There is no single answer to how hot ceramic can be heated, as the term "ceramic" covers a vast range of materials with dramatically different properties. While common pottery may crack above 1200°C (2200°F), advanced technical ceramics can remain stable at temperatures exceeding 2200°C (4000°F). The specific limit is dictated entirely by the material's chemical composition and crystalline structure.
The question isn't just about a ceramic's maximum temperature, but also about its ability to withstand rapid temperature changes. Understanding the specific type of ceramic and its intended application is critical to avoiding catastrophic failure from heat or thermal shock.

Why "Ceramic" is Too Broad a Term
The properties of a ceramic are a direct result of its raw materials and manufacturing process. We can broadly separate them into two categories: traditional clay-based ceramics and modern technical ceramics.
Traditional Ceramics (Pottery & Cookware)
These are the materials most people think of, made primarily from natural clays and minerals. Their temperature limits are defined by the point at which they vitrify (turn glass-like) or their glazes begin to fail.
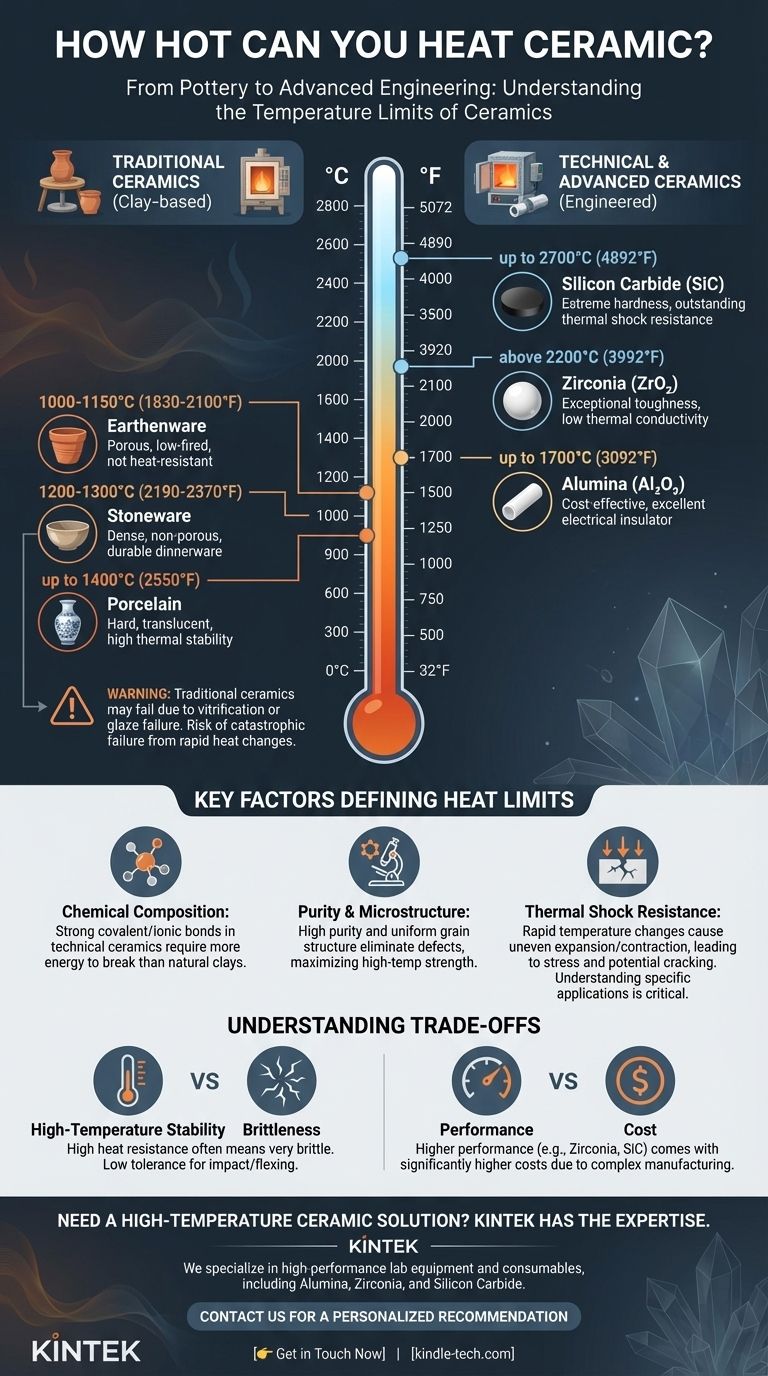
- Earthenware: A porous, low-fired ceramic that is typically fired between 1000-1150°C (1830-2100°F). It is not very strong or heat-resistant.
- Stoneware: A dense, non-porous ceramic fired at higher temperatures, usually 1200-1300°C (2190-2370°F). It is durable and often used for dinnerware and bakeware.
- Porcelain: A very hard, translucent ceramic fired at the highest temperatures for traditional pottery, up to 1400°C (2550°F). It is known for its strength and high thermal stability compared to other clays.
