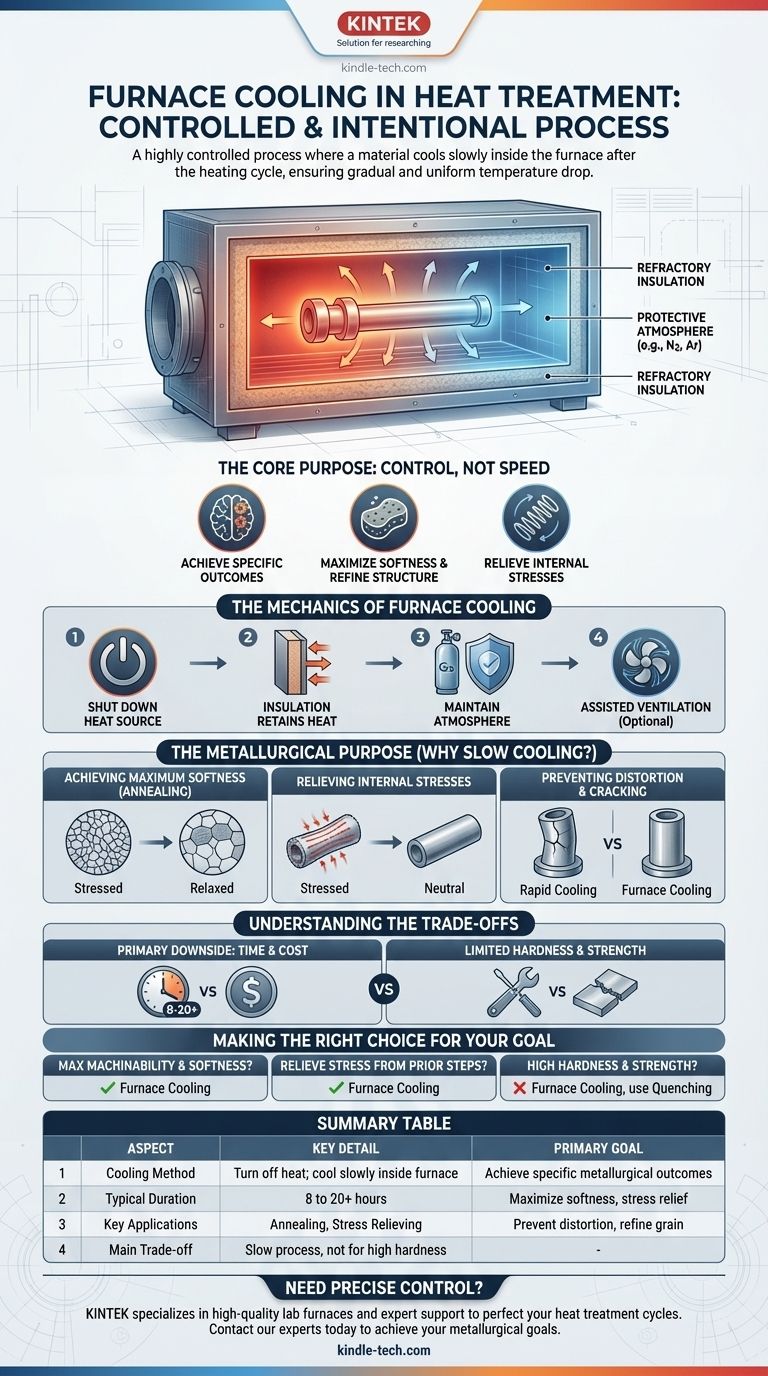
Furnace cooling is a highly controlled, intentional process used in heat treatment where a material is cooled slowly inside the furnace itself after the heating cycle is complete. The process relies on shutting off the heat source and allowing the insulated furnace chamber and the material within it to cool down together, often over many hours, ensuring a gradual and uniform temperature drop.
The core purpose of furnace cooling is not speed, but control. This deliberately slow process is chosen to achieve specific metallurgical outcomes, primarily to maximize softness, refine the grain structure, and relieve internal stresses that other, faster cooling methods would introduce.

The Mechanics of Furnace Cooling
The process may seem passive, but it is a carefully managed phase of heat treatment. Several key components and principles work together to control the cooling rate.
Shutting Down the Heat Source
The first and most obvious step is turning off the furnace's heating elements or gas burners. This action stops the introduction of new thermal energy into the system.
