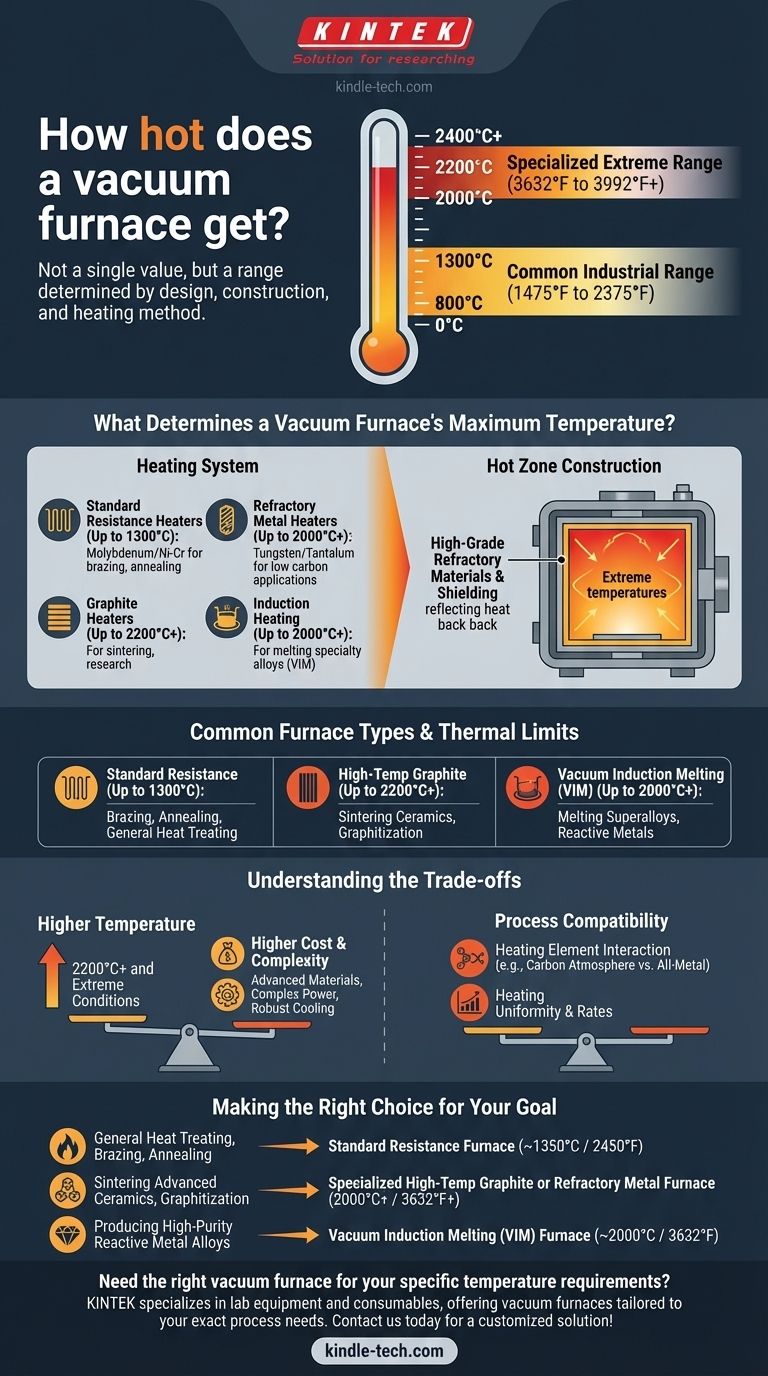
The maximum temperature of a vacuum furnace is not a single value but a range determined by its specific design, construction, and heating method. While many common industrial furnaces operate in the range of 800°C to 1300°C (1475°F to 2375°F), specialized furnaces using graphite or refractory metal heating elements can achieve temperatures of 2200°C (3992°F) and beyond.
The term "vacuum furnace" covers a wide array of technologies for different industrial processes. Therefore, the critical question is not for a single maximum temperature, but rather: which type of vacuum furnace has the thermal capability required for your specific material and process?
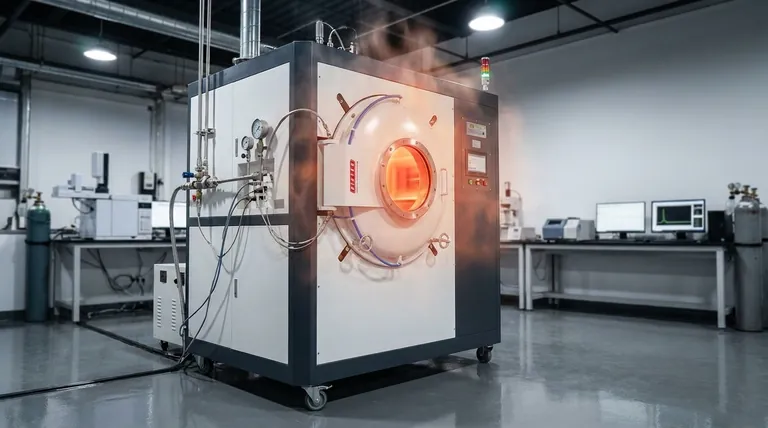

What Determines a Vacuum Furnace's Maximum Temperature?
