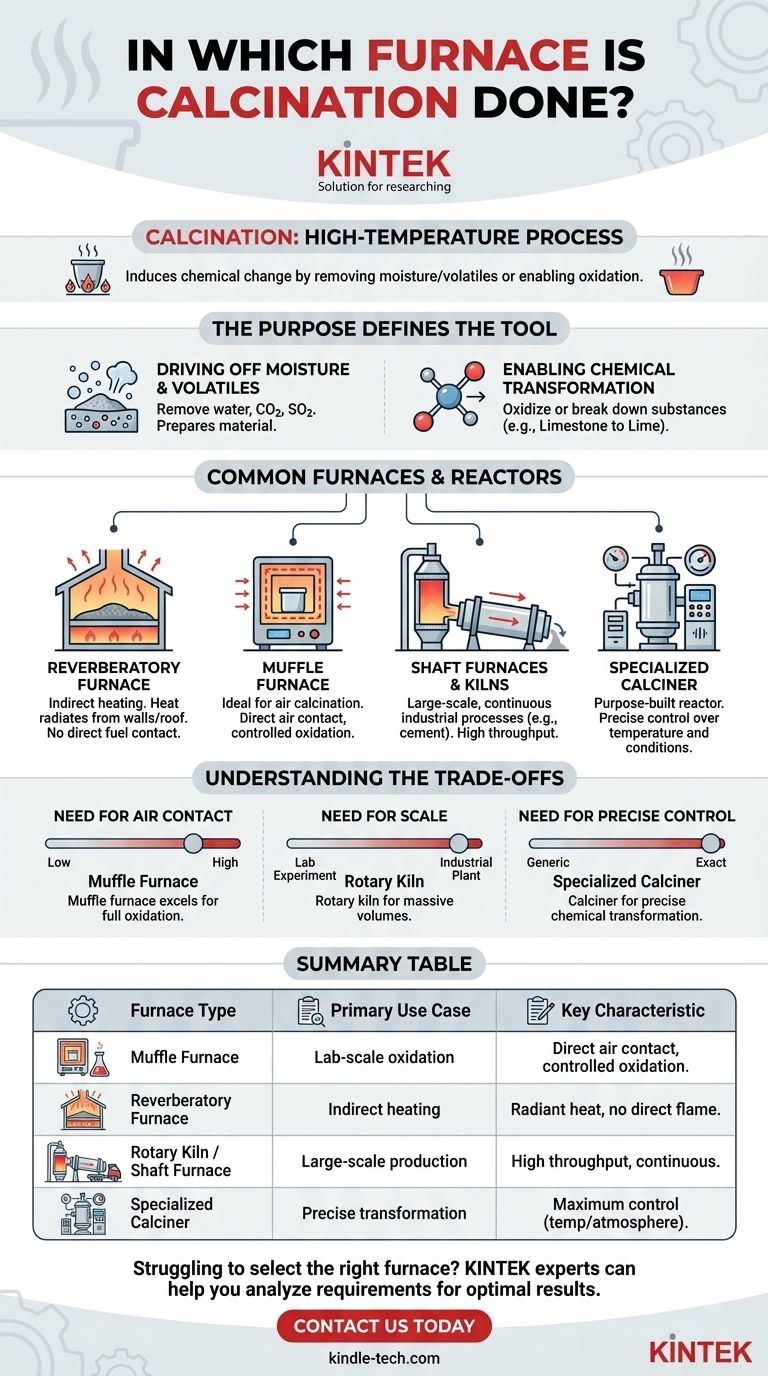
Calcination is a high-temperature process performed in several types of industrial furnaces and specialized reactors. The most common types include reverberatory furnaces, muffle furnaces, and shaft furnaces or kilns, with the specific choice depending entirely on the material and the desired outcome.
The term "calcination furnace" does not refer to a single piece of equipment. Instead, it describes a category of high-temperature reactors whose design is dictated by the core purpose of the process: to induce a chemical change by removing moisture, volatile compounds, or enabling oxidation.