Technical & Advanced Ceramics (Engineered Materials)
These materials are not made from natural clay but are synthesized from highly pure inorganic compounds like oxides, carbides, and nitrides. They are engineered for extreme performance in industrial, aerospace, and medical applications.
- Alumina (Aluminum Oxide, Al₂O₃): A very common and cost-effective technical ceramic. It serves as an excellent electrical insulator and can operate continuously at temperatures up to 1700°C (3092°F).
- Zirconia (Zirconium Dioxide, ZrO₂): Known for exceptional toughness and low thermal conductivity. It maintains its strength at high temperatures and can be used in applications above 2200°C (3992°F).
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): Extremely hard and has outstanding thermal shock resistance. It does not melt at normal pressures but rather decomposes at temperatures around 2700°C (4892°F).
Key Factors That Define a Ceramic's Heat Limit
It’s not just one property, but a combination of factors that determines a ceramic's thermal performance.
Chemical Composition & Bonding
The strong covalent and ionic bonds in technical ceramics like silicon carbide require far more energy (heat) to break than the bonds in the complex silicates found in natural clay. This fundamental difference in atomic structure is the primary reason for their superior temperature resistance.
Purity and Microstructure
Impurities in a ceramic can create points of weakness or lower the material's melting point. Technical ceramics are manufactured with highly controlled purity and a dense, uniform grain structure to eliminate these defects and maximize strength at high temperatures.
The Critical Role of Thermal Shock
A material's maximum temperature is only half the story. Thermal shock is the stress induced in a material when different parts of it expand or contract at different rates due to rapid temperature changes.
Because ceramics are poor heat conductors, heating or cooling one part of an object quickly creates immense internal stress. This stress easily exceeds the material's strength, causing it to crack. This is why an oven-safe stoneware dish can shatter if you pour cold water on it while it's hot.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a ceramic for a high-temperature application involves balancing competing properties. There is no single "best" material.
High-Temperature Resistance vs. Brittleness
Ceramics that are exceptionally stable at high temperatures are almost always very brittle. While they resist heat, they have very low tolerance for mechanical impact or flexing.
Performance vs. Cost
There is a direct and steep correlation between a ceramic's performance and its price. Alumina offers a great balance for many applications, but moving to higher-performance materials like zirconia or silicon carbide increases the cost significantly due to complex manufacturing processes.
Machinability
Traditional ceramics are shaped when they are soft (as clay) and then fired. Technical ceramics are often manufactured into a rough shape and then must be machined with extremely hard diamond tools. This post-processing is slow and expensive, adding to the final cost.
Choosing the Right Ceramic for Your Application
Your choice must be guided by your specific goal and operating conditions.
- If your primary focus is home baking or pottery: Traditional stoneware and porcelain are ideal, as they are designed to withstand the heat of a kitchen oven or hobbyist kiln (up to ~1300°C).
- If your primary focus is building a furnace or kiln: Refractory ceramics like alumina, mullite, or specialized firebricks are necessary to handle continuous, high operating temperatures (1500-1800°C).
- If your primary focus is an extreme-environment application (e.g., rocket nozzles, turbine blades, or cutting tools): You must use advanced technical ceramics like zirconia, silicon carbide, or ceramic matrix composites designed for temperatures above 2000°C.
Understanding the specific type of ceramic is the first step to harnessing its incredible thermal capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Ceramic Type | Typical Maximum Temperature | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Earthenware | 1000-1150°C (1830-2100°F) | Porous, low-fired, common pottery |
| Stoneware | 1200-1300°C (2190-2370°F) | Dense, non-porous, durable for dinnerware |
| Porcelain | Up to 1400°C (2550°F) | Hard, translucent, high thermal stability |
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | Up to 1700°C (3092°F) | Cost-effective, excellent electrical insulator |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | Above 2200°C (3992°F) | Exceptional toughness, low thermal conductivity |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to 2700°C (4892°F) | Extreme hardness, outstanding thermal shock resistance |
Need a High-Temperature Ceramic for Your Lab?
Choosing the right ceramic is critical for your application's success and safety. Whether you're building a furnace, designing a high-temperature experiment, or need durable labware, KINTEK has the expertise and products to help.
We specialize in supplying high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a wide range of advanced technical ceramics like alumina, zirconia, and silicon carbide. Our team can help you select the perfect material based on your specific temperature requirements, thermal shock resistance, and budget.
Contact us today to discuss your project and get a personalized recommendation. Let KINTEK be your partner in achieving precise and reliable high-temperature results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Aluminum Oxide Al2O3 Heat Sink for Insulation
People Also Ask
- Is silicon carbide better than ceramic? Discover the Superior Technical Ceramic for Your Application
- What is the strongest ceramics? Silicon Carbide Leads in Hardness & Thermal Strength
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide ceramics? Solve Extreme Engineering Challenges
- What are the properties of SiC? Unlock High-Temperature, High-Frequency Performance
- Which is harder silicon carbide or tungsten carbide? Discover the Key to Material Selection



















