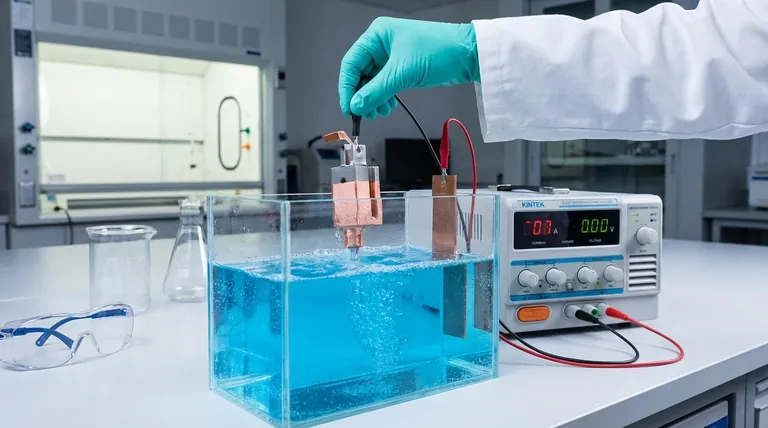
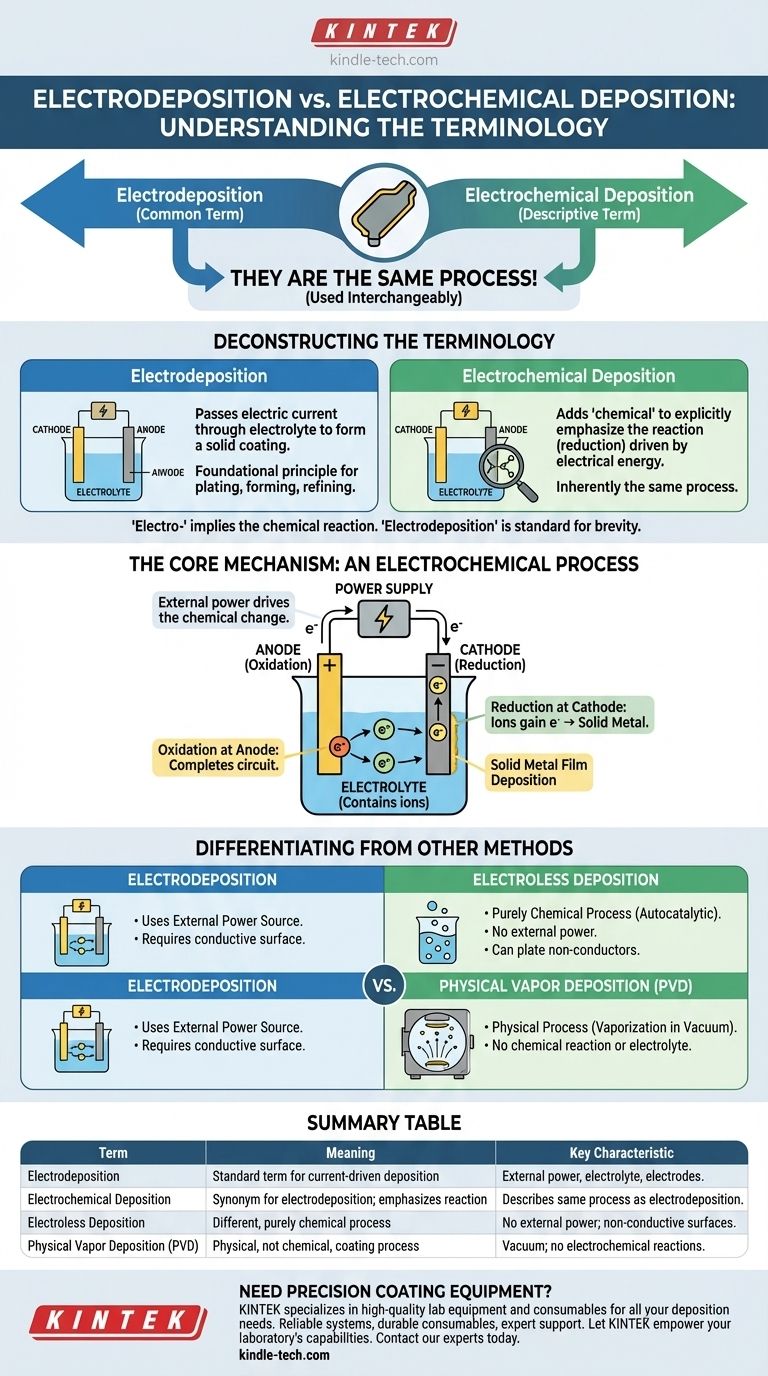
In practice, there is no difference between electrodeposition and electrochemical deposition. The two terms are used interchangeably to describe the exact same process of depositing a material onto a conductive surface using an electric current.