The Purpose of Calcination Defines the Tool
Before selecting a furnace, it's critical to understand what the calcination process is designed to achieve. The furnace is simply the tool used to create the necessary controlled, high-temperature environment.
Driving Off Moisture and Volatiles
The most fundamental goal of calcination is to heat a substance to drive off absorbed water or volatile chemical components.
This includes removing compounds like carbon dioxide (CO2) or sulfur dioxide (SO2), which prepares the material for subsequent processing.
Enabling Chemical Transformation
Calcination is also used to trigger specific chemical changes. This can involve oxidizing part or all of a substance or breaking it down into a new compound.
The most prominent industrial example is in cement production, where calcination decomposes calcium carbonate into calcium oxide (lime) and carbon dioxide.
Common Furnaces and Reactors for Calcination
While various configurations exist, a few designs are consistently used for calcination due to their ability to manage heat and atmospheric conditions effectively.
The Reverberatory Furnace
This furnace is a common choice where heat needs to be applied to the material without direct contact from the fuel source. Heat radiates from the roof and walls onto the substance being processed.
The Muffle Furnace
A muffle furnace is exceptionally well-suited for processes that require the material to have full and direct contact with the air inside the chamber.
This makes it an ideal choice for air calcination, where oxidizing a substance is a primary objective.
Shaft Furnaces and Kilns
For large-scale, continuous industrial processes, shaft furnaces or rotary kilns are often used. A kiln is a thermally insulated chamber used for high-temperature processes like drying, hardening, or chemical changes.
These are the workhorses of the cement industry, capable of processing massive volumes of material efficiently.
The Specialized Calciner
In many modern applications, a purpose-built reactor called a calciner is used. This is often a cylindrical structure designed to provide extremely precise control over temperature and other process conditions, ensuring a consistent final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of furnace is a critical engineering decision based on trade-offs between atmosphere control, material handling, and scale. There is no single "best" furnace for all applications.
The Need for Air Contact
If the goal is to fully oxidize a material, a furnace that maximizes air exposure is necessary. A muffle furnace excels here, as it allows air to circulate freely around the sample.
The Need for Scale
A small laboratory experiment has vastly different equipment needs than a large industrial plant. While a lab might use a programmable muffle furnace, a cement plant requires a massive rotary kiln to be economical.
The Need for Precise Control
When the final product's quality depends on exact temperature profiles and reaction times, a generic furnace may not be sufficient. A specialized calciner is designed specifically for this level of control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate equipment, you must first define the primary objective of your calcination process.
- If your primary focus is complete oxidation in a controlled setting: A muffle furnace provides the direct air contact necessary for this reaction.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, continuous industrial production: A rotary kiln or shaft furnace is designed to handle high throughput efficiently.
- If your primary focus is achieving a precise chemical transformation: A purpose-built calciner offers the most control over temperature and atmospheric conditions.
Ultimately, understanding your end goal is the key to selecting the right tool to achieve it.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Use Case | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Muffle Furnace | Lab-scale oxidation, precise air calcination | Direct air contact, ideal for controlled oxidation |
| Reverberatory Furnace | Indirect heating of materials | Heat radiates from walls/roof, no direct flame contact |
| Rotary Kiln / Shaft Furnace | Large-scale, continuous production (e.g., cement) | High throughput, efficient for industrial volumes |
| Specialized Calciner | Precise chemical transformations | Maximum control over temperature and atmosphere |
Struggling to select the right calcination furnace for your specific material and production goals? The wrong equipment can lead to inconsistent results and wasted resources. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with expert guidance. Our team can help you analyze your process requirements—from precise oxidation in a muffle furnace to scaling up with a kiln—to ensure you achieve optimal results. Contact us today to discuss your application and find the perfect solution for your lab. Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of ash determination? Choosing the Right Technique for Accurate Mineral Analysis
- What is the process of dry ashing of sample treatment? A Guide to High-Temperature Mineral Analysis
- What is the temperature of furnace exhaust? A Key Indicator of Efficiency and Safety
- What is the optimal temperature for ashing in a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise and Efficient Results
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and an oven? Choose the Right High-Temperature Tool



















