogen furnace is not generated by combustion. It is almost always produced electrically, which keeps the atmosphere pure and uncontaminated.
The Induction Heating Method
A common and highly efficient method is induction heating. A hollow copper coil, carrying a high-frequency alternating current, is wrapped around the chamber holding the workpiece.
This coil generates a powerful, fluctuating magnetic field. The magnetic field passes through the workpiece, inducing strong electrical currents (called eddy currents) within the metal itself.
The metal's natural resistance to these internal currents generates intense, rapid heat directly inside the part. The furnace walls remain relatively cool while the workpiece heats from within, offering incredible speed and precision.
The Resistance Heating Method
Another method involves using robust heating elements made of materials like graphite or molybdenum. Electric current is passed through these elements, causing them to glow hot and radiate heat onto the workpiece, similar to a conventional electric oven but on a much more powerful scale.
A Typical Operational Cycle
Operating a hydrogen furnace requires a strict, safety-oriented procedure to manage the reactive gases involved.
Loading and Purging
First, the workpiece is loaded into the furnace chamber. The chamber is then sealed, and all the air (which is ~21% oxygen) is removed. This is typically done by flushing the chamber multiple times with an inert gas like nitrogen.
Introducing Hydrogen and Heating
Only after the oxygen level is confirmed to be near zero is hydrogen gas introduced into the chamber. Gas flow is precisely controlled using flow meters. Once the hydrogen atmosphere is stable, the electric heating system (induction or resistance) is activated to bring the workpiece to the target temperature.
Processing and Cooling
The workpiece is held at the specified temperature for a set duration to achieve the desired metallurgical change, such as annealing (softening) or brazing (joining). Afterward, the heating system is turned off, and the part is cooled in a controlled manner, still under the protective hydrogen atmosphere.
Final Purge and Unloading
Once the workpiece has cooled to a safe temperature, the hydrogen gas is purged from the chamber using nitrogen again. This ensures no flammable hydrogen can mix with air when the furnace door is opened for unloading.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While powerful, hydrogen furnaces require a clear understanding of their operational demands and potential hazards.
The Flammability Risk
The primary risk is the flammability of hydrogen. Hydrogen gas can form an explosive mixture with oxygen in the air. The multi-step purging process with inert gas is a non-negotiable safety critical step to prevent this from ever happening.
Potential for Material Embrittlement
For certain metals, particularly some high-strength steels, hydrogen can be absorbed into the material's structure at high temperatures. This can lead to a condition called hydrogen embrittlement, which reduces the material's ductility and can cause it to crack. This requires careful management of process parameters.
System Complexity and Cost
Hydrogen furnaces are sophisticated systems that require specialized gas handling infrastructure, advanced safety interlocks, and skilled operators. This makes them a more complex and costly solution compared to standard atmosphere or vacuum furnaces.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The choice to use a hydrogen furnace is driven by the need for ultimate purity and surface quality in material processing.
- If your primary focus is an absolutely clean, oxide-free surface finish: Hydrogen's power as a reducing agent is unmatched, delivering a bright finish that is impossible to achieve in other atmospheres.
- If your primary focus is creating the strongest possible bonds for brazing or sintering: The pure, active atmosphere prevents the formation of contaminants and oxides that would otherwise weaken the metallurgical joints.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature uniformity and process speed: Hydrogen's high thermal conductivity ensures the entire part heats and cools evenly and quickly, providing superior process control.
By mastering the controlled application of hydrogen, you can achieve a level of material quality and precision that other heat-treating methods cannot match.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Atmosphere | Acts as a powerful reducing agent to strip oxides and prevent oxidation. |
| Electric Heating | Provides pure, contaminant-free heat via induction or resistance methods. |
| High Thermal Conductivity | Ensures rapid, uniform heating and cooling for precise process control. |
| Critical Safety Purging | Uses inert gas purges to manage the flammability risk of hydrogen gas. |
Achieve Oxide-Free Perfection in Your Lab
If your processes demand the ultimate in surface purity and material integrity for annealing, brazing, or sintering, a hydrogen furnace is the solution. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including hydrogen furnaces, designed to meet the rigorous needs of modern laboratories.
Our expertise ensures you get a system that delivers superior results safely and efficiently. Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our hydrogen furnaces can enhance your research and production quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are hydrogen furnaces used for? Achieve Purity and Speed in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the primary benefits of using hydrogen firing for sintering parts? Achieve Peak Density & Corrosion Resistance
- When would you need to use a controlled atmosphere? Prevent Contamination and Control Reactions
- Why is an industrial furnace with hydrogen atmosphere control necessary for the pre-sintering of Fe-Cr-Al materials?
- Why must a hydrogen-reducing atmosphere be maintained for tungsten annealing? Ensure Purity in High-Temp Processing



















