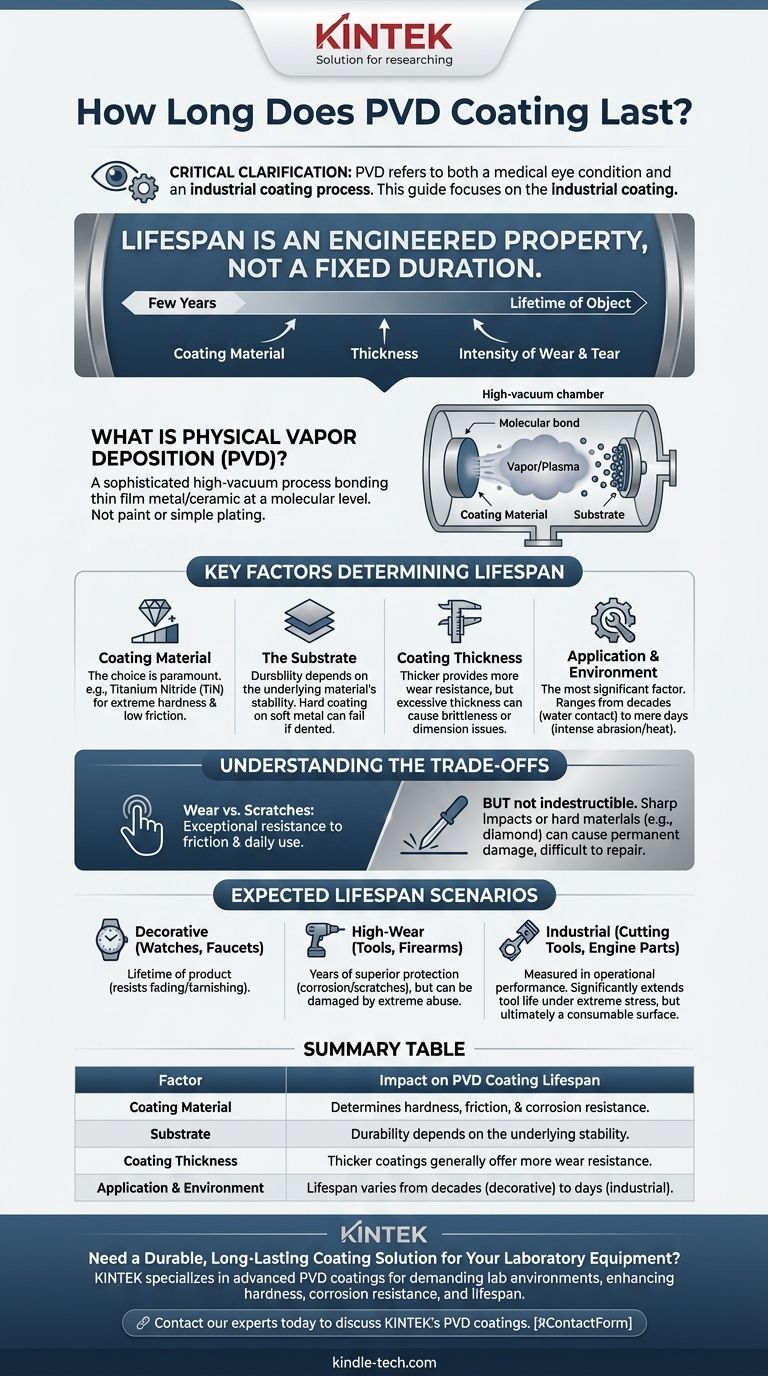
Before we begin, it's critical to clarify. The acronym "PVD" refers to two vastly different things: a medical eye condition (Posterior Vitreous Detachment) and an industrial coating process (Physical Vapor Deposition). This guide focuses on the industrial coating, as its longevity is a question of material science and engineering. If you are seeking information on the eye condition, its symptoms typically resolve over six months, though eye floaters can sometimes persist longer.
The lifespan of a Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating is not a fixed duration but an engineered property. It can range from a few years to the lifetime of the object, depending entirely on the coating material, its thickness, and the intensity of wear and tear it is designed to withstand.

