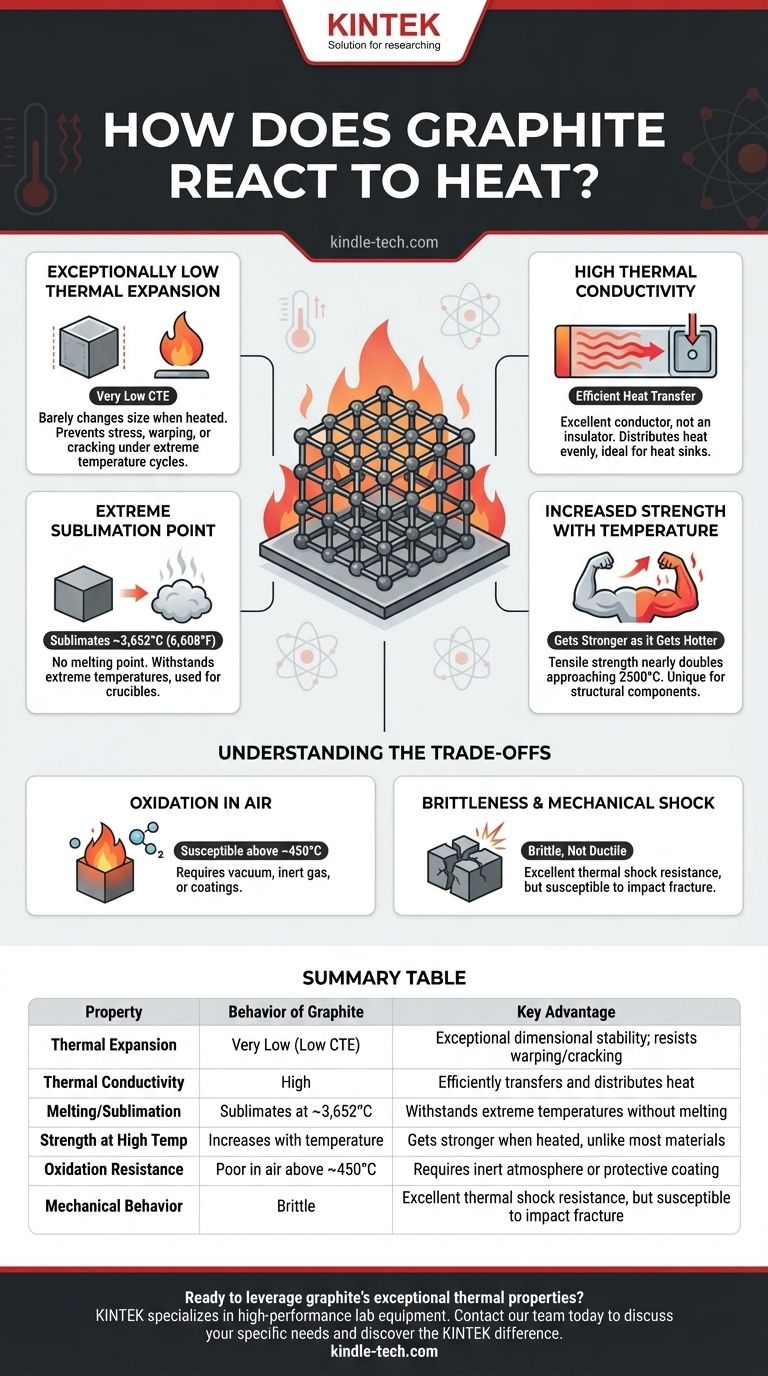
In response to heat, graphite demonstrates exceptional stability and performance, making it one of the most reliable materials for high-temperature applications. Unlike most substances, it has a remarkably low coefficient of thermal expansion, meaning it barely changes size when heated. Furthermore, it possesses high thermal conductivity and maintains its structural integrity at temperatures that would vaporize most metals.
The core takeaway is that graphite's reaction to heat is not a single behavior but a combination of unique properties: it resists expansion, efficiently transfers heat, and actually gets stronger as temperatures rise, all before finally sublimating at an extremely high point.
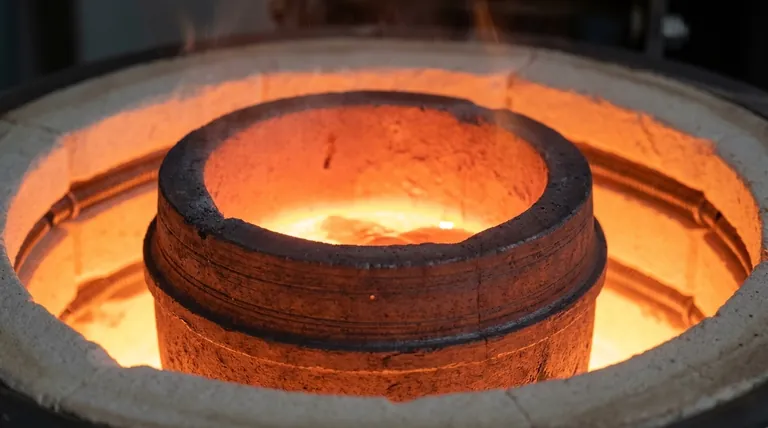

The Core Thermal Properties of Graphite
To understand why graphite is a cornerstone material in high-temperature engineering, we must look beyond a single metric and examine its cluster of thermal characteristics.
