To properly care for a glassy carbon sheet, it should be dried immediately after cleaning using a gentle stream of nitrogen gas or by allowing it to air-dry at room temperature. For storage, it must be placed in a clean, dry, non-corrosive environment, with a desiccator being the ideal choice for long-term preservation to protect its sensitive surface from contamination.
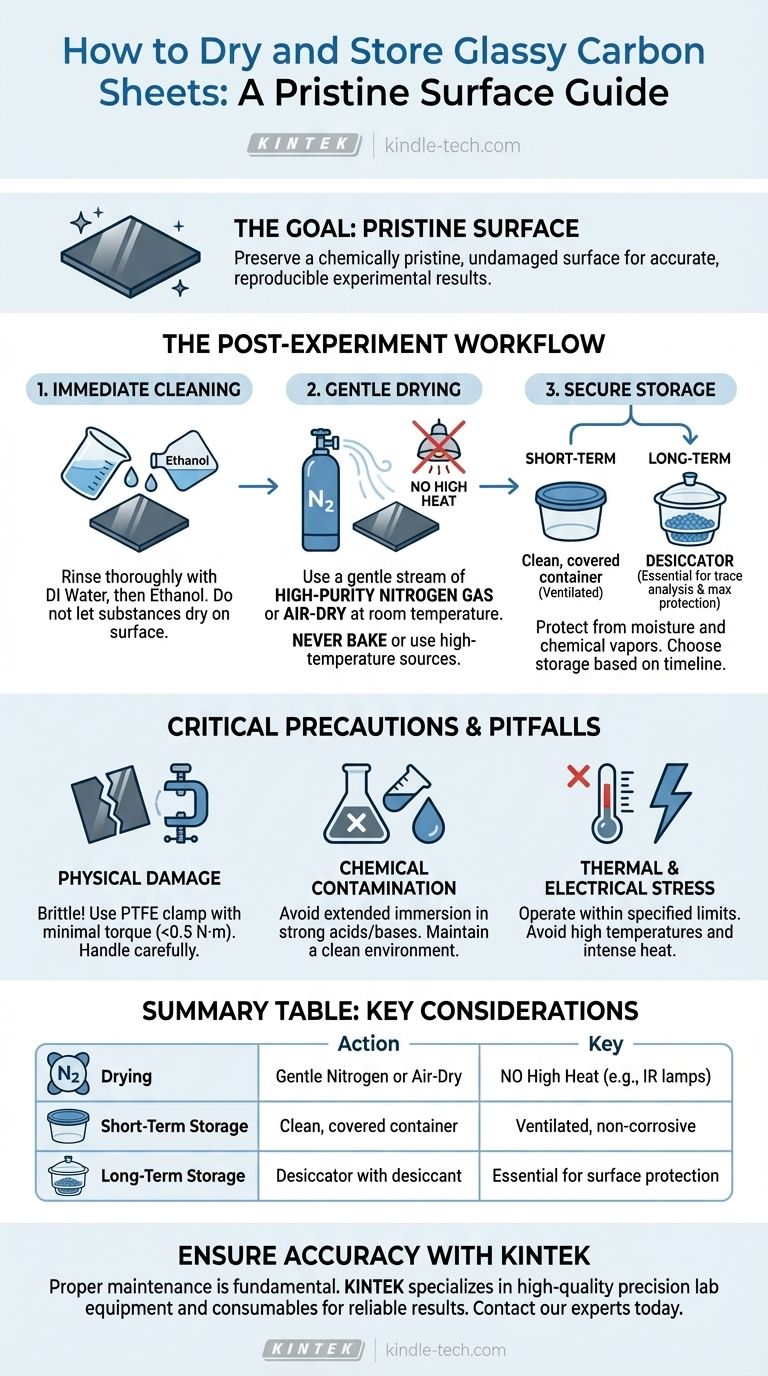
The core objective is not simply to dry and store the material, but to preserve a chemically pristine and physically undamaged surface. Every step, from cleaning to storage, is critical for ensuring the accuracy and reproducibility of your experimental results.

The Importance of a Pristine Surface
Glassy carbon is valued in electrochemistry for its wide potential window, chemical inertness, and low background current. However, its performance is entirely dependent on the condition of its surface.
Why Surface Condition is Critical
The surface of the glassy carbon is where all electrochemical reactions occur. Any form of contamination, from airborne particles to residual chemicals, can block active sites, introduce unwanted side reactions, or alter the material's conductive properties.