The term "electrochemical deposition" is simply a more descriptive, but redundant, way of saying "electrodeposition." The "electro-" prefix already implies that the deposition is driven by an electrochemical reaction. For clarity and conciseness, "electrodeposition" is the standard and more common term.

Deconstructing the Terminology
To understand why these terms are synonymous, it’s helpful to break down what each word implies. The confusion arises from verbiage, not from any difference in the underlying science.
What "Electrodeposition" Means
Electrodeposition is a process where an electric current is passed through a solution (an electrolyte) to cause dissolved metal ions to form a solid coating onto an electrode. It is the foundational principle behind electroplating, electroforming, and electrorefining.
The process always involves an external power source, a cathode (the object to be coated), an anode, and an electrolyte containing the ions to be deposited.
What "Electrochemical Deposition" Means
Adding the word "chemical" to create "electrochemical deposition" is done to explicitly highlight the nature of the reaction. It emphasizes that the deposition is the result of a chemical change—specifically, a reduction reaction—driven by electrical energy.
While technically correct, it's redundant. All electrodeposition is inherently an electrochemical process. You cannot have one without the other.
Why They Are Used Interchangeably
The scientific and engineering communities treat the terms as synonyms. "Electrodeposition" is overwhelmingly preferred due to its brevity. You might see "electrochemical deposition" used in academic papers or textbooks when an author wants to be particularly explicit for educational purposes, but it does not describe a different technique.
The Core Mechanism: An Electrochemical Process
Regardless of the term you use, the underlying mechanism is the same. Understanding this mechanism clarifies why the "chemical" part is already included in the "electro-" part.
The Role of the Electric Current
An external power supply creates a potential difference between two electrodes submerged in the electrolyte. This electrical energy is what drives a chemical reaction that would not occur spontaneously.
Reduction at the Cathode
The surface to be coated is set up as the cathode (the negative electrode). Positively charged metal ions from the electrolyte are attracted to the cathode. At the surface, they gain electrons (a process called reduction) and are deposited as a neutral, solid metal film.
This transformation of an ion in solution into a solid atom on a surface is the "deposition" and it is fundamentally a chemical change.
Oxidation at the Anode
To complete the electrical circuit, a corresponding reaction must occur at the anode (the positive electrode). Typically, the anode material is oxidized, dissolving into the electrolyte as ions, or another reaction (like the evolution of oxygen from water) takes place.
Differentiating from Other Deposition Methods
The real distinction you need to understand is not between "electrodeposition" and "electrochemical deposition," but between electrodeposition and other coating techniques that do not use an external electric current.
Electroless Deposition
This is the most common point of confusion. Electroless deposition is a purely chemical process that does not use an external power source. The deposition is driven by an autocatalytic chemical reaction within the solution itself. This method is used to plate non-conductive surfaces, which is impossible with standard electrodeposition.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
PVD is a completely different category of coating technology. It is a physical process, not a chemical one. In PVD, a solid material is vaporized in a vacuum and condenses onto the substrate, atom by atom. There are no chemical reactions or electrolytes involved.
How to Use These Terms Correctly
Clarity in technical communication is paramount. Here is how to apply this understanding.
- If your primary focus is standard communication: Use "electrodeposition." It is the correct, concise, and most widely understood term in industry and academia.
- If you are explaining the concept for the first time: You might use "electrochemical deposition" once to emphasize that the process involves a chemical reaction, before reverting to the standard term.
- If you are distinguishing from other techniques: Be explicit. State that you are using "electrodeposition, not electroless deposition," to prevent critical misunderstandings.
Ultimately, knowing that these two terms refer to the same process empowers you to read technical literature and communicate with colleagues without confusion.
Summary Table:
| Term | Meaning | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Electrodeposition | Standard term for depositing material using an electric current. | Uses an external power source, electrolyte, and electrodes. |
| Electrochemical Deposition | Synonym for electrodeposition; emphasizes the chemical reaction. | Describes the same process as electrodeposition. |
| Electroless Deposition | A different, purely chemical process. | No external power source; used for non-conductive surfaces. |
| Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | A physical, not chemical, coating process. | Occurs in a vacuum; no electrolyte or electrochemical reactions. |
Need Precision Coating Equipment for Your Lab?
Understanding the nuances of deposition techniques is key to selecting the right equipment for your research or production needs. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your deposition and coating applications.
We provide:
- Reliable electrodeposition/plating systems.
- Durable consumables and electrolytes.
- Expert support to help you choose the perfect solution for your specific materials and substrates.
Let KINTEK empower your laboratory's capabilities. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can meet your precise requirements and enhance your workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
People Also Ask
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is the plasma CVD process? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