The Role of Furnace Insulation
Industrial furnaces are built with heavy-duty refractory insulation designed to retain heat efficiently. During the cooling phase, this same insulation prevents heat from escaping too quickly, becoming the primary factor dictating the slow cooling rate.
Maintaining the Protective Atmosphere
As the references note, furnaces often use a controlled atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen, argon) to prevent oxidation and other surface reactions at high temperatures. This atmosphere is maintained throughout the slow cooling cycle to protect the material's surface integrity until it is cool enough to be exposed to air.
Assisting Cooling with Ventilation
For certain processes requiring a slightly faster but still controlled cool-down, sealed fans are used. These fans circulate the inert atmosphere within the furnace, promoting more uniform temperature distribution and slightly accelerating heat transfer to the furnace's water-cooled walls or dedicated heat exchangers.
Why Choose Slow Cooling? The Metallurgical Purpose
The cooling rate is arguably the most critical variable in determining the final microstructure, and therefore the mechanical properties, of a metal part.
Achieving Maximum Softness (Annealing)
Furnace cooling is the defining characteristic of annealing. This slow rate allows the metal's internal crystal structure sufficient time to transform into its softest, most stable state. For steel, this means ensuring a full transformation into a coarse pearlite structure, which is ideal for subsequent machining.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Manufacturing processes like welding, casting, or heavy machining introduce significant internal stresses into a material. A slow furnace cool, often called stress relieving, allows the material's atoms to gently reposition themselves, relaxing these stresses and reducing the risk of distortion or cracking later in the component's life.
Preventing Distortion and Cracking
Rapid cooling (quenching) creates a severe temperature gradient between the surface and the core of a part, inducing massive internal stress. Furnace cooling minimizes this thermal shock, making it essential for complex shapes or brittle materials that would otherwise warp or crack.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While furnace cooling provides significant metallurgical benefits, it is not the right choice for every application. Its primary trade-offs are time and the resulting material properties.
The Primary Downside: Time and Cost
Furnace cooling is exceptionally slow, often taking 8 to 20 hours or more. This long cycle time occupies expensive furnace equipment, reduces production throughput, and increases the overall cost per part.
Limited Hardness and Strength
This process produces the softest and most ductile condition possible for a given metal. It is fundamentally unsuitable for applications where high hardness and strength are the primary objectives, such as creating tools or wear-resistant surfaces. Those require the exact opposite: rapid quenching.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct cooling method is essential for achieving the desired outcome of any heat treatment process.
- If your primary focus is maximum machinability and softness: Furnace cooling, as part of an annealing cycle, is the correct method to produce the required soft and uniform microstructure.
- If your primary focus is relieving stress from prior manufacturing steps: A controlled furnace cool is the standard and safest procedure to reduce internal stresses and prevent future distortion.
- If your primary focus is achieving high hardness and strength: You must use a rapid cooling method, such as quenching in oil, water, or polymer, as furnace cooling will produce the opposite result.
Ultimately, mastering the cooling rate is fundamental to controlling the final properties and performance of any heat-treated component.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Achieve specific metallurgical outcomes (softness, stress relief) |
| Cooling Method | Turn off heat; material cools slowly inside the insulated furnace |
| Typical Duration | 8 to 20+ hours |
| Key Applications | Annealing (for softness), Stress Relieving |
| Main Trade-off | Slow process, not suitable for achieving high hardness |
Need precise control over your material's properties? The furnace cooling process is key to achieving specific outcomes like maximum softness and stress relief. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab furnaces and expert support you need to perfect your heat treatment cycles. Whether you're annealing, stress relieving, or developing new processes, our equipment is designed for reliability and precision. Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve your metallurgical goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory vacuum oven facilitate the gel content testing of UV-cured silicone rubber films?
- How does vacuum coating work? Achieve Superior Surface Properties with PVD Technology
- Why is gas nitriding typically conducted in a vacuum resistance heating furnace? Unlock Superior Metal Hardening
- What conditions does a vacuum annealing furnace provide for Ti41.5Zr41.5Ni17 films? Optimize Quasicrystal Stability
- What are the different types of carburizing? Choose the Right Process for Your Steel Parts
- Why is a vacuum drying oven required for NCM-811 and LTO? Ensure Stability in Solid-State Battery Assembly
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?
- How does a high-temperature heat treatment furnace facilitate solution annealing? Master Alloy Microstructure Control



