The Goal of Proper Handling
Proper cleaning, drying, and storage procedures are designed to create a reproducible surface. The goal is to ensure that the only variable in your experiment is the one you are intentionally studying, not a contaminated electrode.
The Post-Experiment Workflow
A disciplined post-experiment routine is the most effective way to prolong the life and performance of your glassy carbon sheets. This process should begin the moment an experiment concludes.
Step 1: Immediate Cleaning
The sheet must be cleaned immediately after use to prevent substances from drying and adsorbing onto the surface.
Start by rinsing the surface thoroughly with deionized water. For more stubborn impurities, follow with an ethanol rinse. Some protocols for PTFE-jacketed sheets involve brief, 5-second ultrasonications in solutions like 1:1 nitric acid, followed by ethanol/acetone and finally deionized water.
Step 2: Gentle Drying
Aggressive heating can damage the sheet's surface structure. Never bake the sheet under an infrared lamp or expose it to other high-temperature sources.
The best method is to use a gentle stream of high-purity nitrogen gas to blow the surface dry. Alternatively, you can let the sheet air-dry at room temperature in a clean, dust-free environment.
Step 3: Secure Storage
The storage environment must protect the sheet from moisture and chemical vapors.
For short-term storage, a clean, dry, and ventilated container is sufficient. For long-term storage, a desiccator containing a desiccant is strongly recommended to prevent atmospheric moisture from interacting with the surface.
Common Pitfalls and Handling Precautions
Physical and chemical damage are the two primary risks to a glassy carbon sheet. Avoiding common mistakes is as important as following the correct procedures.
Avoiding Physical Damage
Glassy carbon is brittle. When installing it in a holder or cell, use a PTFE clamp and apply minimal torque—no more than 0.5 N·M—to avoid cracking.
Always handle the sheet carefully, avoiding excessive bending, squeezing, or collisions with hard surfaces.
Preventing Chemical Contamination
Maintain a clean experimental environment to avoid contamination from organic substances or metal compounds.
Do not immerse the sheet in strong acids or bases for extended periods, as this can alter the surface chemistry. An exception is the very specific short-term storage or cleaning protocol of immersing in 1:1 nitric acid, which must be rinsed off completely before use.
Avoiding Thermal and Electrical Stress
Never allow the sheet to come into contact with high-temperature sources. This includes avoiding intense heat from lamps used for drying.
During experiments, always operate within the specified current and voltage limits for the material to prevent irreversible damage to its structure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your storage strategy should align with your experimental timeline and the level of sensitivity required for your work.
- If you are storing the sheet between experiments on the same day: A thorough rinse, air-drying, and placement in a clean, covered container is sufficient.
- If you are storing the sheet overnight or for a few days: Dry it completely with nitrogen and place it in a sealed container in a dry, ventilated area.
- If you are performing long-term storage or trace analysis: Drying with nitrogen and storing in a desiccator is the only way to guarantee a pristine, uncontaminated surface for future use.
Ultimately, treating your glassy carbon sheet with meticulous care is a direct investment in the quality and reliability of your data.
Summary Table:
| Step | Action | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Drying | Use a gentle stream of nitrogen gas or air-dry at room temperature. | Never use high heat (e.g., an infrared lamp). |
| Short-Term Storage | Place in a clean, dry, covered container. | Ensure a ventilated, non-corrosive environment. |
| Long-Term Storage | Store in a desiccator with desiccant. | Essential for trace analysis and maximum surface protection. |
Ensure the accuracy and longevity of your experiments with KINTEK's precision lab equipment.
Properly maintaining sensitive materials like glassy carbon electrodes is fundamental to reproducible science. KINTEK specializes in supplying the high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables—from desiccators to clean handling tools—that your lab needs to achieve reliable results.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect solutions for your laboratory's specific requirements. Get in touch via our contact form to discuss how we can support your research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
People Also Ask
- What is the ideal operating environment for a glassy carbon sheet? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What are the fundamental characteristics of glassy carbon? Discover its Unique Synergy of Properties
- Why is a glassy carbon disc electrode an indispensable consumable? Ensure Reliable Catalyst Evaluation Today
- What are the typical physical specifications for glassy carbon sheets? Unlock Superior Performance for Your Lab
- What is the applicable potential range for an RVC glassy carbon sheet? Master Your Electrochemical Analysis



