Exceptionally Low Thermal Expansion
The most notable property is its very low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE). When most materials get hot, their atoms vibrate more and push apart, causing the material to expand.
Graphite's strong, layered atomic structure resists this effect. This dimensional stability is critical, as it prevents stress, warping, or cracking in components that undergo extreme temperature cycles.
High Thermal Conductivity
Contrary to what one might expect from a heat-resistant material, graphite is an excellent thermal conductor, not an insulator. It efficiently pulls heat away from a source and distributes it evenly.
Think of it as a "heat highway." This property is essential for applications like heat sinks, where the goal is to move thermal energy away from sensitive components as quickly as possible.
Extreme Sublimation Point
Graphite does not have a melting point at atmospheric pressure. Instead, it sublimates—turning directly from a solid into a gas—at an incredibly high temperature of approximately 3,652°C (6,608°F).
This extreme temperature resistance is why graphite is the material of choice for crucibles used to melt steel and other high-temperature alloys.
Increased Strength with Temperature
Perhaps its most counter-intuitive property is that graphite gets stronger as it gets hotter. Most materials, especially metals, lose strength and become softer as temperatures rise.
Graphite's tensile strength nearly doubles from its room-temperature value as it approaches 2500°C. This makes it uniquely suited for structural components inside furnaces and rocket nozzles.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. Graphite's elite thermal performance comes with specific weaknesses that must be managed in any design.
Oxidation in the Presence of Air
The primary limitation of graphite is its susceptibility to oxidation. Being a form of carbon, it will react with oxygen in the air (effectively burning) at elevated temperatures, typically starting around 450°C.
To be used at its highest temperature ranges, graphite must be operated in a vacuum or an inert (non-reactive) gas atmosphere. Alternatively, it can be treated with special anti-oxidation coatings.
Brittleness and Mechanical Shock
Like many ceramic materials, graphite is brittle. It lacks the ductility of metals, meaning it will fracture under sudden impact or high mechanical stress rather than bending or deforming.
While its low CTE provides excellent resistance to thermal shock (cracking from rapid temperature change), careful handling and design are necessary to avoid mechanical failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting graphite is a strategic decision based on its unique profile. Use these guidelines to determine if it fits your project's goals.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability during extreme temperature changes: Graphite's ultra-low CTE makes it a superior choice over almost any metal.
- If your primary focus is managing high heat loads without melting: Graphite's extreme sublimation point and ability to strengthen with heat are its key advantages, but you must account for oxidation.
- If your primary focus is rapid heat dissipation: Graphite's high thermal conductivity makes it an ideal material for heat sinks and thermal spreaders in electronics and industrial processes.
By understanding these distinct thermal behaviors, you can confidently leverage graphite's strengths while mitigating its limitations in your design.
Summary Table:
| Property | Behavior of Graphite | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Expansion | Very Low (Low CTE) | Exceptional dimensional stability; resists warping/cracking |
| Thermal Conductivity | High | Efficiently transfers and distributes heat |
| Melting/Sublimation | Sublimates at ~3,652°C (6,608°F) | Withstands extreme temperatures without melting |
| Strength at High Temp | Increases with temperature | Gets stronger when heated, unlike most materials |
| Oxidation Resistance | Poor in air above ~450°C | Requires inert atmosphere or protective coating |
| Mechanical Behavior | Brittle | Excellent thermal shock resistance, but susceptible to impact fracture |
Ready to leverage graphite's exceptional thermal properties in your lab or process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including graphite components designed for extreme conditions. Our experts can help you select the right materials to enhance your application's efficiency, stability, and safety. Contact our team today to discuss your specific high-temperature needs and discover the KINTEK difference.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the mechanical properties of graphite? Harnessing Rigidity and Managing Brittleness
- Is graphite good in high temperature? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Potential
- Why can graphite withstand heat? Unlocking Its Extreme Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- Is graphite good for high temperature? Unlock Its Full Potential in Controlled Atmospheres
- What is the temperature resistance of graphite? Unlocking Its High-Temp Potential in Your Lab



















