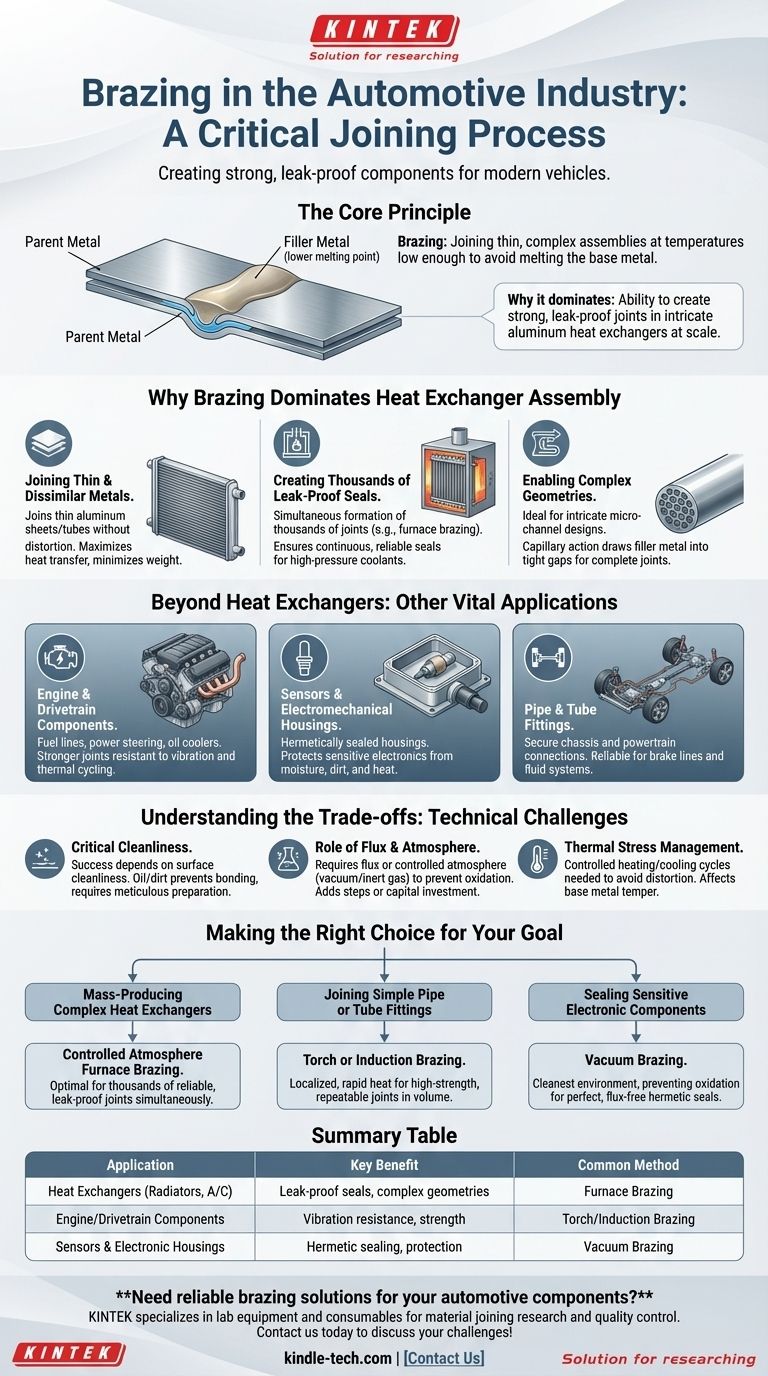
In the automotive industry, brazing is a critical joining process used to manufacture essential components that manage heat and fluids. It is the primary method for assembling aluminum heat exchangers like radiators, air conditioning condensers, and evaporators, as well as various engine and electromechanical parts.
The core reason brazing is indispensable in automotive manufacturing is its ability to create strong, leak-proof joints in thin, complex aluminum assemblies at temperatures low enough to avoid melting the parent metal—a feat that is often impractical or impossible with conventional welding.

Why Brazing Dominates Heat Exchanger Assembly
Modern vehicles rely on compact, efficient heat exchangers to manage everything from engine temperature to cabin climate. Brazing is uniquely suited to produce these intricate components at scale.
