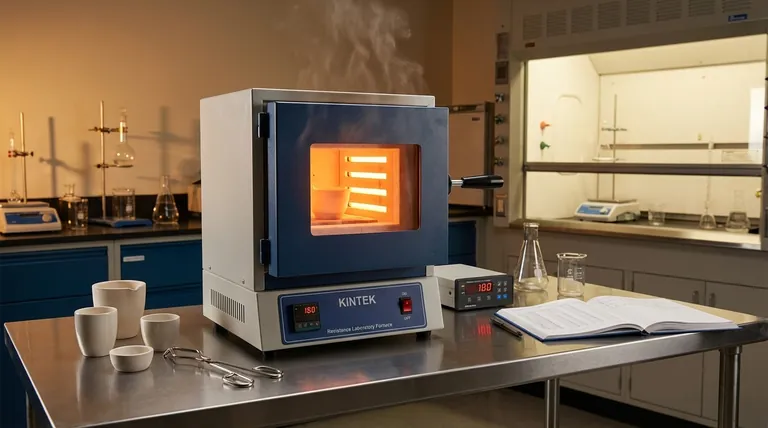
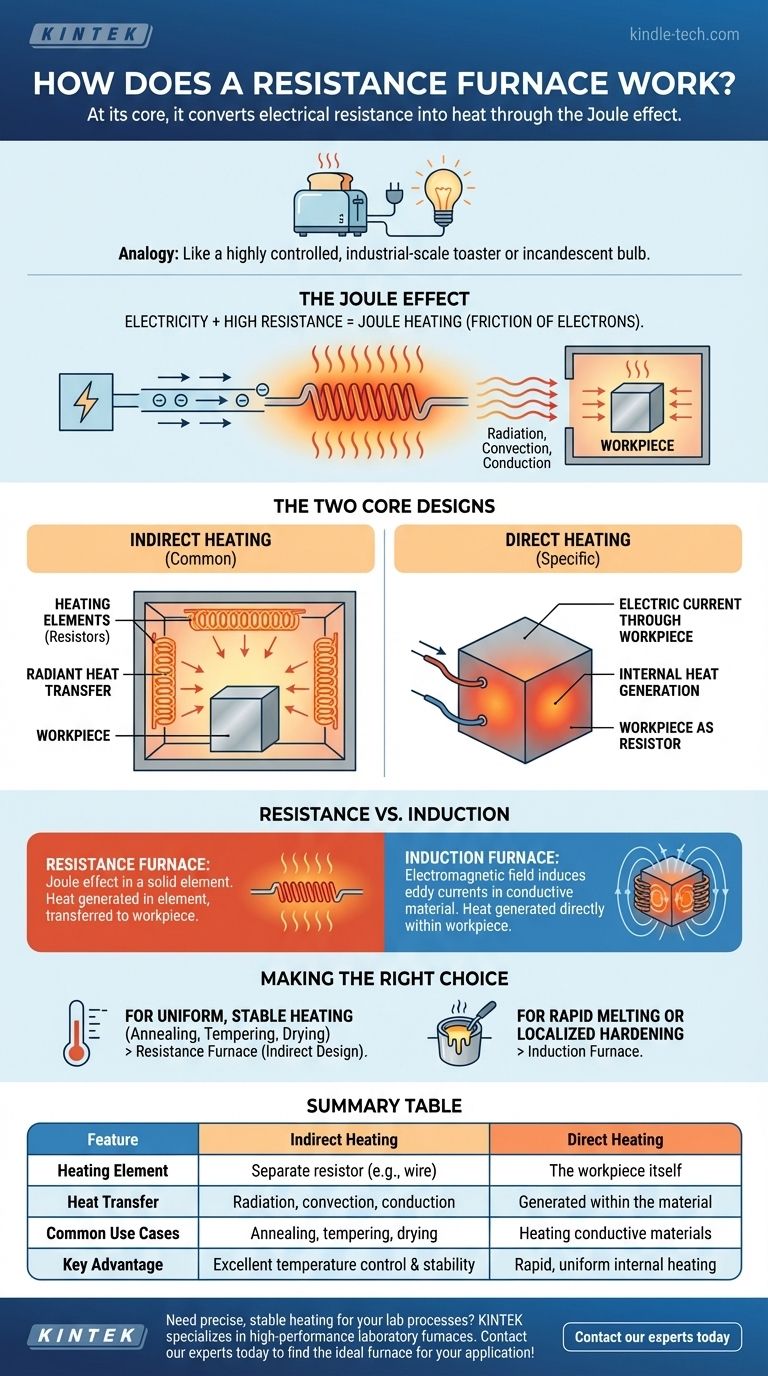
At its core, a resistance furnace operates on a simple, fundamental principle: it passes an electric current through a material that resists the flow of electricity. This resistance converts electrical energy directly into heat through a phenomenon known as the Joule effect. This generated heat is then transferred to the workpiece inside the furnace via radiation, convection, or conduction.