The ultimate temperature rating of a vacuum furnace is a result of an engineered system. The limit is defined by the component with the lowest tolerance for heat.
The Role of the Heating System
The heart of the furnace is its heating system, and the material used for the heating elements is the primary factor limiting temperature.
- Standard Resistance Heaters: Molybdenum or nickel-chromium alloys are common in general-purpose furnaces for applications like brazing and annealing, typically reaching up to 1300°C.
- Graphite Heaters: For higher temperatures, graphite elements are used. These are capable of reaching 2200°C or more, making them ideal for sintering and materials research.
- Refractory Metal Heaters: Elements made from tungsten or tantalum can also achieve temperatures above 2000°C and are chosen when carbon from graphite elements would be detrimental to the workpiece.
- Induction Heating: Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnaces use electromagnetic induction to heat a conductive crucible, which then melts the material inside. These systems regularly achieve temperatures of 2000°C for melting specialty alloys.
Hot Zone Construction
The area containing the heating elements and the workload is called the "hot zone." Its construction is critical for both reaching and containing extreme temperatures.
High-grade refractory materials, such as ceramic fiber insulation or layers of metallic radiation shielding, are used to reflect heat back into the workspace and protect the furnace chamber walls and vacuum seals. A failure in this insulation system defines a hard limit on the furnace's safe operating temperature.
Common Furnace Types and Their Thermal Limits
Different vacuum furnace designs are optimized for different temperature ranges and applications.
Resistance Furnaces (The Workhorse)
These are the most common type of vacuum furnace. They use resistive heating elements and are frequently used for processes that require precise temperature control.
A typical heat-treating cycle might involve holding at 800°C before slowly ramping to 1100°C-1200°C for final processing.
High-Temperature Graphite Furnaces
Built specifically for extreme heat, these furnaces utilize graphite for both the heating elements and the hot zone insulation.
They are capable of sustained operation at temperatures up to 2200°C, necessary for applications like sintering technical ceramics or graphitizing carbon components.
Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) Furnaces
VIM furnaces are designed for melting and casting high-purity metals and alloys. The technology is optimized for reaching the melting point of materials in a clean environment.
These furnaces can readily achieve the 2000°C range required to melt superalloys, titanium, and other reactive metals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace based on its maximum temperature involves balancing several critical factors.
Temperature vs. Cost
The relationship between maximum temperature and cost is exponential. A furnace rated for 2200°C is substantially more expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain than a 1300°C model due to its advanced materials, complex power supply, and robust cooling systems.
Process Compatibility
Higher temperature capability is not always better. The heating element material itself can interact with the parts being processed. For example, the carbon atmosphere from a graphite hot zone can carburize certain metals, which may be undesirable. In such cases, a furnace with all-metal (molybdenum or tungsten) internals is required.
Heating Rates and Uniformity
Achieving a uniform temperature across a large workload becomes more challenging at extreme temperatures. Specialized designs are required to ensure that all parts of the load reach the target temperature at the same time, which adds to the system's complexity and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Base your furnace selection on the specific demands of your process, not just the highest available temperature.
- If your primary focus is general heat treating, brazing, or annealing of standard alloys: A resistance furnace with a maximum temperature around 1350°C (2450°F) is typically the most sufficient and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is sintering advanced ceramics, growing crystals, or graphitization: You will require a specialized high-temperature graphite or refractory metal furnace capable of reaching 2000°C (3632°F) or more.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity, reactive metal alloys like titanium or superalloys: A Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace is the appropriate technology, offering both the necessary temperatures and a tightly controlled melting environment.
Ultimately, defining the specific thermal requirements of your application is the first step toward selecting the correct and most efficient furnace technology.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Common Temperature Range | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Resistance | Up to 1300°C | Brazing, annealing, general heat treating |
| High-Temperature Graphite | Up to 2200°C+ | Sintering ceramics, graphitization |
| Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) | Up to 2000°C+ | Melting superalloys, reactive metals |
Need the right vacuum furnace for your specific temperature requirements? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering vacuum furnaces tailored to your exact process needs—from standard heat treating to high-temperature sintering and melting. Our experts will help you select the perfect system to achieve precise temperature control, uniform heating, and optimal results for your materials. Contact us today to discuss your application and get a customized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the structure of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components & Functions
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What is vacuum furnace high temperature? Unlock the Range for Your Material Processing
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries



