Joining Thin and Dissimilar Metals
Automotive radiators and A/C condensers are built from very thin aluminum sheets and tubes to maximize heat transfer and minimize weight. Brazing uses a filler metal with a lower melting point than the aluminum itself, allowing the components to be joined without distorting or melting the delicate base materials.
Creating Thousands of Leak-Proof Seals
A single heat exchanger can have thousands of individual joints between the tubes, fins, and headers. Brazing, particularly furnace brazing where the entire assembly is heated, allows all of these joints to be formed simultaneously. This process ensures a continuous, leak-proof seal that can reliably contain high-pressure refrigerants and coolants.
Enabling Complex Geometries
The design of modern micro-channel heat exchangers is highly complex, featuring intricate pathways to improve thermal efficiency. Brazing is perfectly suited for these designs, as the molten filler metal is drawn into the tight gaps between parts by capillary action, ensuring a complete and thorough joint throughout the entire structure.
Beyond Heat Exchangers: Other Key Applications
While heat exchangers are the most prominent example, brazing is used for other vital automotive components where strength and reliability are paramount.
Engine and Drivetrain Components
Brazing is used to join pipes and fittings for fuel lines, power steering lines, and transmission oil coolers. In these applications, it provides a joint that is stronger than the parent metals and highly resistant to vibration and thermal cycling.
Sensors and Electromechanical Housings
Many sensors and electronic modules require hermetically sealed housings to protect sensitive internal components from moisture, dirt, and heat. Brazing creates a robust, permanent metal-to-metal seal ideal for this purpose.
Pipe and Tube Fittings
Throughout a vehicle's chassis and powertrain, numerous steel and aluminum tubes must be joined securely. Brazing is a reliable method for attaching fittings and creating strong connections for brake lines and other fluid-carrying systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, brazing is a technically demanding process with specific requirements that present engineering challenges.
The Critical Need for Cleanliness
Brazing success is entirely dependent on the cleanliness of the metal surfaces. Any oil, dirt, or oxidation will prevent the filler metal from wetting and bonding with the parent material, leading to a failed joint. This requires meticulous preparation and handling.
The Role of Flux and Atmosphere
To prevent oxidation during heating, brazing requires either a chemical flux or a controlled, oxygen-free atmosphere (like a vacuum or inert gas). Flux residue must often be cleaned post-braze, adding a step, while controlled atmosphere furnaces represent a significant capital investment.
Thermal Stress Management
Heating an entire assembly to brazing temperature can introduce thermal stress or cause distortion if not managed with proper fixtures and controlled heating/cooling cycles. It can also affect the heat treatment and temper of the base metals, which must be accounted for in the design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific brazing method is chosen based on the component's design, material, and production volume.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing complex heat exchangers: Controlled atmosphere furnace brazing is the optimal method for creating thousands of reliable, leak-proof joints simultaneously.
- If your primary focus is joining simple pipe or tube fittings: Torch brazing or induction brazing provides a more localized and rapid heat source for high-strength, repeatable joints in high volume.
- If your primary focus is sealing sensitive electronic components: Vacuum brazing provides the cleanest possible environment, preventing oxidation and ensuring a perfect, flux-free hermetic seal.
Ultimately, brazing is an enabling technology that allows for the creation of lightweight, efficient, and reliable components that are fundamental to modern vehicle performance.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Common Method |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Exchangers (Radiators, A/C) | Leak-proof seals, complex geometries | Furnace Brazing |
| Engine/Drivetrain Components | Vibration resistance, strength | Torch/Induction Brazing |
| Sensors & Electronic Housings | Hermetic sealing, protection | Vacuum Brazing |
Need reliable brazing solutions for your automotive components? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for material joining research and quality control. Whether you're developing new heat exchangers or testing brazed joints, our expertise can help ensure your processes are efficient and your products are durable. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your automotive manufacturing challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What are some applications of brazing? Join Dissimilar Metals with Strong, Leak-Proof Bonds
- Why would you braze instead of weld? Preserve Material Integrity and Join Dissimilar Metals
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries
- What is the process of vacuum brazing? Achieve High-Purity, Strong Metal Joining



