What is Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)?
Physical Vapor Deposition is a sophisticated finishing process conducted under a high vacuum. It is not a type of paint or a simple chemical bath; it is a process that physically bonds a thin film of metal or ceramic to a surface at a molecular level.
The Coating Process
In PVD, a solid coating material is vaporized into a plasma of atoms or molecules. This vapor is then deposited onto the object being coated, forming a thin, highly-adhered, and exceptionally durable surface.
Why It's So Durable
This process creates a bond that is far superior to traditional plating. Because the coating becomes an integral part of the substrate's surface, it is far less likely to chip, fade, or peel. The result is a finish that improves hardness, reduces friction, and resists oxidation.
Key Factors That Determine PVD Coating Lifespan
There is no single answer to "how long it lasts" because PVD coatings are engineered for specific applications. The lifespan is a direct result of several intentional design choices.
The Coating Material
The choice of material is paramount. A coating of Titanium Nitride (TiN), common on drill bits, is chosen for its extreme hardness and low friction. In contrast, other materials might be chosen for a specific color on a watch case, balancing aesthetics with durability.
The Substrate It's Applied To
The coating is only as durable as the material underneath it. A hard PVD coating on a soft metal can still be damaged if the underlying metal is dented, causing the coating to deform and fail. A proper bond requires a stable and well-prepared substrate.
The Thickness of the Coating
Generally, a thicker coating provides more wear resistance and a longer lifespan. However, there are limits. An excessively thick coating can become brittle or alter the precise dimensions of a component, so thickness is carefully calculated based on the product's function.
The Application and Environment
This is the most significant factor. A PVD-coated faucet that only experiences contact with water and hands may last for decades. A PVD-coated industrial cutting tool subjected to intense heat and abrasion may be designed to last for thousands of operations, which could be mere days of continuous use.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PVD is a superior coating technology, it is essential to understand its practical limitations. It is highly resistant, but not indestructible.
Wear vs. Scratches
PVD coatings provide exceptional resistance to wear from friction and daily use. However, a sharp, direct impact or a deep scratch from a harder material (like diamond or silicon carbide) can still damage the surface.
Damage Is Often Permanent
For most consumer goods, a damaged PVD coating cannot be repaired. The process requires specialized industrial equipment, making it impractical to "touch up" a scratch on a watch or fixture.
Color and Function
The most durable PVD coatings are not always available in every desired color. The final appearance is a property of the material itself, leading to a trade-off between the desired aesthetic and the maximum possible hardness or longevity.
How Long Should You Expect Your PVD Coating to Last?
Evaluate the product's intended use to set a realistic expectation for the lifespan of its PVD coating.
- If your primary focus is decorative items (watches, faucets, jewelry): With reasonable care, the coating should resist fading and tarnishing for the lifetime of the product, far outlasting traditional plating.
- If your primary focus is high-wear consumer goods (firearms, knives, tools): The coating will provide years of superior protection against corrosion and scratches from normal use but can be damaged by extreme abrasion or impact.
- If your primary focus is industrial applications (cutting tools, engine parts): The lifespan is measured in operational performance and is designed to significantly extend the tool's life under extreme stress, but it is ultimately a consumable surface.
A PVD coating is best understood not by a time limit, but by its engineered ability to withstand its intended environment.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on PVD Coating Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Coating Material | Determines hardness, friction, and corrosion resistance (e.g., TiN for tools). |
| Substrate (Base Material) | The coating's durability depends on the stability of the underlying material. |
| Coating Thickness | Generally, thicker coatings offer more wear resistance and a longer life. |
| Application & Environment | Lifespan varies from decades (decorative items) to days (industrial cutting tools). |
Need a Durable, Long-Lasting Coating Solution for Your Laboratory Equipment?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced PVD coatings tailored to the demanding environments of laboratories. Our coatings enhance the hardness, corrosion resistance, and lifespan of your equipment and consumables, from precision tools to sample holders.
Let us engineer a solution that extends the life of your critical lab assets.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's PVD coatings can bring superior performance and value to your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells



