A resistance furnace is best understood as a highly controlled, industrial-scale version of a common household appliance like a toaster or an incandescent light bulb. It leverages the predictable heat generated when electricity struggles to pass through a conductor, making it a workhorse for processes requiring stable and uniform temperatures.

The Fundamental Principle: The Joule Effect
What is the Joule Effect?
The Joule effect, or resistive heating, is a physical law stating that the passage of an electric current through a conductor produces heat.
Imagine electricity as water flowing through a pipe. If the pipe is wide and smooth, the water flows easily. If the pipe is narrow and rough (high resistance), friction is created, which generates heat. In an electrical circuit, this "friction" against the flow of electrons is what creates thermal energy.
From Electricity to Heat
The primary function of a resistance furnace is to be an energy converter. It takes in electrical energy and, using a carefully selected resistive material, transforms it into thermal energy with very high efficiency.
This process is highly controllable. By precisely regulating the voltage and current, you can achieve and maintain extremely stable temperatures within the furnace chamber.
The Two Core Designs of Resistance Furnaces
Resistance furnaces are built around two different methods of applying this principle: indirect heating and direct heating.
Indirect Heating: The Common Approach
This is the most prevalent design. In an indirect furnace, specialized heating elements (resistors) made of high-resistance materials are placed along the walls or ceiling of the furnace chamber.
The electric current flows through these elements, causing them to become extremely hot. This heat then radiates or convects onto the workpiece or material placed inside the furnace, raising its temperature without the electricity ever touching the material itself.
Direct Heating: Using the Material Itself
In a direct heating design, the workpiece or material being heated serves as the resistor. An electric current is passed directly through the material itself.
This method is less common but highly effective for specific applications, particularly with materials that are electrically conductive. It generates heat from within the material, which can lead to very rapid and uniform heating cycles.
Understanding the Key Distinction: Resistance vs. Induction
It is crucial not to confuse resistance heating with induction heating, as they operate on entirely different physical principles.
The Source of Heat
A resistance furnace uses the Joule effect in a solid resistive element (or the workpiece). The heat generation is a direct consequence of electrical resistance.
An induction furnace uses a powerful, fluctuating electromagnetic field. This field induces internal electrical currents (eddy currents) within the conductive material, and these swirling currents generate the heat.
The Method of Heat Generation
In resistance heating, the heat is generated in a distinct element and then transferred to the workpiece.
In induction heating, the heat is generated directly within the workpiece itself with no physical contact. The furnace coil that creates the magnetic field may remain cool while the metal inside becomes molten.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these mechanisms allows you to select the appropriate technology for a specific industrial goal.
- If your primary focus is uniform, stable heating for processes like annealing, tempering, or drying: A resistance furnace, particularly an indirect design, provides exceptional temperature control and environmental stability.
- If your primary focus is rapidly melting conductive metals or applying localized surface hardening: An induction furnace is far superior, as it generates heat directly and instantly within the material itself.
By grasping the core principle of electrical resistance, you can demystify the furnace's operation and appreciate its role as a foundational tool of modern industry.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Indirect Heating | Direct Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Element | Separate resistor (e.g., wire, element) | The workpiece itself |
| Heat Transfer | Radiation, convection, conduction | Generated within the material |
| Common Use Cases | Annealing, tempering, drying | Heating conductive materials |
| Key Advantage | Excellent temperature control & stability | Rapid, uniform internal heating |
Need precise, stable heating for your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory furnaces, including resistance models perfect for annealing, tempering, and heat treatment. Our equipment delivers the uniform temperatures and control your research demands. Contact our experts today to find the ideal furnace for your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results



















