At its core, an electron beam is a highly controlled stream of high-energy electrons manipulated within a vacuum. It is generated by heating a filament to release electrons, which are then rapidly accelerated by a strong voltage gradient. This focused beam of particles serves as a powerful tool for transferring precise amounts of energy to a target.
The true value of an electron beam lies not just in creating a stream of particles, but in its ability to be precisely accelerated and steered by electric and magnetic fields. This control turns a simple physical phenomenon into a versatile instrument for everything from welding to creating advanced optical coatings.
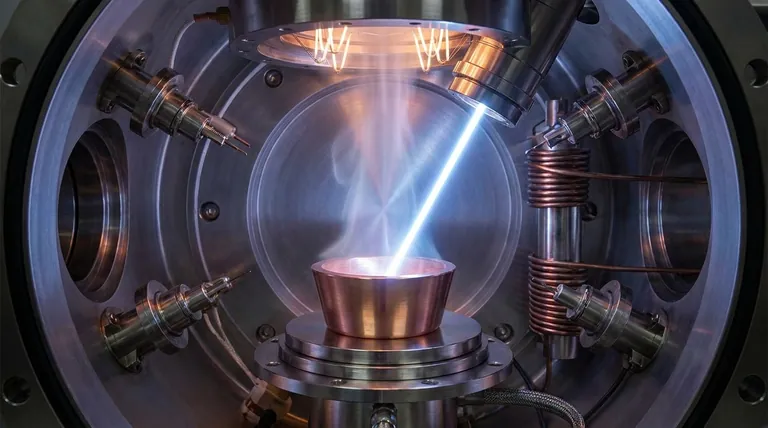
The Three Core Principles of an Electron Beam
To understand how an electron beam works, we must break the process down into three fundamental stages: generation, acceleration, and control. These stages must occur in a vacuum to be effective.
Generation: Releasing the Electrons
The process begins with a simple component, typically a tungsten filament. When this filament is heated to a very high temperature, it undergoes a process called thermionic emission.
This heating gives the electrons within the filament material enough energy to escape from its surface, forming a cloud of free electrons ready to be manipulated.
Acceleration: Creating a High-Energy Stream
Once the electrons are free, a powerful voltage gradient is applied. A high positive voltage (anode) is placed opposite the negatively charged filament (cathode).
This strong electric field forcefully attracts the negatively charged electrons, pulling them away from the filament and accelerating them to extremely high speeds through a vacuum tube.
Control: Steering and Focusing the Beam
A raw, accelerated beam is not useful without control. This is achieved using electromagnets.
By precisely varying the magnetic fields, the electron beam can be focused to a fine point or scanned across a surface in a controlled pattern, much like a pencil drawing a line. This steering capability is what allows the beam to be used for specific tasks.
A Practical Application: Electron Beam Deposition
Understanding the principles is one thing; seeing them in action clarifies their purpose. One common application is electron beam deposition, used to create ultra-thin optical coatings.
The Goal: Vaporizing Material
In this process, the highly focused electron beam is directed at a source material, such as a crucible of granular ceramic or metal.
The intense, concentrated energy from the electrons strikes the material, heating it so rapidly that it vaporizes directly into a gas.
The Process: Creating a Conformal Coating
This vaporized material travels through the vacuum chamber and condenses onto a target surface, such as a lens or a semiconductor wafer.
Through precise computer control of the beam's power and position, engineers can build up exceptionally uniform and pure coatings with a pre-specified thickness, often just a few molecules at a time.
Enhancing the Result
Sometimes, the process is enhanced with a secondary ion beam. This beam bombards the condensing material, increasing its adhesion energy and creating coatings that are denser, more robust, and have less internal stress.
Understanding the Key Requirements
The power of an electron beam comes with specific operational demands and trade-offs that define its use cases.
The Necessity of a Vacuum
The entire process must occur in a high vacuum. If air molecules were present, the electrons would collide with them, scattering the beam and causing it to lose its energy and focus.
This vacuum requirement makes the equipment complex and can limit the size of the objects being processed.
High Voltage and Power
Generating and accelerating electrons requires significant electrical power and high-voltage systems. This has direct implications for the cost, safety protocols, and infrastructure needed to operate the equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use electron beam technology depends entirely on the required outcome.
- If your primary focus is precision energy delivery: The ability to focus a high-energy beam onto a microscopic spot makes it ideal for applications like high-purity welding, micro-machining, or semiconductor manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity, thin-film coatings: Electron beam deposition is a superior method for producing the dense, durable, and highly specific layers required for advanced optics and electronics.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, low-cost surface treatment: The vacuum and high-voltage requirements may make other technologies, such as chemical deposition or spray coatings, a more practical choice.
Ultimately, the electron beam is a powerful and precise tool for manipulating materials at a fundamental level, provided the process operates within its required high-vacuum environment.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Component | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Generation | Tungsten Filament | Heated to release electrons via thermionic emission. |
| Acceleration | High Voltage Gradient | Accelerates electrons to high speeds in a vacuum. |
| Control | Electromagnets | Focuses and steers the beam for precise application. |
Ready to leverage the precision of electron beam technology in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including advanced electron beam systems for deposition, welding, and surface treatment. Our solutions help you achieve superior results in thin-film coating, material processing, and R&D.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and enhance your research capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the container that holds the metal source material called in e-beam evaporation? Ensure Purity and Quality in Your Thin-Film Deposition
- Can I solder copper to copper without flux? The Critical Role of Flux for a Strong Bond
- How thick is the sputter coating for SEM? Achieve Optimal Imaging & Analysis
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials
- How do you calculate coating coverage? A Practical Guide to Accurate Material Estimation



















